Acute Crit Care.
2018 Nov;33(4):276-279. 10.4266/acc.2016.00829.
Iatrogenic Intramural Dissection of the Esophagus after Insertion of a Laryngeal Mask Airway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. md.baeksh@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2441247
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2016.00829
Abstract
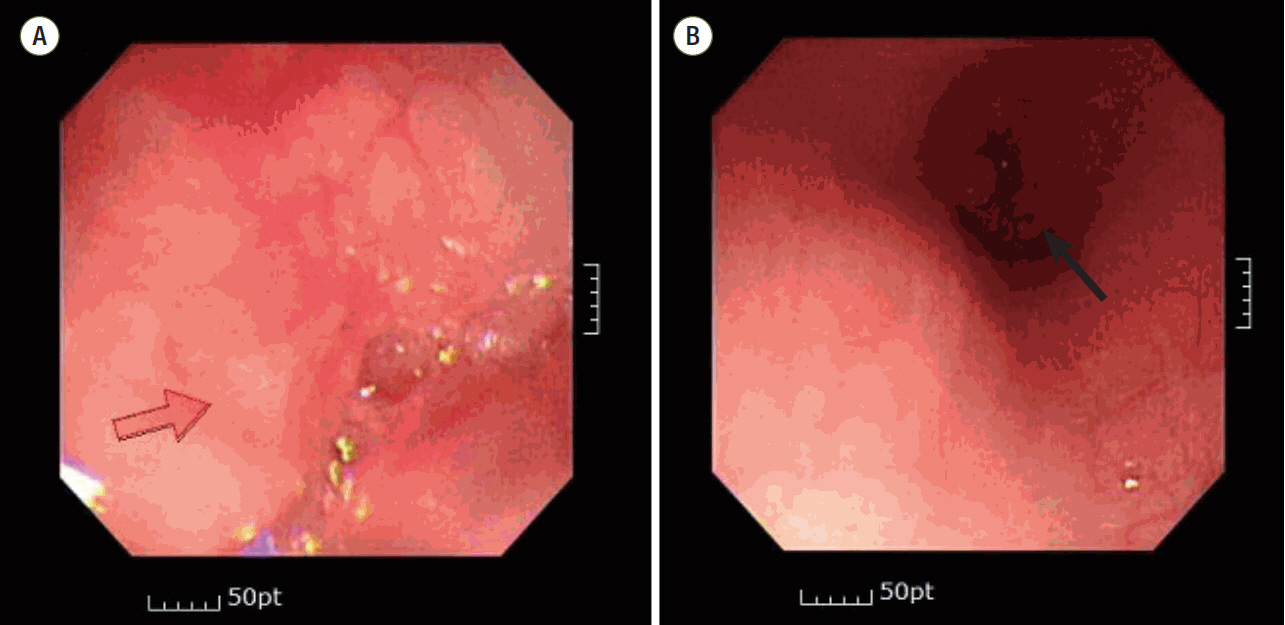
- In pediatric patients, a laryngeal mask airway (LMA) is usually used during minor surgeries that require general anesthesia. No esophageal injury has been reported after insertion of an LMA. We report a case of an esophageal injury with intramural dissection after an i-gel® (size, 1.5; Intersurgical Ltd.) insertion in a pediatric patient. A 2-month-old male infant was hospitalized for left inguinal herniorrhaphy. After induction of anesthesia, a trained resident tried to insert an i-gel®. However, it was only successful after three attempts. Dysphagia was sustained until postoperative day 10, and the pediatrician observed duplication of the esophagus on gastroendoscopy. However, a whitish mucosal lesion, which looked like a scar, was observed, and previous lesions suggestive of esophageal duplication were almost healed on postdischarge day 11. His condition was diagnosed as dysphagia and esophagitis due to an esophageal laceration, not esophageal duplication. He was scheduled for symptomatic treatment with a proton pump inhibitor. In conclusion, although an esophageal injury or perforation in pediatric patients is rare, an LMA insertion or a procedure such as aspiration or nasogastric tube insertion should be performed gently to avoid a possible injury to the esophagus in pediatric patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gander JW, Berdon WE, Cowles RA. Iatrogenic esophageal perforation in children. Pediatr Surg Int. 2009; 25:395–401.
Article2. Derbes VJ, Mitchell RE Jr. Hermann Boerhaaves’ Atrocis, nec descripti prius, morbi historia, the fi rst translation of the classic report of rupture of the esophagus, with annotations. Bull Med Libr Assoc. 1955; 43:217–40.3. Panieri E, Millar AJ, Rode H, Brown RA, Cywes S. Iatrogenic esophageal perforation in children: patterns of injury, presentation, management, and outcome. J Pediatr Surg. 1996; 31:890–5.
Article4. Burgard G, Möllhoff T, Prien T. The effect of laryngeal mask cuff pressure on postoperative sore throat incidence. J Clin Anesth. 1996; 8:198–201.
Article5. Dubost C, Kaswin D, Duranteau A, Jehanno C, Kaswin R. Esophageal perforation during attempted endotracheal intubation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1979; 78:44–51.
Article6. Sticco A, Khettry A, Aldape C, Tortolani A, Velcek F. Iatrogenic esophageal perforation in a premature neonate: a current nonoperative approach to management. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep. 2014; 2:37–9.
Article7. van der Zee DC, Festen C, Severijnen RS, van der Staak FH. Management of pediatric esophageal perforation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998; 95:692–5.
Article8. Noma U, Ali R, Kane R, Donnelly M. Progressive dysphagia post laryngeal mask airway intubation. J Surg Tech Case Rep. 2009; 1:23–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Laryngeal Mask Airway Placement and Tracheal Intubation on Intraocular Pressure
- Effects of Laryngeal Mask Insertion on Cardiovascular Responses during Cesarean Section
- Advantages, Disadvantages, Indications, Contraindications and Surgical Technique of Laryngeal Airway Mask
- Fracture of Laryngeal Mask Airway during General Anesthesia
- Laryngeal Mask Airway