Chonnam Med J.
2019 May;55(2):86-98. 10.4068/cmj.2019.55.2.86.
Recent Advances in Biosensors for Nucleic Acid and Exosome Detection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Bioengineering, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA. jilai@u.washington.edu
- KMID: 2447210
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2019.55.2.86
Abstract
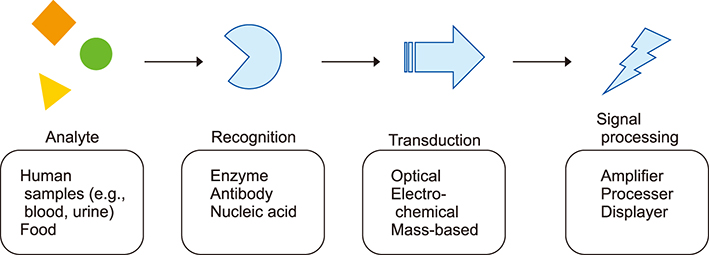
- Biosensors are analytical devices for biomolecule detection that compromise three essential components: recognition moiety, transducer, and signal processor. The sensor converts biomolecule recognition to detectable signals, which has been applied in diverse fields such as clinical monitoring, in vitro diagnostics, food industry etc. Based on signal transduction mechanisms, biosensors can be categorized into three major types: optical biosensors, electrochemical biosensors, and mass-based biosensors. Recently, the need for faster, more sensitive detection of biomolecules has compeled researchers to develop various sensing techniques. In this review, the basic structure and sensing principles of biosensors are introduced. Additionally, the review discusses multiple recent works about nucleic acid and exosome sensing.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Turner APF, Karube I, Wilson GS. Biosensors: fundamentals and applications. Oxford: Oxford University Press;1987. p. 3–12.2. Yoo EH, Lee SY. Glucose biosensors: an overview of use in clinical practice. Sensors (Basel). 2010; 10:4558–4576.
Article3. Tipnis R, Vaddiraju S, Jain F, Burgess DJ, Papadimitrakopoulos F. Layer-by-layer assembled semipermeable membrane for amperometric glucose sensors. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2007; 1:193–200.
Article4. Chambers JP, Arulanandam BP, Matta LL, Weis A, Valdes JJ. Biosensor recognition elements. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2008; 10:1–12.5. Palygin O, Levchenko V, Evans LC, Blass G, Cowley AW Jr, Staruschenko A. Use of enzymatic biosensors to quantify endogenous ATP or H2O2 in the kidney. J Vis Exp. 2015; (104):DOI: 10.3791/53059.
Article6. Marazuela D, Moreno-Bondi MC. Fiber-optic biosensors: an overview. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2002; 372:664–682.7. Janeway C. Immunobiology 5: the immune system in health and disease. 5th ed. New York: Garland Pub;2001. p. 93–122.8. Karube I, Suzuki M. Novel immunosensors. Biosensors. 1986; 2:343–362.
Article9. Duffy MR, Chen TH, Hancock WT, Powers AM, Kool JL, Lanciotti RS, et al. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:2536–2543.
Article10. Kaushik A, Yndart A, Kumar S, Jayant RD, Vashist A, Brown AN, et al. A sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for label-free detection of Zika-virus protein. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:9700.
Article11. Morales MA, Halpern JM. Guide to selecting a biorecognition element for biosensors. Bioconjug Chem. 2018; 29:3231–3239.
Article12. Martinkova P, Kostelnik A, Valek T, Pohanka M. Main streams in the construction of biosensors and their applications. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2017; 12:7386–7403.
Article13. Minunni M. Biosensors based on nucleic acid interaction. Spectroscopy. 2003; 17:613–625.
Article14. Bala A, Górski L. Application of nucleic acid analogues as receptor layers for biosensors. Anal Methods. 2016; 8:236–244.
Article15. Song KM, Lee S, Ban C. Aptamers and their biological applications. Sensors (Basel). 2012; 12:612–631.
Article16. Jayasena SD. Aptamers: an emerging class of molecules that rival antibodies in diagnostics. Clin Chem. 1999; 45:1628–1650.
Article17. Mallikaratchy P. Evolution of complex target SELEX to identify aptamers against mammalian cell-surface antigens. Molecules. 2017; 22:E215.
Article18. Han K, Liang Z, Zhou N. Design strategies for aptamer-based biosensors. Sensors (Basel). 2010; 10:4541–4557.
Article19. Dalirirad S, Steckl AJ. Aptamer-based lateral flow assay for point of care cortisol detection in sweat. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2019; 283:79–86.
