J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2019 Jan;62(1):35-45. 10.3340/jkns.2018.0203.
Four-Year Experience Using an Advanced Interdisciplinary Hybrid Operating Room : Potentials in Treatment of Cerebrovascular Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nsyjee@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2434344
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2018.0203
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To describe our experiences with a fully equipped high-end digital subtraction angiography (DSA) system within a hybrid operating room (OR).
METHODS
A single-plane DSA system with 3-dimensional rotational angiography, cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), and real-time navigation software was used in our hybrid OR. Between April 2014 and January 2018, 191 sessions of cerebrovascular procedures were performed in our hybrid OR. After the retrospective review of all cases, the procedures were categorized into three subcategorical procedures : combined endovascular and surgical procedure, complementary rescue procedure during intervention and surgery, and frameless stereotaxic operation.
RESULTS
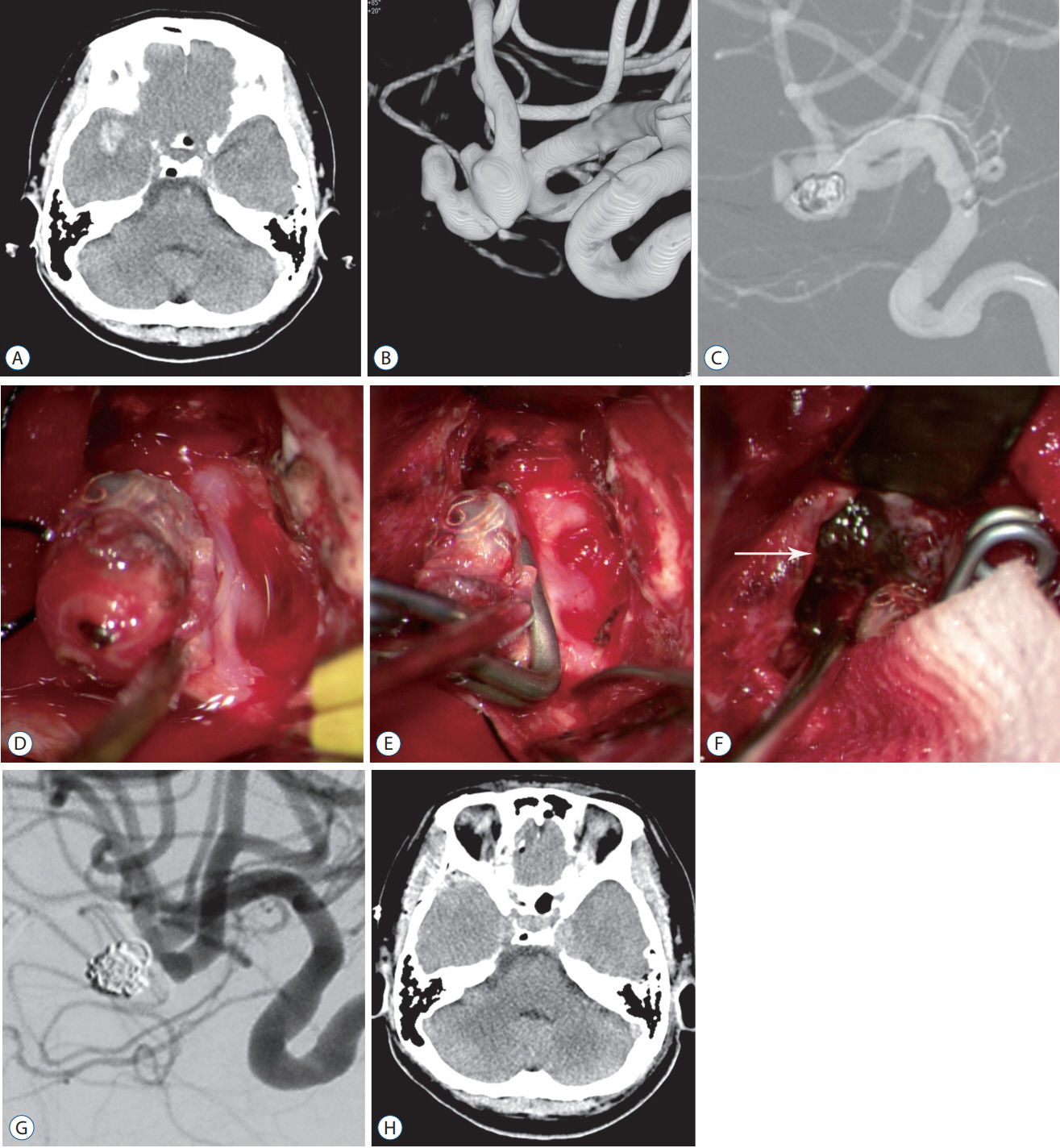
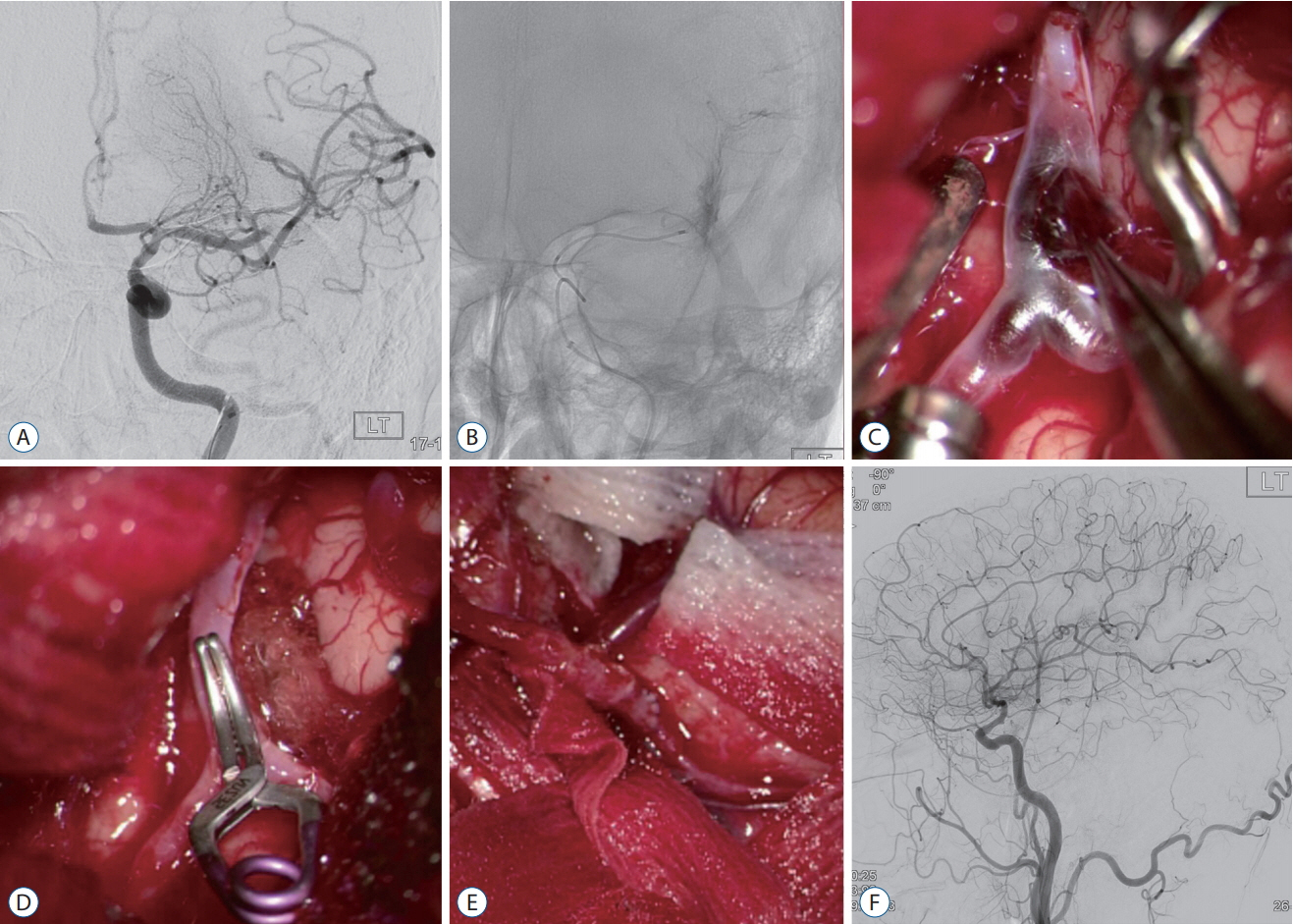
Forty-nine of 191 procedures were performed using hybrid techniques. Four cases of blood blister aneurysms and a ruptured posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm were treated using bypass surgery and endovascular trapping. Eight cases of ruptured aneurysm with intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) were treated by partial embolization and surgical clipping. Six cases of ruptured arteriovenous malformation with ICH were treated by Onyx embolization of nidus and subsequent surgical removal of nidus and ICH. Two (5.4%) of the 37 cases of pre-mature rupture during clipping were secured by endovascular coil embolization. In one (0.8%) complicated case of 103 intra-arterial thrombectomy procedures, emergency surgical embolectomy with bypass surgery was performed. In 27 cases of ICH, frameless stereotaxic hematoma aspiration was performed using XperGuide® system (Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherlands). All procedures were performed in single sessions without any procedural complications.
