Neurointervention.
2019 Mar;14(1):35-42. 10.5469/neuroint.2018.01067.
External Ventricular Drainage before Endovascular Treatment in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Acute Period: Its Relation to Hemorrhagic Complications
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Ajou University Hospital, Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Inha University Hospital, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Stroke Center, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ns.joonho.chung@gmail.com
- 5Severance Institute for Vascular and Metabolic Research, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2446780
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2018.01067
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to report the authors' experience with external ventricular drainage (EVD) before endovascular treatment (EVT) in patients with acute aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) and to investigate its relation to hemorrhagic complications. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between March 2010 and December 2017, a total of 122 patients were recruited who had an aSAH, underwent EVT to secure the ruptured aneurysm, and had EVD performed within 72 hours of rupture. The pre-embo EVD group (n=67) comprised patients who underwent EVD before EVT, and the post-embo EVD group (n=55) comprised those who underwent EVD after EVT.
RESULTS
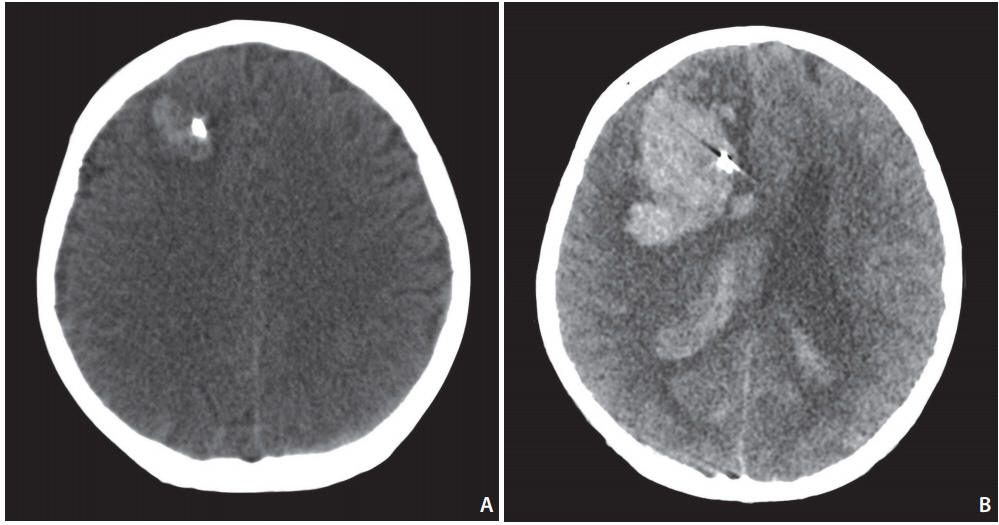
Overall, EVD-related hemorrhage occurred in 18 patients (14.8%): six (8.9%) in the pre-embo EVD group and 12 (21.8%) in the post-embo EVD group (P=0.065). No rebleeding occurred between EVD and EVT in the pre-embo EVD group. Clinical outcomes at discharge did not differ significantly between groups (P=0.384). At discharge, the final modified Rankin Scale score in patients who experienced pre-embo rebleeding was better in the pre-embo EVD group than in the post-embo EVD group (P=0.041). Current use of an antiplatelet agent or anticoagulant on admission (odds ratio [OR], 2.928; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.234-7.439; P=0.042) and stent use (OR, 2.430; 95% CI, 1.524-7.613; P=0.047) remained independent risk factors for EVD-related hemorrhagic complications.
CONCLUSION
EVD before EVT in patients with aSAH in acute period did not increase the rate of rebleeding as well as EVD-related hemorrhagic complications. Thus, performing EVD before EVT may be beneficial by normalizing increased intracranial pressure. Especially in patients with rebleeding before the ruptured aneurysm is secured, pre-embo EVD may improve clinical outcomes at discharge.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Commentary to: External Ventricular Drainage before Endovascular Treatment in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Acute Period: Its Relation to Hemorrhagic Complications
Harsh Deora, Rafael Martinez-Perez, Amit Agrawal, Luis Rafael Moscote-Salazar
Neurointervention. 2020;15(1):49-51. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2019.00171.