Article20. Fenzl C, Genslein C, Domonkos C, Edwards KA, Hirsch T, Baeumner AJ. Investigating non-specific binding to chemically engineered sensor surfaces using liposomes as models. Analyst. 2016; 141:5265–5273.
Article21. Kim JP, Lee BY, Lee J, Hong S, Sim SJ. Enhancement of sensitivity and specificity by surface modification of carbon nanotubes in diagnosis of prostate cancer based on carbon nanotube field effect transistors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009; 24:3372–3378.
Article22. Grandin HM, Textor M. Intelligent surfaces in biotechnology: scientific and engineering concepts, enabling technologies, and translation to bio-oriented applications. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons;2012. p. 71–122.23. Mammen M, Choi SK, Whitesides GM. Polyvalent interactions in biological systems: implications for design and use of multivalent ligands and inhibitors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1998; 37:2754–2794.
Article24. Mejri MB, Baccar H, Baldrich E, Del Campo FJ, Helali S, Ktari T, et al. Impedance biosensing using phages for bacteria detection: generation of dual signals as the clue for in-chip assay confirmation. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010; 26:1261–1267.
Article25. Liu Y, Yu D, Zeng C, Miao Z, Dai L. Biocompatible graphene oxide-based glucose biosensors. Langmuir. 2010; 26:6158–6160.
Article26. Reimhult E, Höök F. Design of surface modifications for nanoscale sensor applications. Sensors (Basel). 2015; 15:1635–1675.27. Ma H, He J, Liu X, Gan J, Jin G, Zhou J. Surface initiated polymerization from substrates of low initiator density and its applications in biosensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010; 2:3223–3230.
Article28. Sethi RS. Transducer aspects of biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 1994; 9:243–264.
Article29. Ahuja D, Parande D. Optical sensors and their applications. J Sci Res Rev. 2012; 1:60–68.30. McGrath MJ, Ni Scanaill C. Sensing and seonsor fundamentals. In : McGrath MJ, Ni Scanaill C, Nafus D, editors. Sensor technologies: healthcare, wellness and environmental applications. Berkeley: Apress;2013. p. 15–50.31. Mehrvar M, Abdi M. Recent developments, characteristics, and potential applications of electrochemical biosensors. Anal Sci. 2004; 20:1113–1126.
Article32. Afzal A, Mujahid A, Schirhagl R, Bajwa SZ, Latif U, Feroz S. Gravimetric viral diagnostics: QCM based biosensors for early detection of viruses. Chemosensors. 2017; 5:7.
Article33. Damborský P, Švitel J, Katrlík J. Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016; 60:91–100.
Article34. Dey D, Goswami T. Optical biosensors: a revolution towards quantum nanoscale electronics device fabrication. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011; 2011:348218.
Article35. Syahir A, Usui K, Tomizaki KY, Kajikawa K, Mihara H. Label and label-free detection techniques for protein microarrays. Microarrays (Basel). 2015; 4:228–244.
Article36. Homola J, Yee SS, Gauglitz G. Surface plasmon resonance sensors: review. Sens Actuators B Chem. 1999; 54:3–15.
Article37. Hutter E, Fendler JH. Exploitation of localized surface plasmon resonance. Adv Mater. 2004; 16:1685–1706.
Article38. Säfsten P, Klakamp SL, Drake AW, Karlsson R, Myszka DG. Screening antibody-antigen interactions in parallel using Biacore A100. Anal Biochem. 2006; 353:181–190.
Article39. Luchansky MS, Washburn AL, Martin TA, Iqbal M, Gunn LC, Bailey RC. Characterization of the evanescent field profile and bound mass sensitivity of a label-free silicon photonic microring resonator biosensing platform. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010; 26:1283–1291.
Article40. Flueckiger J, Schmidt S, Donzella V, Sherwali A, Ratner DM, Chrostowski L, et al. Sub-wavelength grating for enhanced ring resonator biosensor. Opt Express. 2016; 24:15672–15686.
Article41. Thévenot DR, Tóth K, Durst RA, Wilson GS. Electrochemical biosensors: recommended definitions and classification. Anal Lett. 2001; 34:635–659.
Article42. Stradiotto NR, Yamanaka H, Zanoni MVB. Electrochemical sensors: a powerful tool in analytical chemistry. J Braz Chem Soc. 2003; 14:159–173.
Article43. Soldatkin OO, Kucherenko IS, Pyeshkova VM, Kukla AL, Jaffrezic-Renault N, El'skaya AV, et al. Novel conductometric biosensor based on three-enzyme system for selective determination of heavy metal ions. Bioelectrochemistry. 2012; 83:25–30.