CONCLUSION
Hybrid OR with a fully equipped DSA system could provide precise and safe treatment strategies for cerebrovascular diseases. Especially, we could suggest a strategy to cope flexibly in complex lesions or unexpected situations in hybrid OR. CBCT with real-time navigation software could augment the usefulness of hybrid OR.
MeSH Terms
-
Aneurysm
Aneurysm, Ruptured
Angiography
Angiography, Digital Subtraction
Arteries
Arteriovenous Malformations
Blister
Cerebrovascular Disorders*
Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Embolectomy
Embolization, Therapeutic
Emergencies
Hematoma
Intracranial Hemorrhages
Operating Rooms*
Retrospective Studies
Rupture
Surgical Instruments
Thrombectomy
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Braak SJ, van Strijen MJ, van Leersum M, van Es HW, van Heesewijk JP. Real-time 3D fluoroscopy guidance during needle interventions: technique, accuracy, and feasibility. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 194:W445–W451. 2010.
Article2. Chang SH, Shin HS, Lee SH, Koh HC, Koh JS. Rebleeding of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in the immediate postoperative period after coil embolization. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 17:209–216. 2015.
Article3. Chen SF, Kato Y, Kumar A, Tan GW, Oguri D, Oda J, et al. Intraoperative rupture in the surgical treatment of patients with intracranial aneurysms. J Clin Neurosci. 34:63–69. 2016.
Article4. Cho WS, Kim JE, Park SQ, Ko JK, Kim DW, Park JC, et al. Korean clinical practice guidelines for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 61:127–166. 2018.
Article5. Fandino J, Taussky P, Marbacher S, Muroi C, Diepers M, Fathi AR, et al. The concept of a hybrid operating room: applications in cerebrovascular surgery. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 115:113–117. 2013.
Article6. Fong YW, Hsu SK, Huang CT, Hsieh CT, Chen MH, Huang JS, et al. Impact of intraoperative 3-dimensional volume-rendering rotational angiography on clip repositioning rates in aneurysmal surgery. World Neurosurg. 114:e573–e580. 2018.
Article7. Gautschi OP, Smoll NR, Kotowski M, Schatlo B, Tosic M, Stimec B, et al. Non-assisted versus neuro-navigated and XperCT-guided external ventricular catheter placement: a comparative cadaver study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 156:777–785. discussion 785. 2014.
Article8. Hsu CE, Lin TK, Lee MH, Lee ST, Chang CN, Lin CL, et al. The impact of surgical experience on major intraoperative aneurysm rupture and their consequences on outcome: a multivariate analysis of 538 microsurgical clipping cases. PLoS One. 11:e0151805. 2016.
Article9. Jadhav AP, Ribo M, Grandhi R, Linares G, Aghaebrahim A, Jovin TG, et al. Transcervical access in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 6:652–657. 2014.
Article10. Jartti P, Isokangas JM, Karttunen A, Jartti A, Haapea M, Koskelainen T, et al. Early rebleeding after coiling of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Acta Radiol. 51:1043–1049. 2014.
