Korean J Radiol.
2019 Mar;20(3):385-398. 10.3348/kjr.2018.0496.
Comparison of Radioembolization and Sorafenib for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Safety and Efficacy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. m1fenew@daum.net
- KMID: 2438268
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.0496
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare the safety and efficacy of radioembolization with that of sorafenib for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombosis (PVTT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases were searched for studies reporting outcomes in patients with HCC and PVTT treated with radioembolization or sorafenib. Meta-analyses of cumulative overall survival (OS) and Kaplan-Meier survival rates according to the time to progression (TTP) and incidence of adverse events (AEs) were performed. Subgroup analyses were conducted on 1-year OS data.
RESULTS
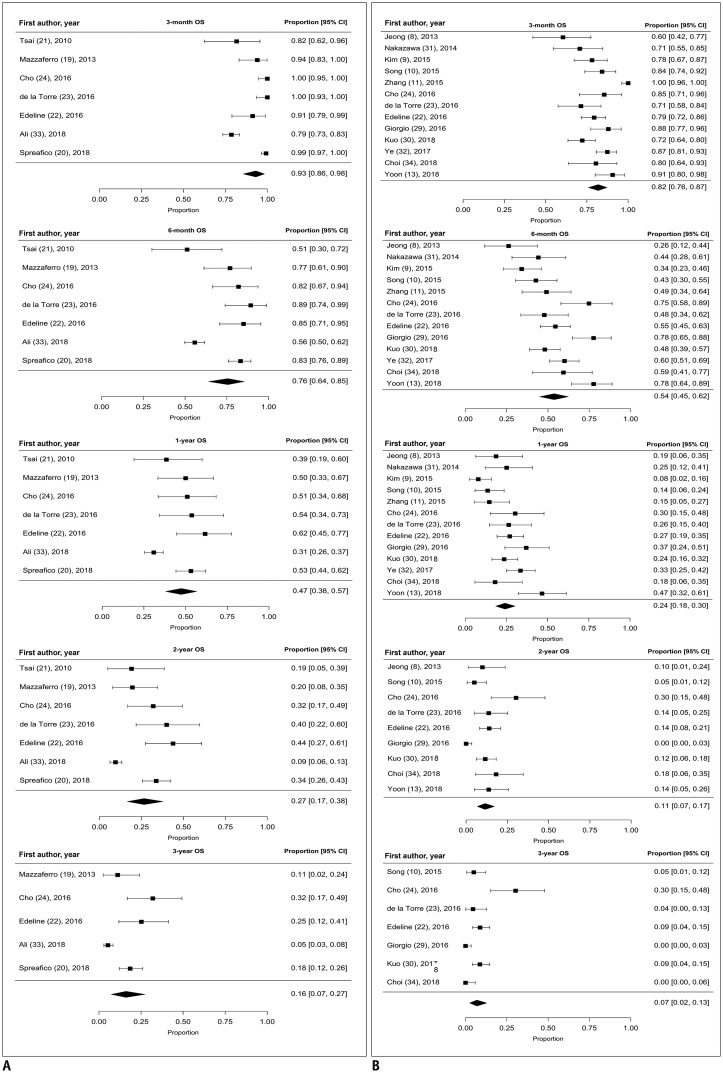
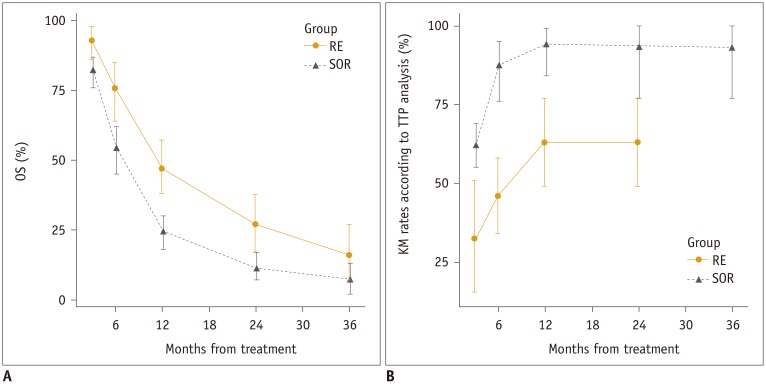
Seventeen studies were identified (four involving radioembolization, 10 involving sorafenib, and three comparing both). Pooled OS rates were higher in the radioembolization group, notably at 6 months {76% (95% confidence interval [CI], 64-85%) vs. 54% (95% CI, 45-62%)} and 1 year (47% [95% CI, 38-57%] vs. 24% [95% CI, 18-30%]); TTP was also longer with radioembolization. In patients undergoing radioembolization, the proportion of patients with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group status 0 (p < 0.0001), Child-Pugh A (p < 0.0001), extrahepatic metastasis (p = 0.0012), and a history of cancer treatment (p = 0.0048) was identified as a significant source of heterogeneity for the 1-year OS. Radioembolization was associated with a lower incidence of grade 3/4 AEs than sorafenib (9% [95% CI, 3-27%] vs. 28% [95% CI, 17-43%]).