Article44. Ward MD, Buttry DA. In situ interfacial mass detection with piezoelectric transducers. Science. 1990; 249:1000–1007.
Article45. Ozalp VC, Bayramoglu G, Erdem Z, Arica MY. Pathogen detection in complex samples by quartz crystal microbalance sensor coupled to aptamer functionalized core-shell type magnetic separation. Anal Chim Acta. 2015; 853:533–540.
Article46. Neethirajan S, Ragavan V, Weng X, Chand R. Biosensors for sustainable food engineering: challenges and perspectives. Biosensors (Basel). 2018; 8:E23.
Article47. Ngo VKT, Nguyen DG, Nguyen HPU, Tran VM, Nguyen TKM, Huynh TP, et al. Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) as biosensor for the detecting of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Adv Nat Sci: Nanosci. 2014; 5:045004.48. White RM, Voltmer FW. Direct piezoelectric coupling to surface elastic waves. Appl Phys Lett. 1965; 7:314.
Article49. Länge K, Rapp BE, Rapp M. Surface acoustic wave biosensors: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008; 391:1509–1519.
Article50. Ju H. Signal amplification for highly sensitive bioanalysis based on biosensors or biochips. J Biochips Tiss Chips. 2012; 2:e114.
Article51. Walker JM, Gingold EB. Molecular biology and biotechnology. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry;2009. p. 521–554.52. Mehrotra P. Biosensors and their applications - a review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2016; 6:153–159.
Article53. Atay S, Pişkin K, Yılmaz F, Çakir C, Yavuz H, Denizli A. Quartz crystal microbalance based biosensors for detecting highly metastatic breast cancer cells via their transferrin receptors. Anal Methods. 2016; 8:153–161.
Article54. Bahadır EB, Sezgintürk MK. Applications of commercial biosensors in clinical, food, environmental, and biothreat/biowarfare analyses. Anal Biochem. 2015; 478:107–120.
Article55. Weibel MK, Bright HJ. The glucose oxidase mechanism. Interpretation of the pH dependence. J Biol Chem. 1971; 246:2734–2744.56. Xu Y, Xiang W, Wang Q, Cheng N, Zhang L, Huang K, et al. A smart sealed nucleic acid biosensor based on endogenous reference gene detection to screen and identify mammals on site. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:43453.
Article57. Wang M, Tang Y, Chen Y, Cao Y, Chen G. Catalytic hairpin assembly-programmed formation of clickable nucleic acids for electrochemical detection of liver cancer related short gene. Anal Chim Acta. 2019; 1045:77–84.
Article58. Guo R, Yin F, Sun Y, Mi L, Shi L, Tian Z, et al. Ultrasensitive simultaneous detection of multiplex disease-related nucleic acids using double-enhanced surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanosensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10:25770–25778.
Article59. Jayanthi VSPKSA, Das AB, Saxena U. Recent advances in biosensor development for the detection of cancer biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017; 91:15–23.
Article60. Omar NAS, Fen YW, Abdullah J, Chik CENCE, Mahdi MA. Development of an optical sensor based on surface plasmon resonance phenomenon for diagnosis of dengue virus E-protein. Sens Biosensing Res. 2018; 20:16–21.
Article61. Diao W, Tang M, Ding S, Li X, Cheng W, Mo F, et al. Highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the detection of HIV-related DNA based on dynamic and structural DNA nanodevices. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018; 100:228–234.
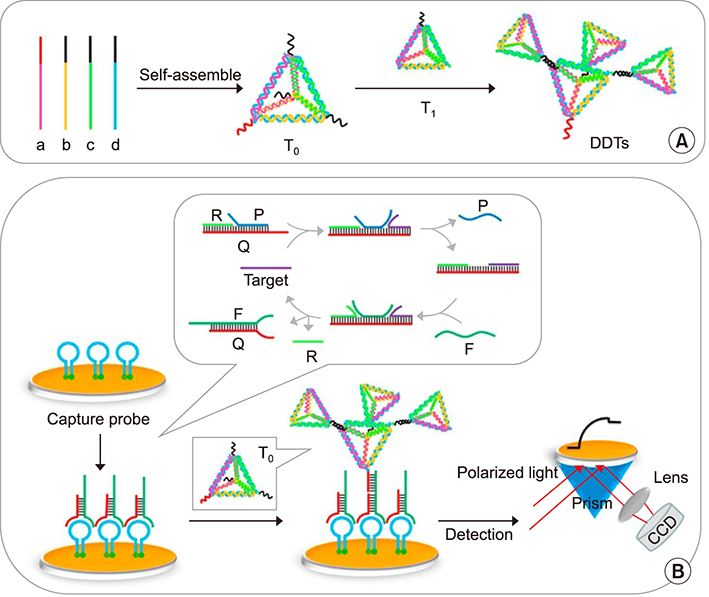
Article62. Xie N, Liu S, Yang X, He X, Huang J, Wang K. DNA tetrahedron nanostructures for biological applications: biosensors and drug delivery. Analyst. 2017; 142:3322–3332.
