Neonatal Med.
2018 Nov;25(4):196-201. 10.5385/nm.2018.25.4.196.
Umbilical Venous Catheter Complication Presenting as Chylous Ascites in a Newborn: Intraperitoneal Extravasation of Total Parenteral Nutrition Infusate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. iamlidia@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2436139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2018.25.4.196
Abstract
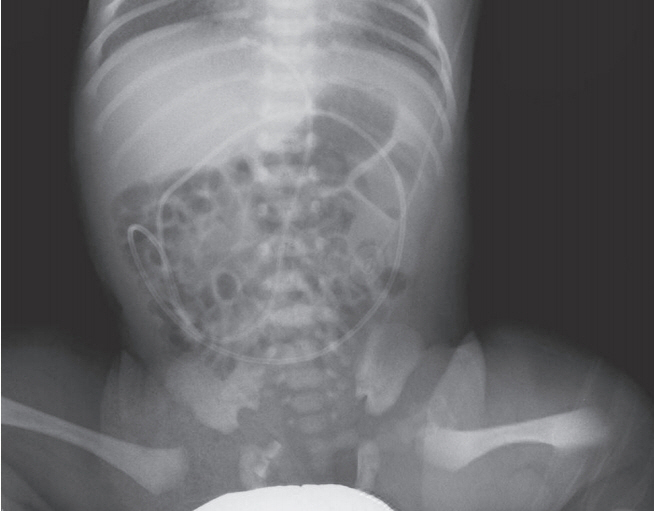
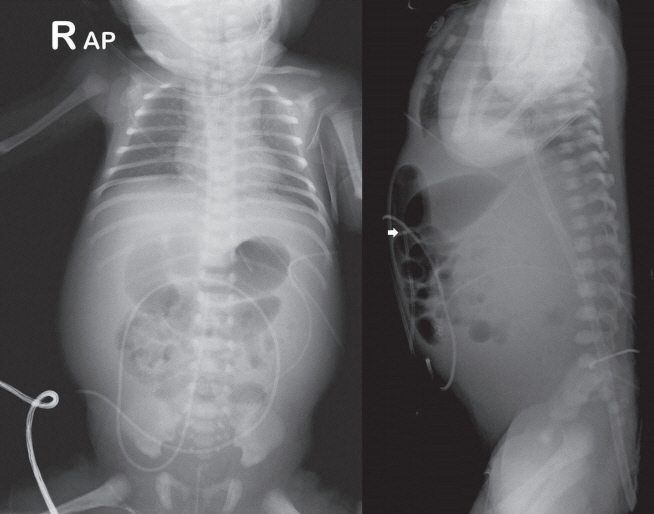
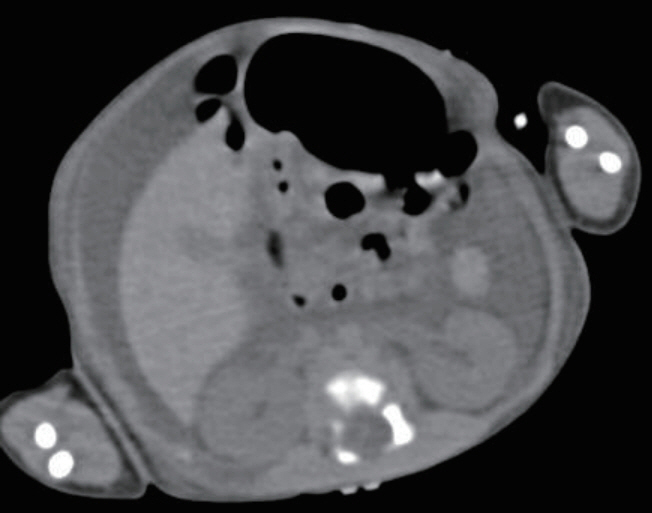
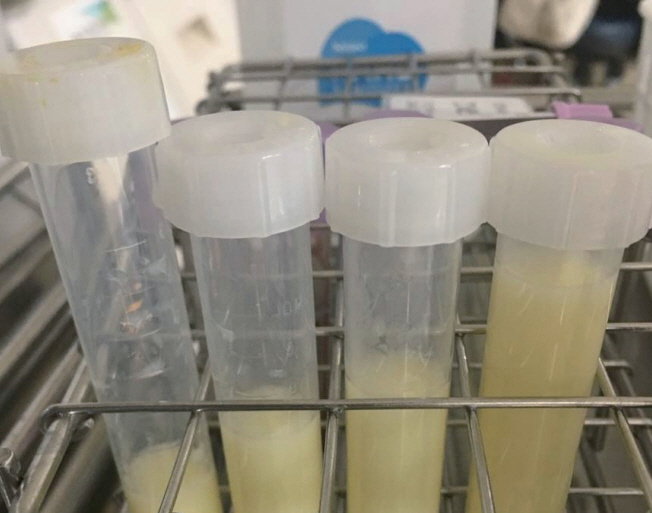
- Umbilical venous catheterization (UVC) is a common practice in intensive neonatal care. However, a malpositioned UVC and its prolonged use may lead to various problems, including mechanical, infectious, and thrombotic complications in various organs such as the liver, lungs, and heart. Congenital chylous ascites is characterized by abnormally high levels of triglycerides in the peritoneal fluid of newborns, which originate from refluxed lymph within the abdominal cavity. Herein, we report a case of an UVC complication presenting as chyloperitoneum simulating congenital chylous ascites in a preterm neonate that resulted from total parenteral nutrition (TPN) extravasation from a malpositioned UVC. Biochemical analysis of intraperitoneal chylous fluid and TPN infusate could help confirm the origin of chyloperitoneum. This case suggests that TPN extravasation from UVC should be considered when chyloperitoneum develops in newborns with an indwelling catheter. UVC positions must also be carefully monitored at regular intervals to recognize associated complications early, particularly in cases with an inevitably malpositioned catheter related to the anatomy of the vessel course.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abiramalatha T, Kumar M, Shabeer MP, Thomas N. Advantages of being diligent: lessons learnt from umbilical venous catheterisation in neonates. BMJ Case Rep. 2016; 2016:bcr2015214073.2. Mutlu M, Aslan Y, Kul S, Yilmaz G. Umbilical venous catheter complications in newborns: a 6-year single-center experience. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016; 29:2817–22.3. Abiramalatha T, Kumar M, Shabeer MP. Pleural effusion caused by a malpositioned umbilical venous catheter in a neonate. BMJ Case Rep. 2015; 2015:bcr2015212705.4. Wu J, Mu D. Vascular catheter-related complications in newborns. J Paediatr Child Health. 2012; 48:E91–5.5. Hermansen MC, Hermansen MG. Intravascular catheter complications in the neonatal intensive care unit. Clin Perinatol. 2005; 32:141–56.6. Tarn AC, Lapworth R. Biochemical analysis of ascitic (peritoneal) fluid: what should we measure? Ann Clin Biochem. 2010; 47(Pt 5):397–407.7. Karagol BS, Zenciroglu A, Gokce S, Kundak AA, Ipek MS. Therapeutic management of neonatal chylous ascites: report of a case and review of the literature. Acta Paediatr. 