Korean J Ophthalmol.
2019 Feb;33(1):70-81. 10.3341/kjo.2018.0085.
Analysis of Positional Relationships of Various Centers in Cataract Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hwtchah@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2434307
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2018.0085
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the positional relationships of various centers in patients undergoing femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery (FLACS).
METHODS
The locations of the pupil center (PC), limbal center (LC) and lens center were analyzed in each patient using optical coherence tomography during FLACS in 35 eyes of 35 patients. Using the preoperative corneal aberrometry device, angle kappa and the location of the visual axis (VA) were calculated. After acquiring the relative horizontal and vertical coordinates of each center, the distance and location among each center were compared. The relative location and distance of each center were statistically evaluated.
RESULTS
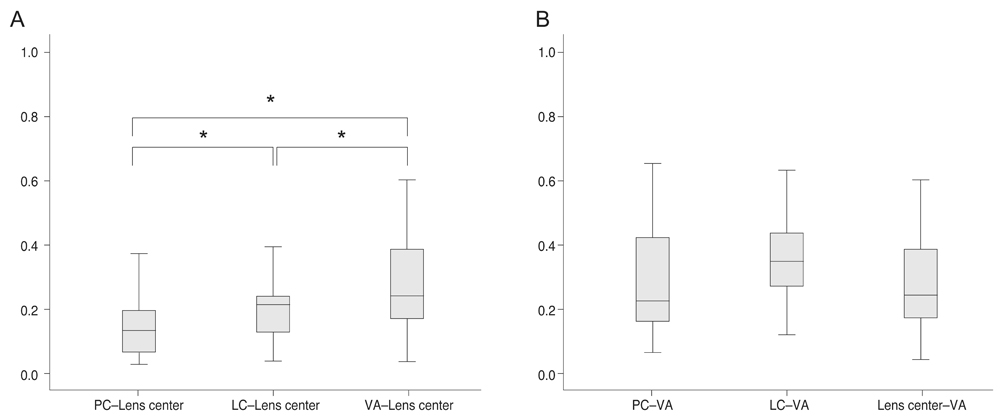
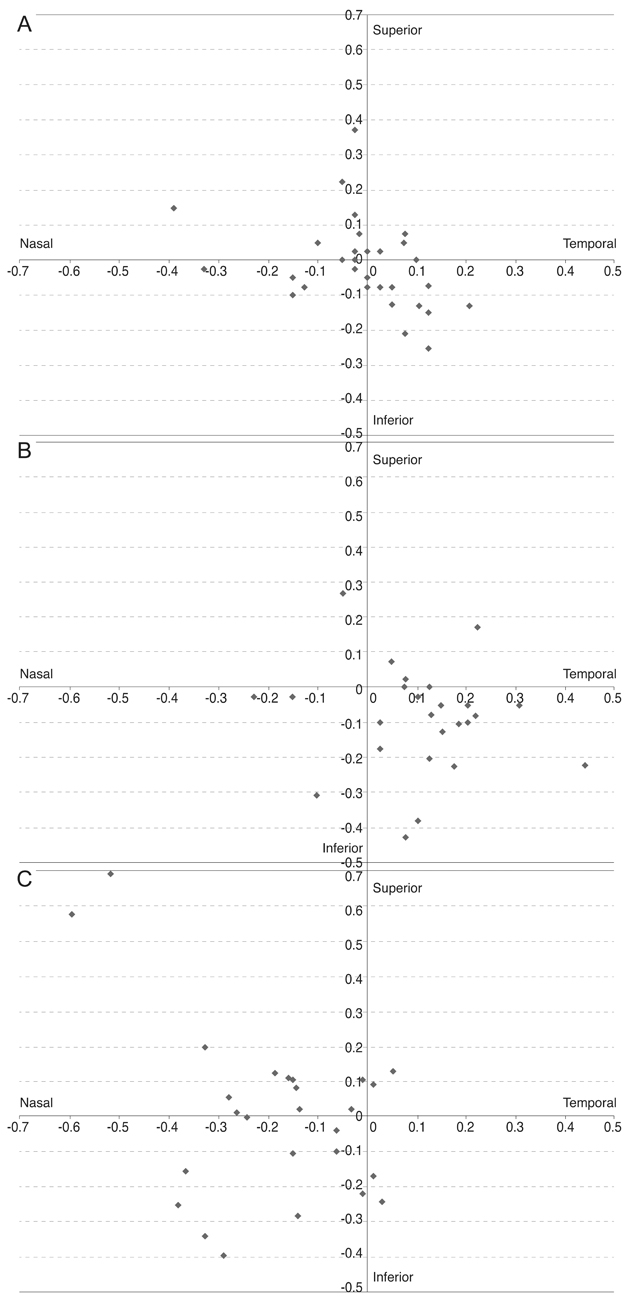
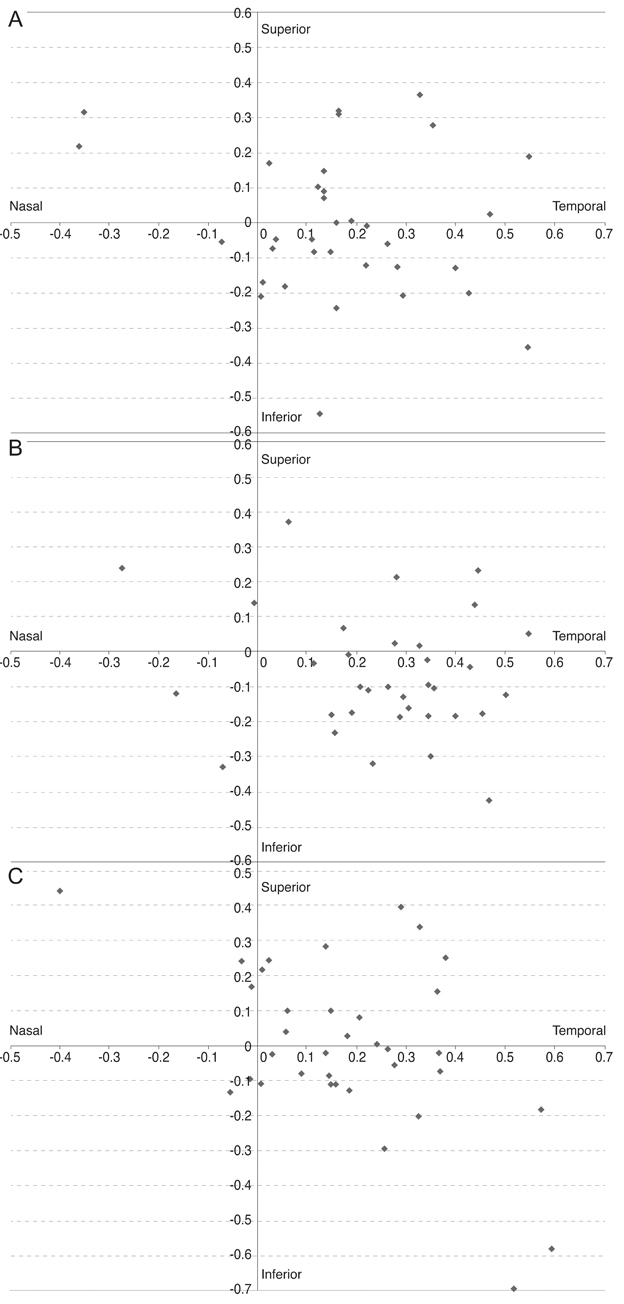
The distance from the PC to the lens center was 0.147 ± 0.103 mm, that from the LC to the lens center was 0.205 ± 0.104 mm, and that from the VA to the lens center was 0.296 ± 0.198 mm. The distance from the PC to the VA was 0.283 ± 0.161 mm, that from the LC to the VA was 0.362 ± 0.153 mm, and that from the lens center to the VA was 0.296 ± 0.198 mm. Among the various centers, the PC was the closest