Prog Med Phys.
2019 Mar;30(1):1-6. 10.14316/pmp.2019.30.1.1.
Skin Dose Comparison of CyberKnife and Helical Tomotherapy for Head-and-Neck Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. holee@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2442415
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2019.30.1.1
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study conducts a comparative evaluation of the skin dose in CyberKnife (CK) and Helical Tomotherapy (HT) to predict the accurate dose of radiation and minimize skin burns in head-and-neck stereotactic body radiotherapy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
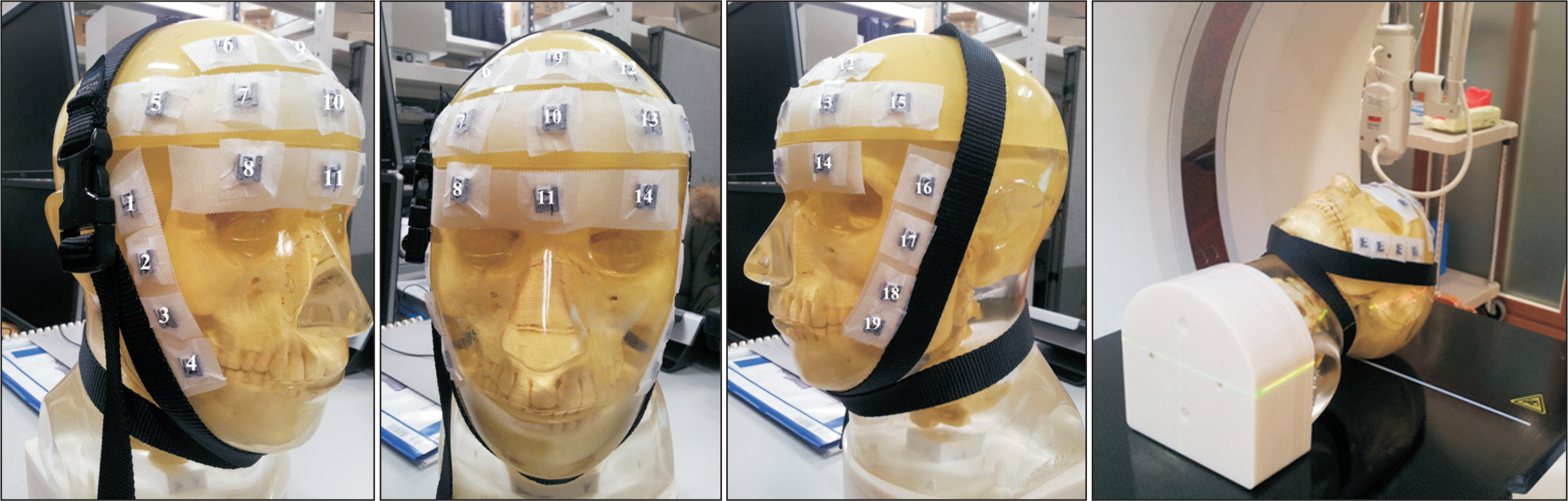
Arbitrarily-defined planning target volume (PTV) close to the skin was drawn on the planning computed tomography acquired from a head-and-neck phantom with 19 optically stimulated luminescent dosimeters (OSLDs) attached to the surface (3 OSLDs were positioned at the skin close to PTV and 16 OSLDs were near sideburns and forehead, away from PTV). The calculation doses were obtained from the MultiPlan 5.1.2 treatment planning system using raytracing (RT), finite size pencil beam (FSPB), and Monte Carlo (MC) algorithms for CK. For HT, t he s kin d ose w as e stimated v ia c onvolution s uperposition ( CS) a lgorithm f rom t he Tomotherapy planning station 5.0.2.5. The prescribed dose was 8 Gy for 95% coverage of the PTV.