Reference
-
1. Gigante P, Hwang BY, Appelboom G, Kellner CP, Kellner MA, Connolly ES. External ventricular drainage following aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br J Neurosurg. 2010; 24:625–632.
Article2. Fountas KN, Kapsalaki EZ, Machinis T, Karampelas I, Smisso HF, Robinson JS. Review of the literature regarding the relationship of rebleeding and external ventricular drainage in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage of aneurysmal origin. Neurosurg Rev. 2006; 29:14–18. discussion 19-20.
Article3. Bratton SL, Chestnut RM, Ghajar J, McConnell Hammond FF, Harris OA, Hartl R, et al. VII. Intracranial pressure monitoring technique. J Neurotrauma. 2007; 24 Suppl 1:S-45-S-54.4. Gardner PA, Engh J, Atteberry D, Moossy JJ. Hemorrhage rates after external ventricular drain placement. J Neurosurg. 2009; 110:1021–1025.
Article5. Hellingman CA, van den Bergh WM, Beijer IS, van Dijk GW, Algra A, van Gijn J, et al. Risk of rebleeding after treatment of acute hydrocephalus in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2007; 38:96–99.
Article6. Hasan D, Vermeulen M, Wijdicks EF, Hijdra A, van Gijn J. Management problems in acute hydrocephalus after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 1989; 20:747–753.
Article7. Paré L, Delfino R, Leblanc R. The relationship of ventricular drainage to aneurysmal rebleeding. J Neurosurg. 1992; 76:422–427.
Article8. Ko JK, Cha SH, Choi BK, Lee JI, Yun EY, Choi CH. Hemorrhage rated associated with two methods of ventriculostomy: external ventricular drainage vs. ventriculoperitoneal shunt procedure. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014; 54:545–551.9. Scholz C, Hubbe U, Deininger M, Deininger MH. Hemorrhage rates of external ventricular drain (EVD), intracranial pressure gauge (ICP) or combined EVD and ICP gauge placement within 48 h of endovascular coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:1399–1402.10. McIver JI, Friedman JA, Wijdicks EF, Piepgras DG, Pichelmann MA, Toussaint LG 3rd, et al. Preoperative ventriculostomy and rebleeding after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:1042–1044.
Article11. Roitberg BZ, Khan N, Alp MS, Hersonskey T, Charbel FT, Ausman JI. Bedside external ventricular drain placement for the treatment of acute hydrocephalus. Br J Neurosurg. 2001; 15:324–327.12. Chung J, Lim YC, Suh SH, Shim YS, Kim YB, Joo JY, et al. Stent-assisted coil embolization of ruptured wide-necked aneurysms in the acute period: incidence of and risk factors for periprocedural complications. J Neurosurg. 2014; 121:4–11.
Article13. Bruder M, Schuss P, Konczalla J, El-Fiki A, Lescher S, Vatter H, et al. Ventriculostomy-related hemorrhage after treatment of acutely ruptured aneurysms: the influence of anticoagulation and antiplatelet treatment. World Neurosurg. 2015; 84:1653–1659.
Article14. Nguyen TA, Diodati JG, Pharand C. Resistance to clopidogrel: a review of the evidence. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 45:1157–1164.
Article15. Colwell AS, Reish RG, Kuter DJ, Damjanovic B, Austen WG Jr, Fogerty AE. Abdominal contouring procedures increase activity of the coagulation cascade. Ann Plast Surg. 2012; 69:129–133.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Commentary to: External Ventricular Drainage before Endovascular Treatment in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Acute Period: Its Relation to Hemorrhagic Complications
- Effectiveness of Preoperative Extra-Ventricular Drainage in Poor Grade Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- The Utility and Benefits of External Lumbar CSF Drainage after Endovascular Coiling on Aneurysmal ubarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Influence of Routine Intraoperative Ventricular Drainage on the Incidence of Aneurysmal Rebleeding
- Analysis of the Effect of Initial External Ventricular Drainage in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage on the Late Onset of Hydrocephalus