Ann Dermatol.
2019 Jun;31(3):357-358. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.357.
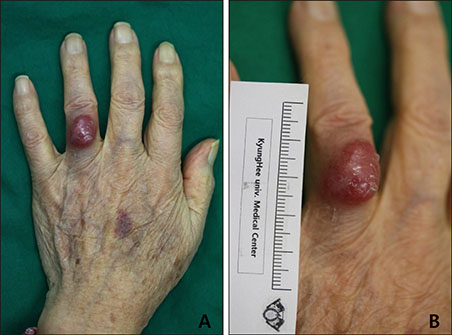
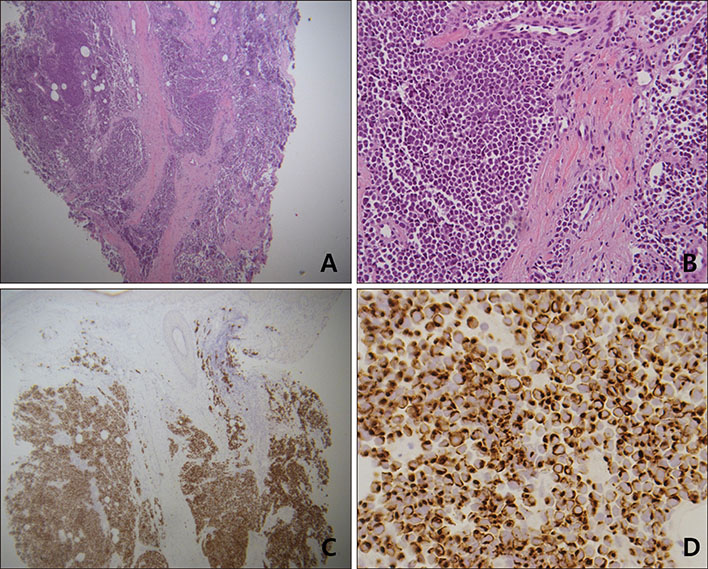
A Case of Merkel Cell Carcinoma on the Finger
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. mdfamily@naver.com
- KMID: 2444877
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.357
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hughes MP, Hardee ME, Cornelius LA, Hutchins LF, Becker JC, Gao L. Merkel cell carcinoma: epidemiology, target, and therapy. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2014; 3:46–53.
Article2. Coggshall K, Tello TL, North JP, Yu SS. Merkel cell carcinoma: an update and review: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and staging. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018; 78:433–442.3. Chun SM, Yun SJ, Lee SC, Won YH, Lee JB. Merkel cell polyomavirus is frequently detected in Korean patients with merkel cell carcinoma. Ann Dermatol. 2013; 25:203–207.
Article4. Spalvieri C, Brunelli F, Bachmeyer CC. Merkel cell tumour of the finger. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2007; 41:149–151.
Article5. Ansai S, Noro S, Ogita A, Fukumoto H, Katano H, Kawana S. Case of Merkel cell carcinoma with squamous cell carcinoma possibly arising in chronic radiodermatitis of the hand. J Dermatol. 2015; 42:207–209.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- A Case of Merkel Cell Carcinoma Concurrent with Bowen's Disease
- Primary Merkel cell carcinoma of the salivary gland: a clinicopathologic study of four cases with a review of literature
- A Case of Merkel Cell Carcinoma in the Auricle
- Cervical Spinal Metastasis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma