Korean J Ophthalmol.
2019 Apr;33(2):181-188. 10.3341/kjo.2018.0098.
Effect of High Myopia on Optic Nerve Head by Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy in Nepalese Eyes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Civil Service Hospital, Minbhavan, Kathmandu, Nepal.
- 2BP Koirala Lions Centre for Ophthalmic Studies, Institute of Medicine, Maharajgunj Medical Campus, Kathmandu, Nepal. gs101lg@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2442623
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2018.0098
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare parameters of confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (Heidelberg Retinal Tomograph [HRT] II) in high myopia with age- and sex-matched emmetropes.
METHODS
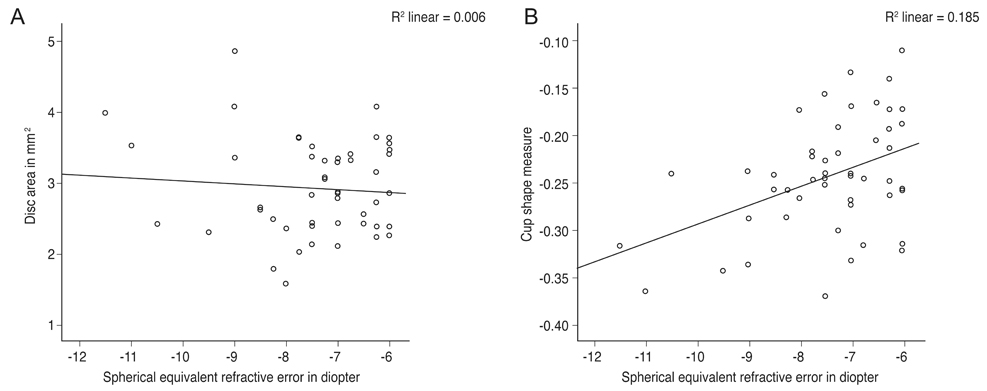
A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted among Nepalese subjects aged 18 to 35 years at BP Koirala Lions Centre for Ophthalmic Studies, Institute of Medicine, Maharajgunj, Kathmandu from November 2015 to October 2016. Fifty consecutive subjects with high myopia (spherical equivalent ranging from −6.00 to −12.00 diopters) and age- and sex-matched emmetropic subjects were enrolled for comparison. Correlations between disc area and other HRT parameters, asymmetry between the right and left eyes, and comparisons between male and female subjects in both high myopic and emmetropic groups were evaluated.
RESULTS
Disc area was not significantly (p = 0.11) larger in high myopic eyes than in emmetropic eyes. HRT parameters in highly myopic eyes involved smaller cup parameters and greater rim parameters compared with emmetropic eyes. Disc area was found to be significantly positively correlated with inter disc parameters and significantly negatively correlated with rim to disc area ratio in the high myopia group. Disc area and other intra-disc parameters showed significant correlations between right and left eyes in both high myopia and emmetropia, and no significant differences between males and females from a Nepalese population.
CONCLUSIONS
Characteristics of HRT parameters in high myopic eyes involved smaller cup parameters and greater rim parameters compared with emmetropic eyes in a Nepalese population. The effect of disc area on HRT parameters differed significantly only in height variation contour by emmetropic eyes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hyung SM, Kim DM, Hong C, Youn DH. Optic disc of the myopic eye: relationship between refractive errors and morphometric characteristics. Korean J Ophthalmol. 1992; 6:32–35.
Article2. Samarawickrama C, Wang XY, Huynh SC, et al. Effects of refraction and axial length on childhood optic disk parameters measured by optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 144:459–461.
Article3. Hoh ST, Lim MC, Seah SK, et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness variations with myopia. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:773–777.
Article4. Bae SH, Kang SH, Feng CS, et al. Influence of myopia on size of optic nerve head and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2016; 30:335–343.
Article5. Vernon SA, Hawker MJ, Ainsworth G, et al. Laser scanning tomography of the optic nerve head in a normal elderly population: the Bridlington eye assessment project. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:2823–2828.
Article6. Zangwill LM, Chan K, Bowd C, et al. Heidelberg retina tomograph measurements of the optic disc and parapapillary retina for detecting glaucoma analyzed by machine learning classifiers. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:3144–3151.
Article7. Tong L, Chan YH, Gazzard G, et al. Heidelberg retinal tomography of optic disc and nerve fiber layer in singapore children: variations with disc tilt and refractive error. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:4939–4944.
Article8. American Optometric Association. Optometric clinical practice guideline: care of patients with myopia [Internet]. St. Louis: American Optometric Association;2006. cited 2019 Feb 9. Available from: https://www.aoa.org/documents/optometrists/CPG-15.pdf.9. Tsutsumi T, Tomidokoro A, Saito H, et al. Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy in high myopic eyes in a population-based setting. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50:5281–5287.
Article10. Leung CK, Cheng AC, Chong KK, et al. Optic disc measurements in myopia with optical coherence tomography and confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:3178–3183.
Article11. Jonas JB, Gusek GC, Naumann GO. Optic disk morphometry in high myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988; 226:587–590.
Article12. Xu L, Li Y, Wang S, et al. Characteristics of highly myopic eyes: the Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:121–126.13. Mardin CY, Horn FK, Jonas JB, Budde WM. Preperimetric glaucoma diagnosis by confocal scanning laser tomography of the optic disc. Br J Ophthalmol. 1999; 83:299–304.
Article14. Ford BA, Artes PH, McCormick TA, et al. Comparison of data analysis tools for detection of glaucoma with the Heidelberg retina tomograph. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:1145–1150.
Article15. Tan JC, Hitchings RA. Reference plane definition and reproducibility in optic nerve head images. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:1132–1137.
Article16. Mitchell P, Hourihan F, Sandbach J, Wang JJ. The relationship between glaucoma and myopia: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:2010–2015.17. Wong TY, Klein BE, Klein R, et al. Refractive errors, intraocular pressure, and glaucoma in a white population. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:211–217.18. Suzuki Y, Iwase A, Araie M, et al. Risk factors for open-angle glaucoma in a Japanese population: the Tajimi Study. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:1613–1617.19. Xu L, Li J, Cui T, et al. Refractive error in urban and rural adult Chinese in Beijing. Ophthalmology. 2005; 112:1676–1683.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Topographic Measurement of the Optic Nerve Head with Confocal Scanning Laser Tomography in Normal Third Decade of Korean
- Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on the Morphometric Analysis of the Optic Nerve Head
- Topographic Measurements of the Optic Nerve Head with Confocal Scanning Laser Tomography in Normal Subjects and Patients with Glaucoma
- The Effect of Optic Disc Size or Age on Evaluation of Optic Disc Parameters
- Topographic Measurements of the Optic Nerve Head with Confocal Scanning Laser Tomography in Normal Koreans