Article63. Klinghammer S, Uhlig T, Patrovsky F, Böhm M, Schütt J, Pütz N, et al. Plasmonic biosensor based on vertical arrays of gold nanoantennas. ACS Sens. 2018; 3:1392–1400.
Article64. Shen Y, Liu S, Yang J, Wang L, Tan X, He Y. A novel and sensitive turn-on fluorescent biosensor for the DNA detection using Sm3+-modulated glutathione-capped CdTe quantum dots. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2014; 199:389–397.
Article65. Takalkar S, Baryeh K, Liu G. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of DNA. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017; 98:147–154.
Article66. Zheng J, Li N, Li C, Wang X, Liu Y, Mao G, et al. A nonenzymatic DNA nanomachine for biomolecular detection by target recycling of hairpin DNA cascade amplification. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018; 107:40–46.
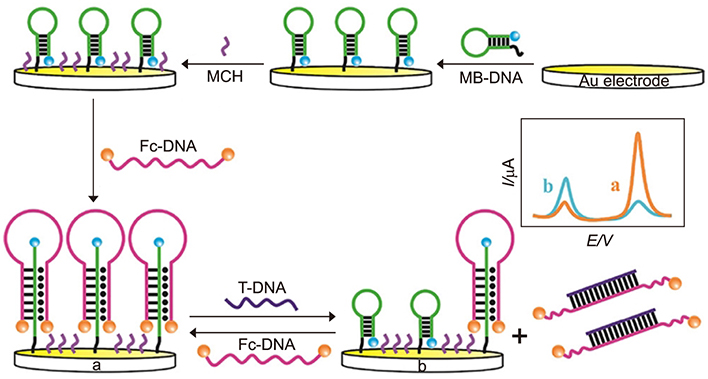
Article67. Touhami A. Biosensors and nanobiosensors: design and applications. In : Seifalian A, de Mel A, Kalaskar DM, editors. Nanomedicine. Cheshire: One Central Press;2014. p. 374–403.68. Yunus S, Jonas AM, Lakard B. Potentiometric biosensors. In : Roberts GCK, editor. Encyclopedia of biophysics. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg;2013. p. 1941–1946.69. Yao J, Zhang Z, Deng Z, Wang Y, Guo Y. An enzyme free electrochemical biosensor for sensitive detection of miRNA with a high discrimination factor by coupling the strand displacement reaction and catalytic hairpin assembly recycling. Analyst. 2017; 142:4116–4123.
Article70. Mikuła E, Silva CE, Kopera E, Zdanowski K, Radecki J, Radecka H. Highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor based on redox - active monolayer for detection of anti-hemagglutinin antibodies against swine-origin influenza virus H1N1 in sera of vaccinated mice. BMC Vet Res. 2018; 14:328.
Article71. Zhang J, Wang J, Zhang X, He F. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli based on 16S rDNA nanogap network electrochemical biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018; 118:9–15.
Article72. Teengam P, Siangproh W, Tuantranont A, Henry CS, Vilaivan T, Chailapakul O. Electrochemical paper-based peptide nucleic acid biosensor for detecting human papillomavirus. Anal Chim Acta. 2017; 952:32–40.
Article73. Jeong S, Park J, Pathania D, Castro CM, Weissleder R, Lee H. Integrated magneto-electrochemical sensor for exosome analysis. ACS Nano. 2016; 10:1802–1809.
Article74. Varmira K, Mohammadi G, Mahmoudi M, Khodarahmi R, Rashidi K, Hedayati M, et al. Fabrication of a novel enzymatic electrochemical biosensor for determination of tyrosine in some food samples. Talanta. 2018; 183:1–10.
Article75. Wang K, Feng M, He MQ, Zhai FH, Dai Y, He RH, et al. DNA-fueled target recycling-induced two-leg DNA walker for amplified electrochemical detection of nucleic acid. Talanta. 2018; 188:685–690.
Article76. Xiong E, Li Z, Zhang X, Zhou J, Yan X, Liu Y, et al. Triple-helix molecular switch electrochemical ratiometric biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acids. Anal Chem. 2017; 89:8830–8835.
Article77. Zhao T, Zhang HS, Tang H, Jiang JH. Nanopore biosensor for sensitive and label-free nucleic acid detection based on hybridization chain reaction amplification. Talanta. 2017; 175:121–126.