to the lens center, whereas the LC and VA were the farthest. Based on the location of the lens center, the PC, LC, and VA exhibited differences in the X and Y coordinate positions (vertical p = 0.004, horizontal p < 0.001). Among them, the LC was significantly inferior and temporal compared to the PC (vertical p = 0.026, horizontal p = 0.023). Based on the location of the VA, the respective locations of the PC, LC and lens center in two dimensions did not significantly differ (vertical p = 0.310, horizontal p = 0.926).
CONCLUSIONS
This study demonstrated the positional and locational relationships between the centers regarding FLACS. The locations of the PC, LC, and VA were different from the lens center with the PC being the closest. Surgeons should be aware of these positional relationships, especially in FLACS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gimbel HV, Neuhann T. Development, advantages, and methods of the continuous circular capsulorhexis technique. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990; 16:31–37.
Article2. Gimbel HV, Neuhann T. Continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991; 17:110–111.
Article3. Mutlu FM, Bilge AH, Altinsoy HI, Yumusak E. The role of capsulotomy and intraocular lens type on tilt and decentration of polymethylmethacrylate and foldable acrylic lenses. Ophthalmologica. 1998; 212:359–363.
Article4. Taketani F, Matuura T, Yukawa E, Hara Y. Influence of intraocular lens tilt and decentration on wavefront aberrations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:2158–2162.