CONCLUSION
Compared with sorafenib, radioembolization is a safer and more effective treatment for HCC with PVTT and is associated with prolonged survival, delayed tumor progression, and fewer grade 3/4 AEs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:394–424. PMID: 30207593.
Article2. European Association For The Study Of The Liver. European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 56:908–943. PMID: 22424438.3. Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A, Vilana R, Ayuso Mdel C, Sala M, et al. Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology. 1999; 29:62–67. PMID: 9862851.
Article4. Schöniger-Hekele M, Müller C, Kutilek M, Oesterreicher C, Ferenci P, Gangl A. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Central Europe: prognostic features and survival. Gut. 2001; 48:103–109. PMID: 11115830.5. Cabibbo G, Enea M, Attanasio M, Bruix J, Craxì A, Cammà C. A meta-analysis of survival rates of untreated patients in randomized clinical trials of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010; 51:1274–1283. PMID: 20112254.
Article6. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022. PMID: 21374666.
Article7. Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS, Sirlin CB, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, et al. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2018; 67:358–380. PMID: 28130846.
Article8. Jeong SW, Jang JY, Shim KY, Lee SH, Kim SG, Cha SW, et al. Practical effect of sorafenib monotherapy on advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombosis. Gut Liver. 2013; 7:696–703. PMID: 24312711.
Article9. Kim GA, Shim JH, Yoon SM, Jung J, Kim JH, Ryu MH, et al. Comparison of chemoembolization with and without radiation therapy and sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a propensity score analysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015; 26:320–329. PMID: 25612807.
Article10. Song DS, Song MJ, Bae SH, Chung WJ, Jang JY, Kim YS, et al. A comparative study between sorafenib and hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. J Gastroenterol. 2015; 50:445–454. PMID: 25027973.
Article11. Zhang Y, Fan W, Wang Y, Lu L, Fu S, Yang J, et al. Sorafenib with and without transarterial chemoembolization for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with main portal vein tumor thrombosis: a retrospective analysis. Oncologist. 2015; 20:1417–1424. PMID: 26446238.
Article12. Pinter M, Sieghart W, Graziadei I, Vogel W, Maieron A, Königsberg R, et al. Sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma from mild to advanced stage liver cirrhosis. Oncologist. 2009; 14:70–76. PMID: 19144684.
Article13. Yoon SM, Ryoo BY, Lee SJ, Kim JH, Shin JH, An JH, et al. Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization plus external beam radiotherapy vs sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma with macroscopic vascular invasion: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018; 4:661–669. PMID: 29543938.14. Vilgrain V, Pereira H, Assenat E, Guiu B, Ilonca AD, Pageaux GP, et al. SARAH Trial Group. Efficacy and safety of selective internal radiotherapy with yttrium-90 resin microspheres compared with sorafenib in locally advanced and inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (SARAH): an open-label randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017; 18:1624–1636. PMID: 29107679.15. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:25–34. PMID: 19095497.
Article16. Joo I, Kim HC, Kim GM, Paeng JC. Imaging evaluation following 90Y radioembolization of liver tumors: what radiologists should know. Korean J Radiol. 2018; 19:209–222. PMID: 29520178.17. Lee EW, Alanis L, Cho SK, Saab S. Yttrium-90 selective internal radiation therapy with glass microspheres for hepatocellular carcinoma: current and updated literature review. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:472–488. PMID: 27390539.
Article18. Iñarrairaegui M, Thurston KG, Bilbao JI, D'Avola D, Rodriguez M, Arbizu J, et al. Radioembolization with use of yttrium-90 resin microspheres in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010; 21:1205–1212. PMID: 20598574.
Article19. Mazzaferro V, Sposito C, Bhoori S, Romito R, Chiesa C, Morosi C, et al. Yttrium-90 radioembolization for intermediate-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase 2 study. Hepatology. 2013; 57:1826–1837. PMID: 22911442.
Article20. Spreafico C, Sposito C, Vaiani M, Cascella T, Bhoori S, Morosi C, et al. Development of a prognostic score to predict response to Yttrium-90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion. J Hepatol. 2018; 68:724.
Article21. Tsai AL, Burke CT, Kennedy AS, Moore DT, Mauro MA, Dixon RD, et al. Use of yttrium-90 microspheres in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010; 21:1377–1384. PMID: 20691606.
