Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2019 May;23(2):187-191. 10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.2.187.
Endovascular treatment of psuedoaneurysm arising from common hepatic artery bifurcation with complete disruption of gastroduodenal artery and high flow arterioportal fistula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neuro and Vascular Interventional Radiology, Kovai Medical Center and Hospital Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India. dr.mathewcherian@gmail.com
- KMID: 2448775
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.2.187
Abstract
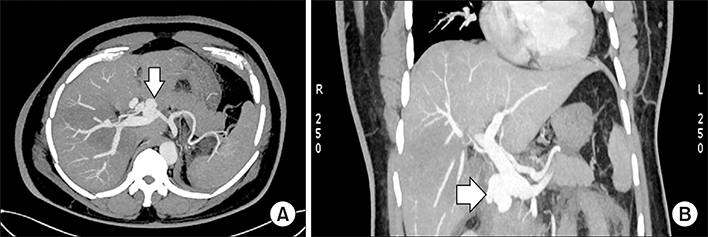
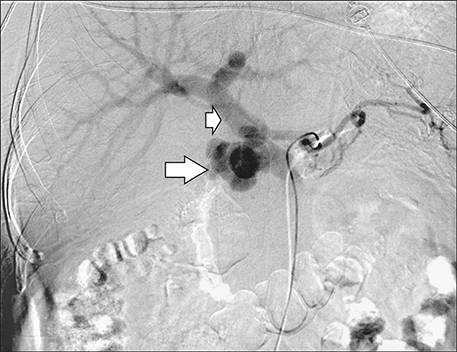
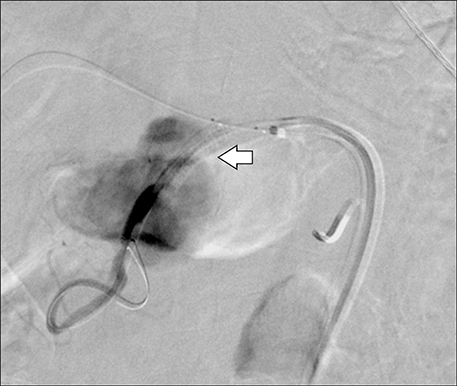
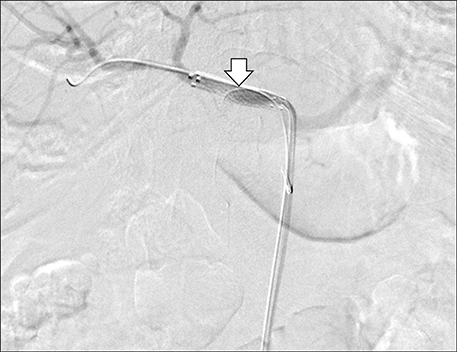
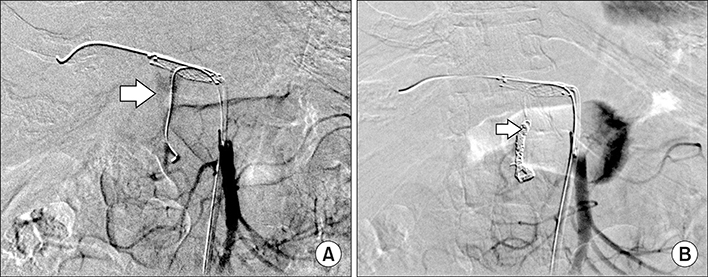
- Arterio-portal fistulas (APFs) are characterized by anomalous communication between arteries and the portal vein (PV) system. Treatment of APF is imperative as an emergency or if there is development of portal hypertension/heart failure in chronic cases. Both endovascular and surgical managements can be attempted, however since endovascular management carries comparatively low intra and post procedural morbidity it is mostly preferred. This is a case report on endovascular management of post-traumatic pseudoaneurysm arising from bifurcation of common hepatic artery with complete disruption of the gastroduodenal artery and high-flow APF. This report describes the intraprocedure challenges in exclusion of fistula from the circulation, without disruption of portal system and anticipation of recruitment of new collateral feeders to the fistula immediate post exclusion with its embolization, which needs appropriate positioning of the catheter prior to exclusion of the fistula.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hirakawa M, Nishie A, Asayama Y, Ishigami K, Ushijima Y, Fujita N, et al. Clinical outcomes of symptomatic arterioportal fistulas after transcatheter arterial embolization. World J Radiol. 2013; 5:33–40.
Article2. Khosla A, White B, Kalva S, Pillai A. Endovascular management of a post-traumatic complex arterioportal fistula. J Vasc Med Surg. 2015; DOI: 10.4172/2329-6925.1000198.
Article3. Zhang WG, Li Z, Ding PX, Ren JZ, Ma J, Zhou PL, et al. Endovascular treatment of an unusual primary arterioportal fistula complicated by cavernous transformation of the portal vein caused by portal thrombosis. Ann Vasc Surg. 2014; 28:491.e5–491.e8.
Article4. Han P, Yang L, Huang XW, Zhu XQ, Chen L, Wang N, et al. A traumatic hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm and arterioportal fistula, with severe diarrhea as the first symptom: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e9893.5. Kumar A, Ahuja CK, Vyas S, Kalra N, Khandelwal N, Chawla Y, et al. Hepatic arteriovenous fistulae: role of interventional radiology. Dig Dis Sci. 2012; 57:2703–2712.
Article6. Tomczak R, Helmberger T, Görich J, Schütz A, Merkle E, Brambs HJ, et al. [Abdominal arteriovenous and arterio-portal fistulas: etiology, diagnosis, therapeutic possibilities]. Z Gastroenterol. 1997; 35:555–562. German.7. Vauthey JN, Tomczak RJ, Helmberger T, Gertsch P, Forsmark C, Caridi J, et al. The arterioportal fistula syndrome: clinicopathologic features, diagnosis, and therapy. Gastroenterology. 1997; 113:1390–1401.
Article8. Guzman EA, McCahill LE, Rogers FB. Arterioportal fistulas: introduction of a novel classification with therapeutic implications. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006; 10:543–550.
Article9. Bouziane Z, Ghissassi B, Bouayad M, Sefiani Y, Lekehal B, El Mesnaoui A, et al. Successful endovascular management of postoperative arterio portal fistula. Ann Vasc Surg. 2011; 25:385.e1–385.e3.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous hepatic arterioportal fistula in extrahepatic portal vein obstruction: Combined endovascular and surgical management
- Gastroesophageal Bleeding Due to Intrahepatic Arterioportal Fistula: A Case Report of Treatment with Occlusive Balloon and Coils
- Right Gastroepiploic Artery Transposition for a Common Hepatic Artery and Proper Hepatic Artery Aneurysm Repair
- Analysis of branching patterns of middle hepatic artery using A-P and oblique view hepatic angiography
- Anomalous Vessels Encountered during Hepatoduodenal and / or Aortocaval Lymph Node Dissection