Article5. Baumeister M, Buhren J, Kohnen T. Tilt and decentration of spherical and aspheric intraocular lenses: effect on higher-order aberrations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1006–1012.
Article6. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Anterior capsule contraction and intraocular lens decentration and tilt after hydrogel lens implantation. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001; 85:1294–1297.
Article7. Moshirfar M, Hoggan RN, Muthappan V. Angle K appa and its importance in refractive surgery. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2013; 6:151–158.8. Prakash G, Prakash DR, Agarwal A, et al. Predictive factor and kappa angle analysis for visual satisfactions in patients with multifocal IOL implantation. Eye (Lond). 2011; 25:1187–1193.
Article9. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Correlation between pupillary size and intraocular lens decentration and visual acuity of a zonal-progressive multifocal lens and a monofocal lens. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:2011–2017.
Article10. de Vries NE, Webers CA, Touwslager WR, et al. Dissatisfaction after implantation of multifocal intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:859–865.
Article11. Soler V, Benito A, Soler P, et al. A randomized comparison of pupil-centered versus vertex-centered ablation in LASIK correction of hyperopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011; 152:591–599.
Article12. Kermani O, Oberheide U, Schmiedt K, et al. Outcomes of hyperopic LASIK with the NIDEK NAVEX platform centered on the visual axis or line of sight. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:S98–103.
Article13. Packer M, Teuma EV, Glasser A, Bott S. Defining the ideal femtosecond laser capsulotomy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015; 99:1137–1142.
Article14. Cekic O, Batman C. The relationship between capsulorhexis size and anterior chamber depth relation. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1999; 30:185–190.15. Tackman RN, Kuri JV, Nichamin LD, Edwards K. Anterior capsulotomy with an ultrashort-pulse laser. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:819–824.
Article16. Nagy ZZ, Kranitz K, Takacs AI, et al. Comparison of intraocular lens decentration parameters after femtosecond and manual capsulotomies. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:564–569.
Article17. Friedman NJ, Palanker DV, Schuele G, et al. Femtosecond laser capsulotomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:1189–1198.
Article18. Kranitz K, Takacs A, Mihaltz K, et al. Femtosecond laser capsulotomy and manual continuous curvilinear capsulorrhexis parameters and their effects on intraocular lens centration. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:558–563.
Article19. Park JH, Lee KH, Lee DJ. Comparison of continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis parameters between femtosecond laser and conventional cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:1800–1807.
Article20. Mihaltz K, Knorz MC, Alio JL, et al. Internal aberrations and optical quality after femtosecond laser anterior capsulotomy in cataract surgery. J Refract Surg. 2011; 27:711–716.
Article21. Filkorn T, Kovacs I, Takacs A, et al. Comparison of IOL power calculation and refractive outcome after laser refractive cataract surgery with a femtosecond laser versus conventional phacoemulsification. J Refract Surg. 2012; 28:540–544.
Article22. Bafna S. Capsulotomy centration in laser cataract surgery. [place unknown]: Eyeworld Asia-Pacific;2014. p. 33–34.23. Rosales P, De Castro A, Jimenez-Alfaro I, Marcos S. Intraocular lens alignment from purkinje and Scheimpflug imaging. Clin Exp Optom. 2010; 93:400–408.
Article24. Basmak H, Sahin A, Yildirim N, et al. Measurement of angle kappa with synoptophore and Orbscan II in a normal population. J Refract Surg. 2007; 23:456–460.
Article25. Kanellopoulos AJ. Topography-guided hyperopic and hyperopic astigmatism femtosecond laser-assisted LASIK: long-term experience with the 400 Hz eye-Q excimer platform. Clin Ophthalmol. 2012; 6:895–901.
Article26. Yang Y, Thompson K, Burns SA. Pupil location under mesopic, photopic, and pharmacologically dilated conditions. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002; 43:2508–2512.27. Walsh G. The effect of mydriasis on the pupillary centration of the human eye. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1988; 8:178–182.
Article28. Wyatt HJ. The form of the human pupil. Vision Res. 1995; 35:2021–2036.
Article29. Lee YE, Joo CK. Assessment of lens center using optical coherence tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and photographs of the anterior segment of the eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015; 56:5512–5518.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Positional Intraocular Pressure between Phakic and Pseudophakic Eyes after Cataract Surgery in a Single Eye
- Positional Vertigo Showing Direction-Changing Positional Nystagmus after Chronic Otitis Media Surgery: Is It Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo?
- Diagnosis and treatment of positional plagiocephaly
- Positional Dizziness and Vertigo without Nystagmus and Orthostatic Hypotension
- Central Positional Nystagmus in Focal Dentate Nucleus Lesion