Article11. Kawamura Y, Sayama T, Maehara N, Nishimura A, Iihara K. Ruptured aneurysm of an aberrant internal carotid artery successfully treated with simultaneous intervention and surgery in a hybrid operating room. World Neurosurg. 102:695.e1–695.e5. 2017.
Article12. Lee SM, Park CM, Lee KH, Bahn YE, Kim JI, Goo JM. C-arm cone-beam CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung nodules: clinical experience in 1108 patients. Radiology. 271:291–300. 2014.
Article13. Mori R, Yuki I, Kajiwara I, Nonaka Y, Ishibashi T, Karagiozov K, et al. Hybrid operating room for combined neuroendovascular and endoscopic treatment of ruptured cerebral aneurysms with intraventricular hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 89:727.e9–727.e12. 2016.
Article14. Murayama Y, Irie K, Saguchi T, Ishibashi T, Ebara M, Nagashima H, et al. Robotic digital subtraction angiography systems within the hybrid operating room. Neurosurgery. 68:1427–1432. discussion 1433. 2011.
Article15. Murayama Y, Arakawa H, Ishibashi T, Kawamura D, Ebara M, Irie K, et al. Combined surgical and endovascular treatment of complex cerebrovascular diseases in the hybrid operating room. J Neurointerv Surg. 5:489–493. 2013.
Article16. Nesbit GM, Nesbit EG, Hamilton BE. Integrated cone-beam CT and fluoroscopic navigation in treatment of head and neck vascular malformations and tumors. J Neurointerv Surg. 3:186–190. 2011.
Article17. Ohta T, Murao K, Miyake K, Takemoto K, Nakazawa K. Risk factors for early hemorrhagic complications after endovascular coiling of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 35:2136–2139. 2014.
Article18. Park J, Son W, Park KS, Kang DH, Shin IH. Intraoperative premature rupture of middle cerebral artery aneurysms: risk factors and sphenoid ridge proximation sign. J Neurosurg. 125:1235–1241. 2016.
Article19. Park JH, Mun JH, Shin DS, Kim BT. Novel hybrid operating table for neuroendovascular treatment. Turk Neurosurg. 2017; [Epub ahead of print].
Article20. Ritter D, Orman J, Schmidgunst C, Graumann R. 3D soft tissue imaging with a mobile C-arm. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 31:91–102. 2007.
Article21. Satoh A, Sugiyama T, Hongo K, Kakizawa Y, Ishihara S, Matsutani M. Nationwide surveillance of ic anterior (or dorsal) wall aneurysm: with special reference to its dissecting nature. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 103:51–55. 2008.
Article22. Shah SS, Gersey ZC, Nuh M, Ghonim HT, Elhammady MS, Peterson EC. Microsurgical versus endovascular interventions for blood-blister aneurysms of the internal carotid artery: systematic review of literature and meta-analysis on safety and efficacy. J Neurosurg. 127:1361–1373. 2017.
Article23. Shen SC, Tsuei YS, Chen WH, Shen CC. Hybrid surgery for dural arteriovenous fistula in the neurosurgical hybrid operating suite. J Neurointerv Surg. 7:e6. 2015.
Article24. Siewerdsen JH, Moseley DJ, Burch S, Bisland SK, Bogaards A, Wilson BC, et al. Volume CT with a flat-panel detector on a mobile, isocentric C-arm: pre-clinical investigation in guidance of minimally invasive surgery. Med Phys. 32:241–254. 2005.
Article25. White AC, Roark CD, Case DE, Kumpe DA, Seinfeld J. Factors associated with rerupture of intracranial aneurysms after endovascular treatment: a retrospective review of 11years experience at a single institution and review of the literature. J Clin Neurosci. 44:53–62. 2017.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The experience of surgery and endovascular procedure of cerebrovascular disease in the hybrid operating room; Multi-axis robotic C-arm DSA system
- Roadmapping technique in the hybrid operating room for the microsurgical treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms
- Pattern and degree of radiation exposure during endovascular surgery performed using a mobile C-arm or in a hybrid room
- Hybrid operating room applications in the increasingly complex endovascular era: the trump card of modern vascular surgery
- Penetrating Liver Trauma Treated with a Multidisciplinary Approach in the Hybrid Emergency Room: All in One Room