2010; 99:1307–10.8. Lopez-Gutierrez JC, Tovar JA. Chylothorax and chylous ascites: management and pitfalls. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014; 23:298–302.9. Shukla H, Ferrara A. Rapid estimation of insertional length of umbilical catheters in newborns. Am J Dis Child. 1986; 140:786–8.10. Michel F, Brevaut-Malaty V, Pasquali R, Thomachot L, Vialet R, Hassid S, et al. Comparison of ultrasound and X-ray in determining the position of umbilical venous catheters. Resuscitation. 2012; 83:705–9.11. Ades A, Sable C, Cummings S, Cross R, Markle B, Martin G. Echocardiographic evaluation of umbilical venous catheter lacement. J Perinatol. 2003; 23:24–8.12. Dunn PM. Localization of the umbilical catheter by post-mortem measurement. Arch Dis Child. 1966; 41:69–75.13. Tsui BC, Richards GJ, Van Aerde J. Umbilical vein catheterization under electrocardiogram guidance. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005; 15:297–300.14. Hagerott HE, Kulkarni S, Restrepo R, Reeves-Garcia J. Clinicalradiologic features and treatment of hepatic lesions caused by inadvertent infusion of parenteral nutrition in liver parenchyma due to malposition of umbilical vein catheters. Pediatr Radiol. 2014; 44:810–5.15. Gulcan H, Hanta D, Torer B, Temiz A, Demir S. Hepatic laceration as a life-threatening complication of umbilical venous catheterization. Turk J Pediatr. 2011; 53:342–5.16. Guzoglu N, Erdeve O, Yilmaz Y, Dilmen U. Intraperitoneal extravasation from umbilical venous catheter in differential diagnosis of neonatal chylous ascites. Acta Paediatr. 2010; 99:1284.17. Shareena I, Khu YS, Cheah FC. Intraperitoneal extravasation of total parental nutrition infusate from an umbilical venous catheter. Singapore Med J. 2008; 49:e35. –6.18. Coley BD, Seguin J, Cordero L, Hogan MJ, Rosenberg E, Reber K. Neonatal total parenteral nutrition ascites from liver erosion by umbilical vein catheters. Pediatr Radiol. 1998; 28:923–7.19. Ramasethu J. Complications of vascular catheters in the neonatal intensive care unit. Clin Perinatol. 2008; 35:199–222.20. Cohen M, Sprigg A, Roberts I, Bustani P. Subcapsular haematoma and multifocal necrosis as fatal liver complications following umbilical vein catheterisation in a premature baby. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2006; 16:55–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Central Venous Vascular Erosion Complicating Extravasation of Total Parenteral Nutrition
- A case of persistent chylous ascites after staging operation for primary fallopian tubal cancer
- A case of post-operative chylous ascites after a splenorenal shunt operation in a child with congenital hepatic fibrosis
- Chylous ascites caused by acute pancreatitis with portal vein thrombosis
- Umbilical vs peripheral vein catheterization for parenteral nutrition in sick premature neonates