RESULTS
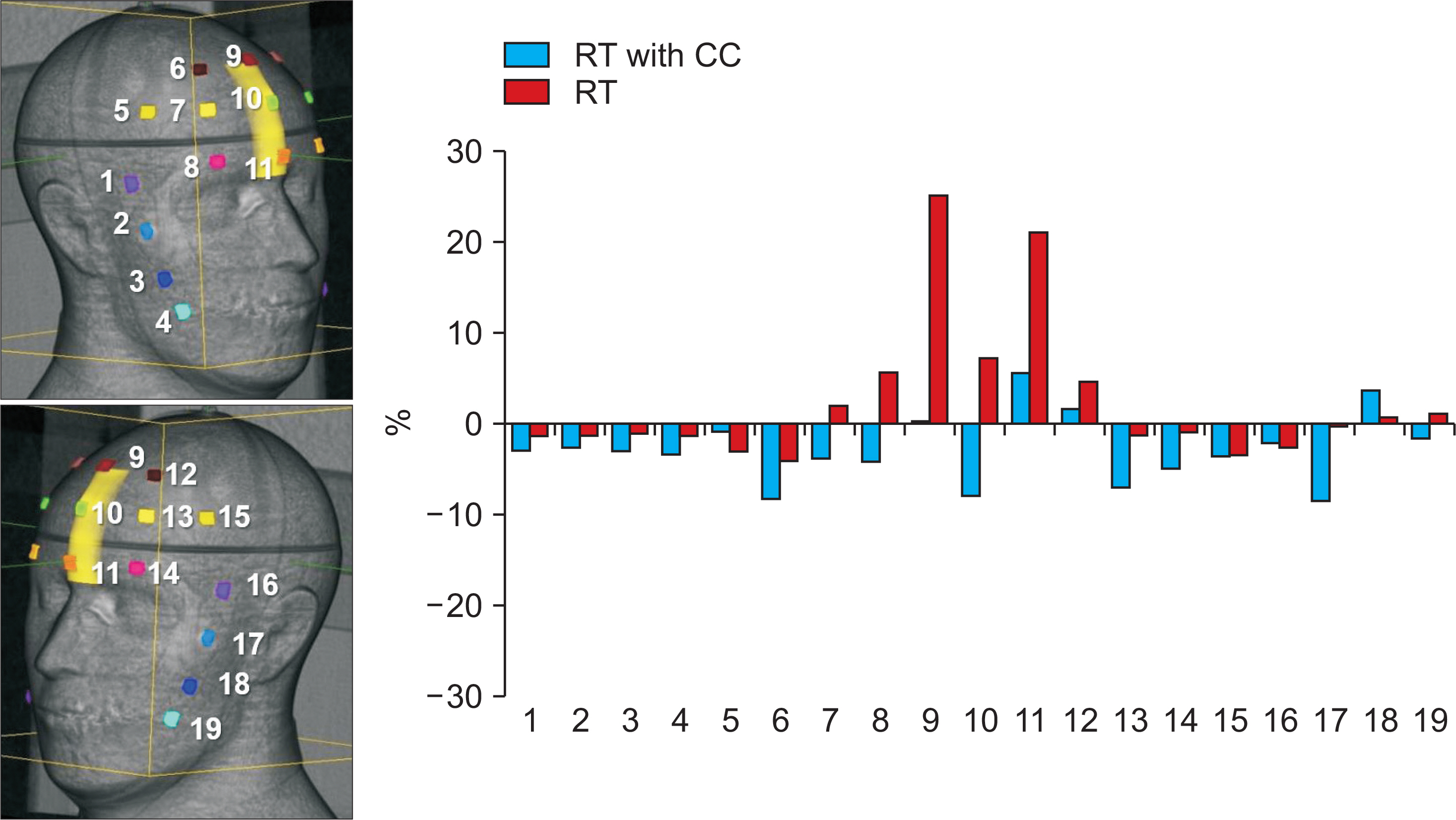
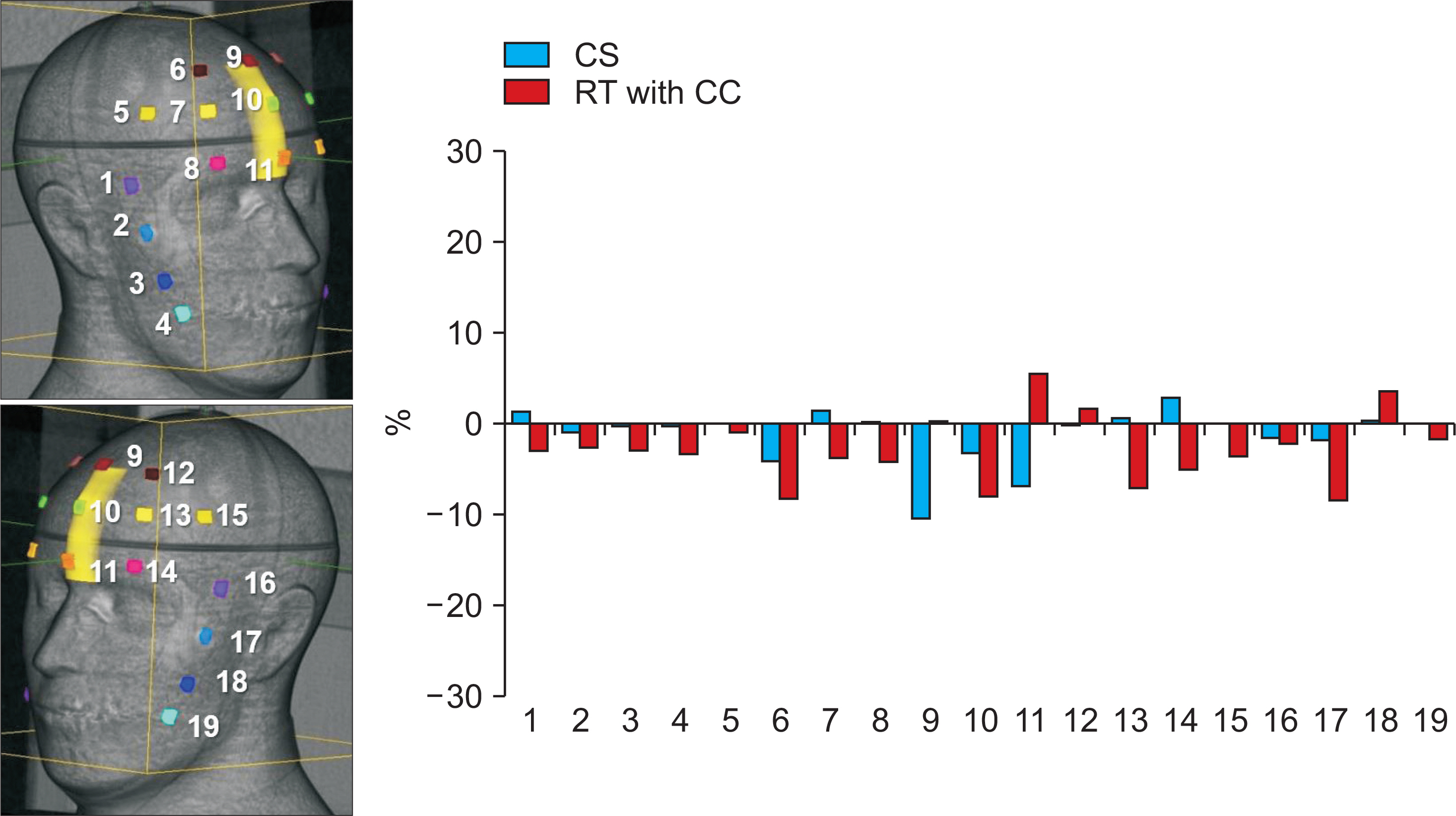
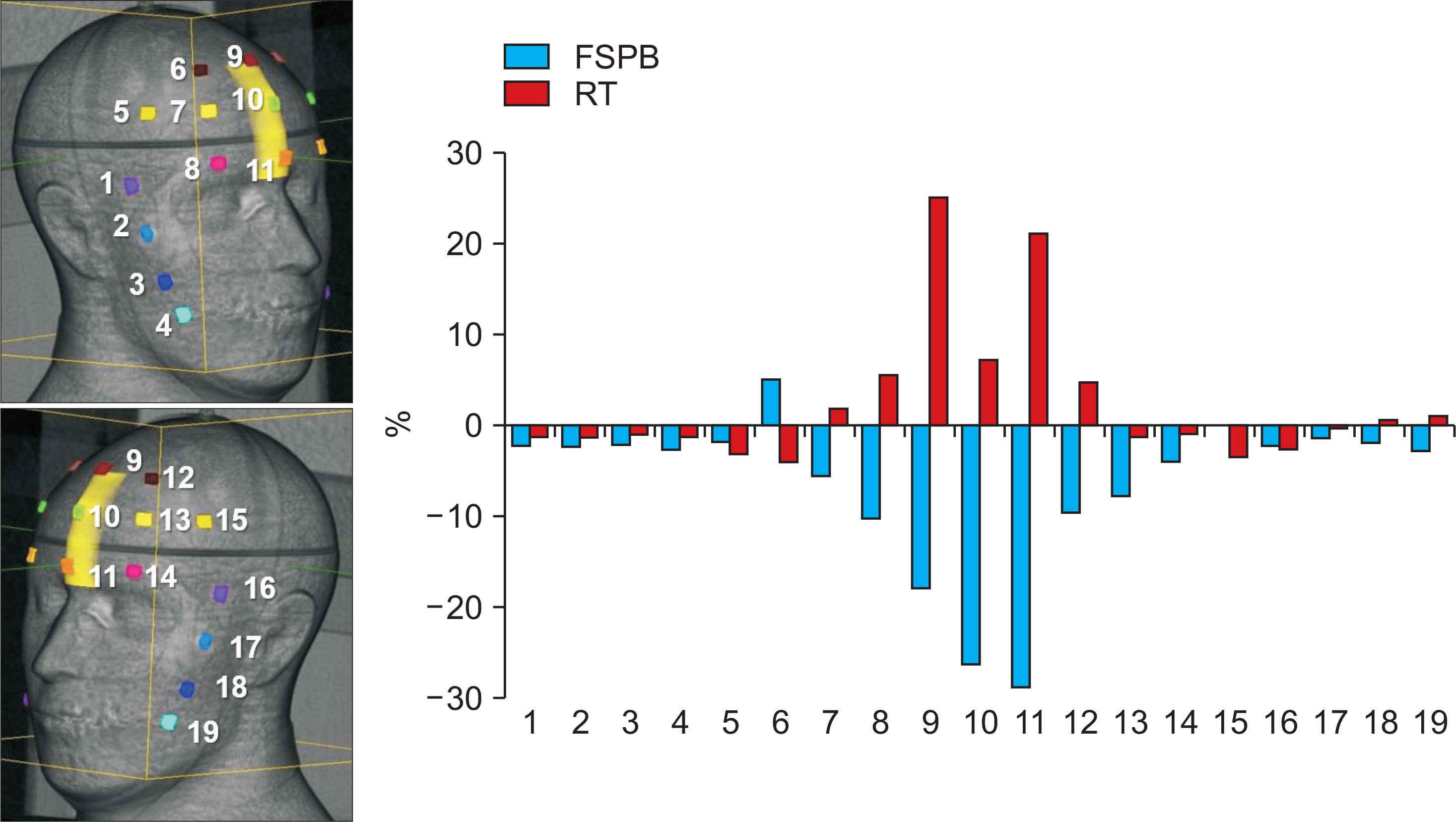
AND CONCLUSIONS: The mean differences between calculation and measurement values were −1.2±3.1%, 2.5±7.9%, −2.8±3.8%, −6.6±8.8%, and −1.4±1.8% in CS, RT, RT with contour correction (CC), FSPB, and MC, respectively. FSPB showed a dose error comparable to RT. CS and RT with CC led to a small error as compared to FSPB and RT. Considering OSLDs close to PTV, MC minimized the uncertainty of skin dose as compared to other algorithms.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.Guadagnolo BA., Zagars GK., Araujo D., Ravi V., Shellenberg-er TD., Sturgis EM. Outcomes after definitive treatment for cutaneous angiosarcoma of the face and scalp. Head Neck. 2011. 33(5):661–67.