Article22. Edeline J, Crouzet L, Campillo-Gimenez B, Rolland Y, Pracht M, Guillygomarc'h A, et al. Selective internal radiation therapy compared with sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016; 43:635–643. PMID: 26455499.
Article23. de la Torre MA, Buades-Mateu J, de la Rosa PA, Lué A, Bustamante FJ, Serrano MT, et al. A comparison of survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein invasion treated by radioembolization or sorafenib. Liver Int. 2016; 36:1206–1212. PMID: 26910784.
Article24. Cho YY, Lee M, Kim HC, Chung JW, Kim YH, Gwak GY, et al. Radioembolization is a safe and effective treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: a propensity score analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0154986. PMID: 27149067.
Article25. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151:W65–W94. PMID: 19622512.
Article26. Quality assessment tool for case series studies. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Web site. Accessed June 14, 2018. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools.27. Lee J, Kim KW, Choi SH, Huh J, Park SH. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies evaluating diagnostic test accuracy: a practical review for clinical researchers-Part II. Statistical methods of meta-analysis. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:1188–1196. PMID: 26576107.
Article28. Sterne JA, Egger M, Smith GD. Systematic reviews in health care: investigating and dealing with publication and other biases in meta-analysis. BMJ. 2001; 323:101–105. PMID: 11451790.
Article29. Giorgio A, Merola MG, Montesarchio L, Merola F, Santoro B, Coppola C, et al. Sorafenib combined with radio-frequency ablation compared with sorafenib alone in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma invading portal vein: a western randomized controlled trial. Anticancer Res. 2016; 36:6179–6183. PMID: 27793949.
Article30. Kuo YH, Wu IP, Wang JH, Hung CH, Rau KM, Chen CH, et al. The outcome of sorafenib monotherapy on hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Invest New Drugs. 2018; 36:307–314. PMID: 28466374.
Article31. Nakazawa T, Hidaka H, Shibuya A, Okuwaki Y, Tanaka Y, Takada J, et al. Overall survival in response to sorafenib versus radiotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein tumor thrombosis: propensity score analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014; 14:84. PMID: 24886354.
Article32. Ye SL, Chen X, Yang J, Bie P, Zhang S, Liu F, et al. Evaluation of sorafenib in Chinese unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients with prior surgery and portal vein tumor thrombosis: a subset analysis of GIDEON study data. Tumour Biol. 2017; 39:1010428317695030. PMID: 28349781.
Article33. Ali R, Gabr A, Abouchaleh N, Al Asadi A, Mora RA, Kulik L, et al. Survival analysis of advanced HCC treated with radioembolization: comparing impact of clinical performance status versus vascular invasion/metastases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018; 41:260–269. PMID: 28879621.
Article34. Choi JH, Chung WJ, Bae SH, Song DS, Song MJ, Kim YS, et al. Randomized, prospective, comparative study on the effects and safety of sorafenib vs. hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018; 82:469–478. PMID: 29982870.
Article35. Senthilnathan S, Memon K, Lewandowski RJ, Kulik L, Mulcahy MF, Riaz A, et al. Extrahepatic metastases occur in a minority of hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with locoregional therapies: analyzing patterns of progression in 285 patients. Hepatology. 2012; 55:1432–1442. PMID: 22109811.
Article36. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, BlancJF , et al. SHARP Investigators Study Group. Sorafenibin advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:378–390. PMID: 18650514.37. Omata M, Cheng AL, Kokudo N, Kudo M, Lee JM, Jia J, et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the managementof hepatocellular carcinoma: a 2017 update. Hepatol Int. 2017; 11:317–370. PMID: 28620797.38. Kim JH, Shim JH, Yoon HK, Ko HK, Kim JW, Gwon DI. Chemoembolization related to good survival for selectedpatients with hepatocellular carcinoma invading segmentalportal vein. Liver Int. 2018; 38:1646–1654. PMID: 29436101.39. Han K, Kim JH, Ko GY, Gwon DI, Sung KB. Treatmentof hepatocellular carcinoma with portal venous tumorthrombosis: a comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:407–416. PMID: 26755886.40. Chow PKH, Gandhi M, Tan SB, Khin MW, Khasbazar A, Ong J, et al. Asia-Pacific Hepatocellular Carcinoma Trials Group. SIRveNIB: selective internal radiation therapy versus sorafenibin Asia-Pacific patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:1913–1921. PMID: 29498924.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reappraisal of transarterial radioembolization for liver-confined hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: Editorial on “Transarterial radioembolization versus tyrosine kinase inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis”
- Comparing efficacies of different treatment regimens in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus using network meta-analysis
- Locoregional Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis
- Treatments Other than Sorafenib for Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Concurrent transarterial radioembolization and combination atezolizumab/ bevacizumab treatment of infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a case report