Acute Crit Care.
2018 Feb;33(1):16-22. 10.4266/acc.2017.00542.
The Effect of Electrical Muscle Stimulation and In-bed Cycling on Muscle Strength and Mass of Mechanically Ventilated Patients: A Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Anesthesia and Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nswksj@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Nursing, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2436303
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2017.00542
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Critically ill patients experience muscle weakness, which leads to functional disability. Both functional electrical stimulation (FES) and in-bed cycling can be an alternative measure for intensive care unit (ICU) patients who are not feasible for active exercise. The aim of this study was to examine whether FES and in-bed cycling have a positive effect on muscle mass in ICU patients.
METHODS
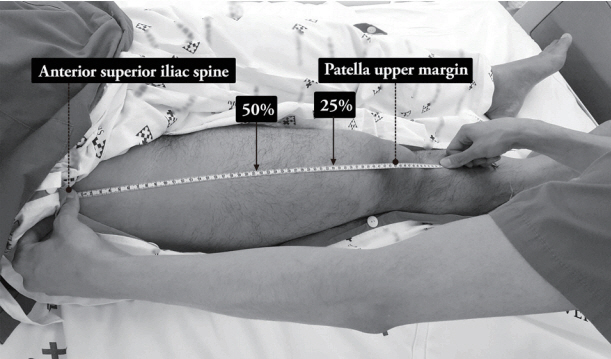
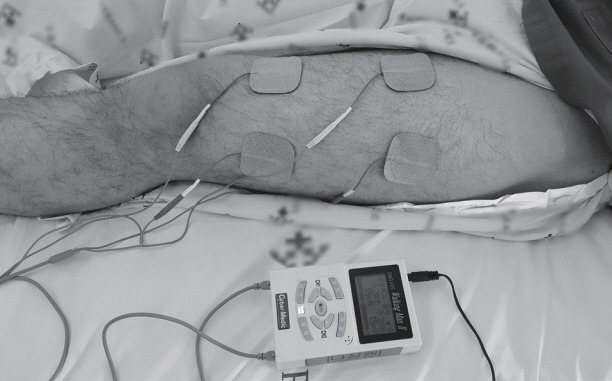
Critically ill patients who received mechanical ventilation for at least 24 hours were included. After passive range of motion exercise, in-bed cycling was applied for 20 minutes, and FES was applied for 20 minutes on the left leg. The right leg received in-bed cycling and the left leg received both FES and in-bed cycling. Thigh circumferences and rectus femoris cross-sectional area (CSA) were assessed with ultrasonography before and after the intervention. Muscle strength was assessed by Medical Research Council scale.
RESULTS
A total of 10 patients were enrolled in this study as a pilot study. Before and after the intervention, the CSA of right rectus femoris increased from 5.08 ± 1.51 cm² to 6.01 ± 2.21 cm², which was statistically significant (P = 0.003). The thigh circumference was also increased and statistically significant (P = 0.006). There was no difference between left and right in regard to FES application. There is no significant change in muscle strength before and after the intervention (right and left, P = 0.317 and P = 0.368, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
In-bed cycling increased thigh circumferences rectus femoris CSA. Adding FES did not show differences.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Rehabilitation and Intensive Care Unit
Deokkyu Kim
Acute Crit Care. 2018;33(1):43-45. doi: 10.4266/acc.2018.00080.
Reference
-
1. Schweickert WD, Hall J. ICU-acquired weakness. Chest. 2007; 131:1541–9.
Article2. De Jonghe B, Sharshar T, Lefaucheur JP, Authier FJ, Durand-Zaleski I, Boussarsar M, et al. Paresis acquired in the intensive care unit: a prospective multicenter study. JAMA. 2002; 288:2859–67.3. Stevens RD, Dowdy DW, Michaels RK, Mendez-Tellez PA, Pronovost PJ, Needham DM. Neuromuscular dysfunction acquired in critical illness: a systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2007; 33:1876–91.4. Ali NA, O’Brien JM Jr, Hoffmann SP, Phillips G, Garland A, Finley JC, et al. Acquired weakness, handgrip strength, and mortality in critically ill patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 178:261–8.