Article78. Liu N, Yang Z, Ou X, Wei B, Zhang J, Jia Y, et al. Nanopore-based analysis of biochemical species. Mikrochim Acta. 2016; 183:955–963.
Article79. Chaudhary M, Gupta A. Microcantilever-based sensors. Def Sci J. 2009; 59:634–641.
Article80. García-Martinez G, Bustabad EA, Perrot H, Gabrielli C, Bucur B, Lazerges M, et al. Development of a mass sensitive quartz crystal microbalance (QCM)-based DNA biosensor using a 50 MHz electronic oscillator circuit. Sensors (Basel). 2011; 11:7656–7664.
Article81. Zappulli V, Friis KP, Fitzpatrick Z, Maguire CA, Breakefield XO. Extracellular vesicles and intercellular communication within the nervous system. J Clin Invest. 2016; 126:1198–1207.
Article82. Tai YL, Chen KC, Hsieh JT, Shen TL. Exosomes in cancer development and clinical applications. Cancer Sci. 2018; 109:2364–2374.
Article83. Ko J, Carpenter E, Issadore D. Detection and isolation of circulating exosomes and microvesicles for cancer monitoring and diagnostics using micro-/nano-based devices. Analyst. 2016; 141:450–460.
Article84. Knauer M, Ivleva NP, Liu X, Niessner R, Haisch C. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based label-free microarray readout for the detection of microorganisms. Anal Chem. 2010; 82:2766–2772.
Article85. Kruszewski S, Skonieczny J. Roughness effects in surface enhanced Raman scattering - evidence for electromagnetic and charge transfer enhancement mechanism. Acta Phys Pol A. 1991; 80:611–620.
Article86. Xu X, Li H, Hasan D, Ruoff RS, Wang AX, Fan DL. Near-field enhanced plasmonic-magnetic bifunctional nanotubes for single cell bioanalysis. Adv Funct Mater. 2013; 23:4332–4338.
Article87. Korotcenkov G. Porous silicon: from formation to application: biomedical and sensor applications. Boca Raton: Taylor and Francis Group, CRC Press;2016. p. 299.88. Tian YF, Ning CF, He F, Yin BC, Ye BC. Highly sensitive detection of exosomes by SERS using gold nanostar@Raman reporter@ nanoshell structures modified with a bivalent cholesterol-labeled DNA anchor. Analyst. 2018; 143:4915–4922.
Article89. Zeng X, Yang Y, Zhang N, Ji D, Gu X, Jornet J, et al. Plasmonic interferometer array biochip as a new mobile medical device for cancer detection. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2019; 25:7201707.
Article90. Zamay TN, Zamay GS, Kolovskaya OS, Zukov RA, Petrova MM, Gargaun A, et al. Current and prospective protein biomarkers of lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2017; 9:E155.
Article91. Thakur A, Qiu G, Ng SP, Guan J, Yue J, Lee Y, et al. Direct detection of two different tumor-derived extracellular vesicles by SAM-AuNIs LSPR biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017; 94:400–407.
Article92. Zhou Q, Rahimian A, Son K, Shin DS, Patel T, Revzin A. Development of an aptasensor for electrochemical detection of exosomes. Methods. 2016; 97:88–93.
Article93. Jauregui R, Srinivasan S, Vojtech LN, Gammill HS, Chiu DT, Hladik F, et al. Temperature-responsive magnetic nanoparticles for enabling affinity separation of extracellular vesicles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10:33847–33856.
Article94. Nehilla BJ, Hill JJ, Srinivasan S, Chen YC, Schulte TH, Stayton PS, et al. A stimuli-responsive, binary reagent system for rapid isolation of protein biomarkers. Anal Chem. 2016; 88:10404–10410.
Article95. Phan JC, Nehilla BJ, Srinivasan S, Coombs RW, Woodrow KA, Lai JJ. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) separation and enrichment via the combination of antiviral lectin recognition and a thermoresponsive reagent system. Pharm Res. 2016; 33:2411–2420.
Article96. Roy D, Nehilla BJ, Lai JJ, Stayton PS. Stimuli-responsive polymer-antibody conjugates via RAFT and tetrafluorophenyl active ester chemistry. Acs Macro Lett. 2013; 2:132–136.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent Advances in Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Lung Disease
- Recommendations for Verification of Multiplex Nucleic Acid Assays for Pathogen Detection
- Detection of leptoapiral DNA by nucleic acid hybridization with 32P-labeld probe
- Cytochemical study on lipase and nucleic acid in Trichomonas vaginalis
- Molecular Diagnosis of Tuberculosis