Article2.Mellenberg DE., Schoeppel SL. Total scalp treatment of mycosis fungoides: the 4× 4 technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993. 27(4):953–58.3.Stelzer KJ., Griffin TW. A randomized prospective trial of radiation therapy for AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993. 27(5):1057–61.
Article4.Katayama S., Haefner MF., Mohr A, et al. Accelerated tomotherapy delivery with TomoEdge technique. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015. 16(2):33–42.
Article5.Sterzing F., Uhl M., Hauswald H, et al. Dynamic jaws and dynamic couch in helical tomotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010. 76(4):1266–73.
Article6.Lee E., Park K., Kim JS., Kim YB., Lee H. Practical Implementation of Patient-Specific Quality Assurance for Small and Multiple Brain Tumors in CyberKnife with Fixed Collimators. Prog Med Phys. 2018. 29(2):53–8.
Article7.Dieterich S., Cavedon C., Chuang CF, et al. Report of AAPM TG 135: quality assurance for robotic radiosurgery. Med Phys. 2011. 38(6):2914–36.
Article8.Yoon J., Park K., Kim JS., Kim YB., Lee H. Acceptance Testing and Commissioning of Robotic Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy M6 System Equipped with InCiseTM 2 Multileaf Collimator. Prog Med Phys. 2018. 29(1):8–15.9.Jursinic PA. Changes in optically stimulated luminescent dosimeter (OSLD) dosimetric characteristics with accumulated dose. Med Phys. 2010. 37(1):132–40.
Article10.Jursinic PA. Characterization of optically stimulated luminescent dosimeters, OSLDs, for clinical dosimetric measurements. Med Phys. 2007. 34(12):4594–604.
Article11.Kim J., Park K., Yoon J, et al. Feasibility Study of a Custom-made Film for End-to-End Quality Assurance Test of Robotic Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy System. Prog Med Phys. 2016. 27(4):189–95.
Article12.Sterpin E., Salvat F., Olivera G., Vynckier S. Monte Carlo evaluation of the convolution/superposition algorithm of Hi–ArtTM tomotherapy in heterogeneous phantoms and clinical cases. Med Phys. 2009. 36(5):1566–75.13.Okoye CC., Patel RB., Hasan S, et al. Comparison of ray tracing and Monte Carlo calculation algorithms for thoracic spine lesions treated with CyberKnife-based stereotactic body radiation therapy. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016. 15(1):196–202.
Article14.Yoon J., Lee E., Park K., Kim JS., Kim YB., Lee H. Patient-Specific Quality Assurance in a Multileaf Collimator-Based CyberKnife System Using the Planar Ion Chamber Array. Prog Med Phys. 2018. 29(2):59–65.
Article15.Mcguinness C., Descovich M., Barani I. CyberKnife image-guided hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy. Image-Guided Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Practical Approach to Guide Treatment of Brain and Spine Tumors: CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group. 2016. 49.
Article16.Kang KM., Jeong BK., Choi HS, et al. Combination effects of tissue heterogeneity and geometric targeting error in stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer using CyberKnife. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015. 16(5):193–204.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of survival rates between patients treated with conventional radiotherapy and helical tomotherapy for head and neck cancer
- Selection of Proper Modality in Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- A case report of a patient with squamous cell carcinoma of the face irradiated using a stereotactic technique
- Comparison of Helical TomoTherapy with Linear Accelerator Base Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy for Head & Neck Cases
- Superficial Dosimetry for Helical Tomotherapy