Ann Lab Med.
2012 Nov;32(6):438-441.
Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala salmonis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. micro.lee@samsung.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
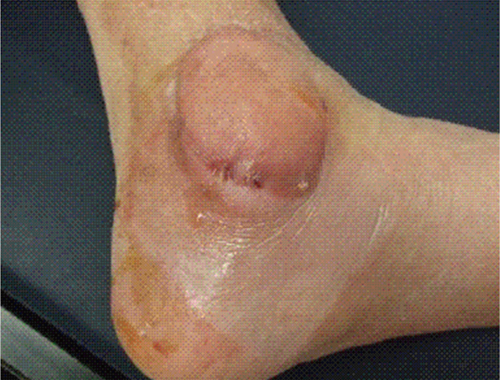
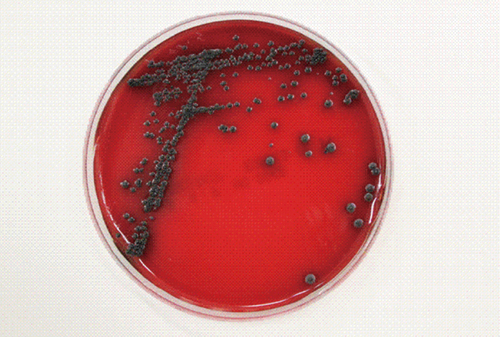
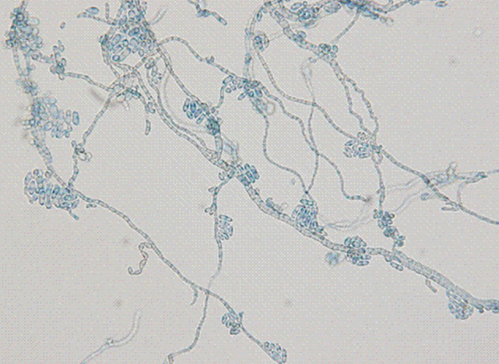
- We report a case of subcutaneous infection in a 55-yr-old Korean diabetic patient who presented with a cystic mass of the ankle. Black fungal colonies were observed after culturing on blood and Sabouraud dextrose agar. On microscopic observation, septated ellipsoidal or cylindrical conidia accumulating on an annellide were visualized after staining with lactophenol cotton blue. The organism was identified as Exophiala salmonis by sequencing of the ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer region. Phaeohyphomycosis is a heterogeneous group of mycotic infections caused by dematiaceous fungi and is commonly associated with immunocompromised patients. The most common clinical manifestations of subcutaneous lesions are abscesses or cystic masses. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case in Korea of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by E. salmonis that was confirmed by molecular analysis and identification of morphological characteristics. This case suggests that E. salmonis infections are no longer restricted to fish.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rinaldi MG. Phaeohyphomycosis. Dermatol Clin. 1996. 14:147–153.
Article2. Madan V, Bisset D, Harris P, Howard S, Beck MH. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala salmonis. Br J Dermatol. 2006. 155:1082–1084.
Article3. Otis EJ, Wolke RE, Blazer VS. Infection of Exophiala salmonis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J Wildl Dis. 1985. 21:61–64.
Article4. Ajello L, Georg LK, Steigbigel RT, Wang CJ. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia. 1974. 66:490–498.
Article5. Suh MK, Kwon SW, Kim TH, Sun YW, Lim JW, Ha GY, et al. A case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala jeanselmei. Korean J Dermatol. 2005. 43:124–127.6. Koga T, Matsuda T, Matsumoto T, Furue M. Therapeutic approaches to subcutaneous mycoses. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003. 4:537–543.
Article7. Ben-Ami R, Lewis RE, Raad II, Kontoyiannis DP. Phaeohyphomycosis in a tertiary care cancer center. Clin Infect Dis. 2009. 48:1033–1041.
Article8. Rossetto AL, Dellatorre G, Pérsio RA, Romeiro JC, Cruz RC. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis on the scrotum caused by Exophiala jeanselmei: case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2010. 85:517–520.9. Ronan SG, Uzoaru I, Nadimpalli V, Guitart J, Manaligod JR. Primary cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis: report of seven cases. J Cutan Pathol. 1993. 20:223–228.
Article10. Suh MK. Phaeohyphomycosis in Korea. Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai Zasshi. 2005. 46:67–70.
Article11. Choi J, Lee Y, Chung HS, Koo JS, Yong D, Kim YS, et al. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Phaeoacremonium species in a kidney transplant patient: the first case in Korea. Korean J Lab Med. 2011. 31:201–204.12. Jeong ES, Shin JH, Shin MG, Suh SP, Ryang DW. Fungemia due to Exophiala dermatitidis. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2010. 13:135–139.13. Kim DS, Yoon YM, Kim SW. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala dermatitidis successfully treated with Itraconazole. Korean J Med Mycol. 1999. 4:79–83.14. Chang CL, Kim DS, Park DJ, Kim HJ, Lee CH, Shin JH. Acute cerebral phaeohyphomycosis due to Wangiella dermatitidis accompanied by cerebrospinal fluid eosinophilia. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:1965–1966.15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by DNA target sequencing. 1st ed. approved guideline, MM18-A. 2008. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.16. Jang JH, Lee JH, Ki CS, Lee NY. Identification of clinical mold isolates by sequence analysis of the internal transcribed spacer region, ribosomal large-subunit D1/D2, and beta-tubulin. Ann Lab Med. 2012. 32:126–132.17. Nomura M, Maeda M, Seishima M. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala jeanselmei in collagen disease patient. J Dermatol. 2010. 37:1046–1050.
Article18. Aoyama Y, Nomura M, Yamanaka S, Ogawa Y, Kitajima Y. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala xenobiotica in a non-Hodgkin lymphoma patient. Med Mycol. 2009. 47:95–99.19. Sharkey PK, Graybill JR, Rinaldi MG, Stevens DA, Tucker RM, Peterie JD, et al. Itraconazole treatment of phaeohyphomycosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990. 23:577–586.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala oligosperma Showing Multiple Cysts
- Phaeohyphomycosis Due to Exophiala dermatitidis Successfully Treated with Itraconazole
- The First Case of Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala xenobiotica in an Immunocompetent Patient in Korea
- A Case of Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala jeanselmei
- A Case of Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala Jeanselmei