Chonnam Med J.
2019 May;55(2):118-119. 10.4068/cmj.2019.55.2.118.
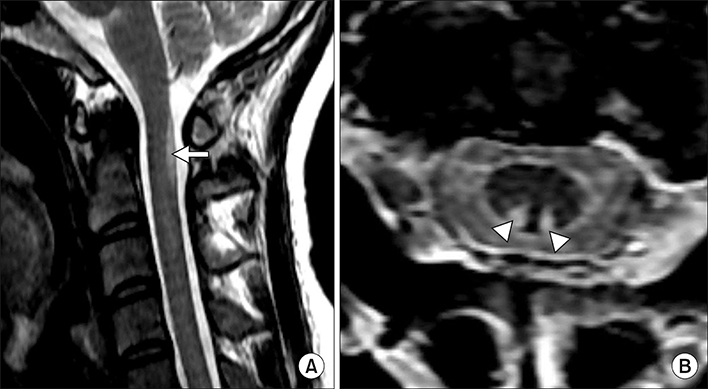
Acute Cervical Myelopathy Following Laughing Gas Abuse
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chonnam National University Hospital and Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. nts0022@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hospital and Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2447215
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2019.55.2.118
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Spectrum of nitrous oxide intoxication related neurological disorders in Korea: a case series and literature review
Jungsoo Lee, Yangmi Park, Hyunkee Kim, Nakhoon Kim, Wonjae Sung, Sanggon Lee, Jinseok Park
Ann Clin Neurophysiol. 2021;23(2):108-116. doi: 10.14253/acn.2021.23.2.108.
Reference
-
1. Cousaert C, Heylens G, Audenaert K. Laughing gas abuse is no joke. An overview of the implications for psychiatric practice. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:859–862.
Article2. Safari A, Emadi F, Jamali E, Borhani-Haghighi A. Clinical and MRI manifestations of nitrous oxide induced vitamin B12 deficiency: a case report. Iran J Neurol. 2013; 12:111–113.3. Chi SI. Complications caused by nitrous oxide in dental sedation. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2018; 18:71–78.
Article4. Kang SW, Hong JM, Namgung DW, Choi YC. Neurological manifestations of myeloneuropathy in patients with nitrous oxide intoxication. J Clin Neurol. 2019; 15:116–117.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome Combined with Acute Cervical Myelopathy
- Unhappy Balloon, Nitrous Oxide-induced Subacute Combined Degeneration of the Spinal Cord: A Review of Case Series
- Acute Cervical Myelopathy Due to Ruptured Disc During Leisure Sports Activity in Adjacent Segment
- Acute Quadriplegia after Lumbar Puncture in a Patient with Misdiagnosed Cervical Myelopathy
- Polyneuropathy Following Nitrous Oxide Abuse