Article5. Elliott D, Davidson JE, Harvey MA, Bemis-Dougherty A, Hopkins RO, Iwashyna TJ, et al. Exploring the scope of post-intensive care syndrome therapy and care: engagement of non-critical care providers and survivors in a second stakeholders meeting. Crit Care Med. 2014; 42:2518–26.6. Schweickert WD, Pohlman MC, Pohlman AS, Nigos C, Pawlik AJ, Esbrook CL, et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009; 373:1874–82.
Article7. Burtin C, Clerckx B, Robbeets C, Ferdinande P, Langer D, Troosters T, et al. Early exercise in critically ill patients enhances short-term functional recovery. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37:2499–505.
Article8. Needham DM, Truong AD, Fan E. Technology to enhance physical rehabilitation of critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37(10 Suppl):S436–41.
Article9. Poulsen JB, Møller K, Jensen CV, Weisdorf S, Kehlet H, Perner A. Effect of transcutaneous electrical muscle stimulation on muscle volume in patients with septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2011; 39:456–61.
Article10. Gerovasili V, Stefanidis K, Vitzilaios K, Karatzanos E, Politis P, Koroneos A, et al. Electrical muscle stimulation preserves the muscle mass of critically ill patients: a randomized study. Crit Care. 2009; 13:R161.
Article11. Kho ME, Molloy AJ, Clarke FJ, Ajami D, Mc-Caughan M, Obrovac K, et al. TryCYCLE: a prospective study of the safety and feasibility of early in-bed cycling in mechanically ventilated patients. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0167561.
Article12. Kho ME, Martin RA, Toonstra AL, Zanni JM, Mantheiy EC, Nelliot A, et al. Feasibility and safety of in-bed cycling for physical rehabilitation in the intensive care unit. J Crit Care. 2015; 30:1419.e1–5.
Article13. Topp R, Ditmyer M, King K, Doherty K, Hornyak J 3rd. The effect of bed rest and potential of prehabilitation on patients in the intensive care unit. AACN Clin Issues. 2002; 13:263–76.
Article14. Garnacho-Montero J, Amaya-Villar R, García-Garmendía JL, Madrazo-Osuna J, Ortiz-Leyba C. Effect of critical illness polyneuropathy on the withdrawal from mechanical ventilation and the length of stay in septic patients. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33:349–54.
Article15. Leijten FS, Harinck-de Weerd JE, Poortvliet DC, de Weerd AW. The role of polyneuropathy in motor convalescence after prolonged mechanical ventilation. JAMA. 1995; 274:1221–5.
Article16. Griffiths RD, Palmer TE, Helliwell T, MacLennan P, MacMillan RR. Effect of passive stretching on the wasting of muscle in the critically ill. Nutrition. 1995; 11:428–32.
Article17. Routsi C, Gerovasili V, Vasileiadis I, Karatzanos E, Pitsolis T, Tripodaki E, et al. Electrical muscle stimulation prevents critical illness polyneuromyopathy: a randomized parallel intervention trial. Crit Care. 2010; 14:R74.
Article18. Patsaki I, Gerovasili V, Sidiras G, Karatzanos E, Mitsiou G, Papadopoulos E, et al. Effect of neuromuscular stimulation and individualized rehabilitation on muscle strength in intensive care unit survivors: a randomized trial. J Crit Care. 2017; 40:76–82.
Article19. Fan E, Ciesla ND, Truong AD, Bhoopathi V, Zeger SL, Needham DM. Inter-rater reliability of manual muscle strength testing in ICU survivors and simulated patients. Intensive Care Med. 2010; 36:1038–43.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Electrical Stimulation for Early Axonal Regeneration after Nerve Surgery in Brachial Plexus Injury
- Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on the Muscle Hypertrophy and Cross Training Effect
- Neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy after knee surgery: a systematic review
- Electroceuticals in Muscle Regeneration: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential
- The Effect of Electrical Stimulation on Spasticity in Hemiplegic Patients