J Korean Fract Soc.
2019 Jan;32(1):21-26. 10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.21.
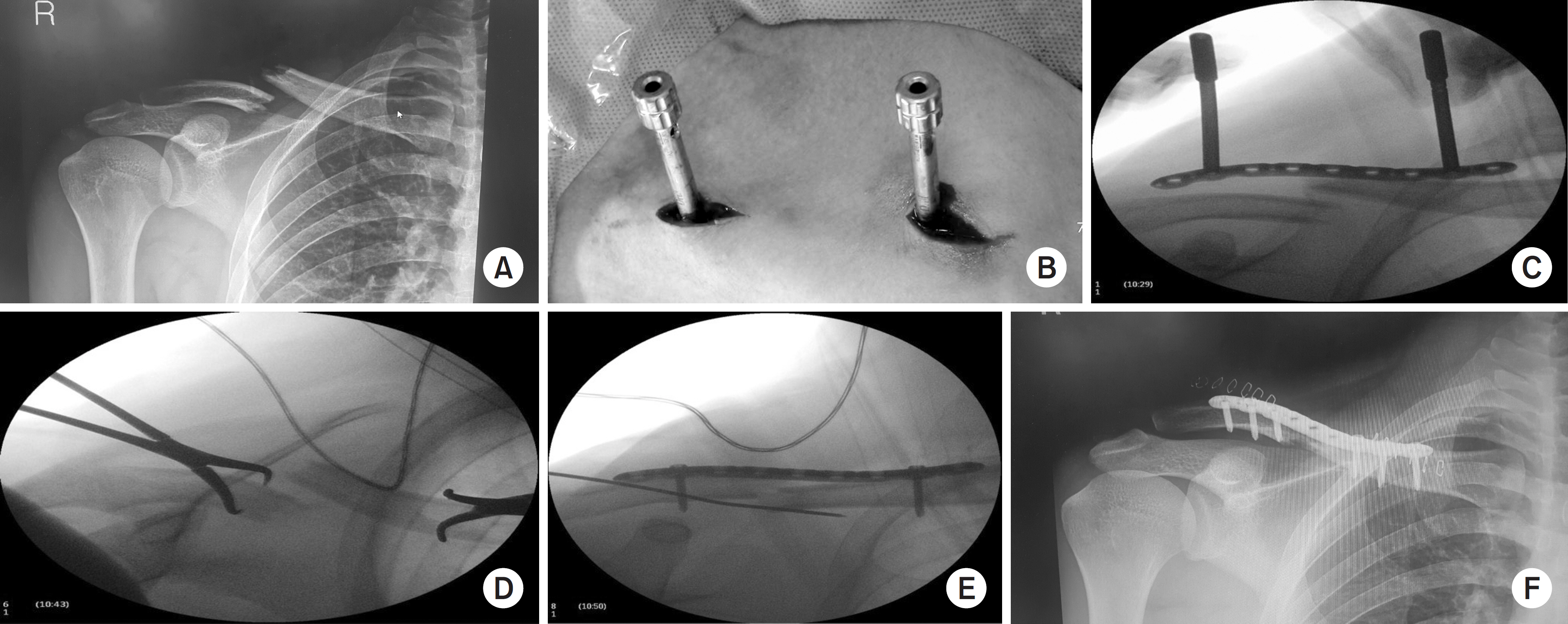
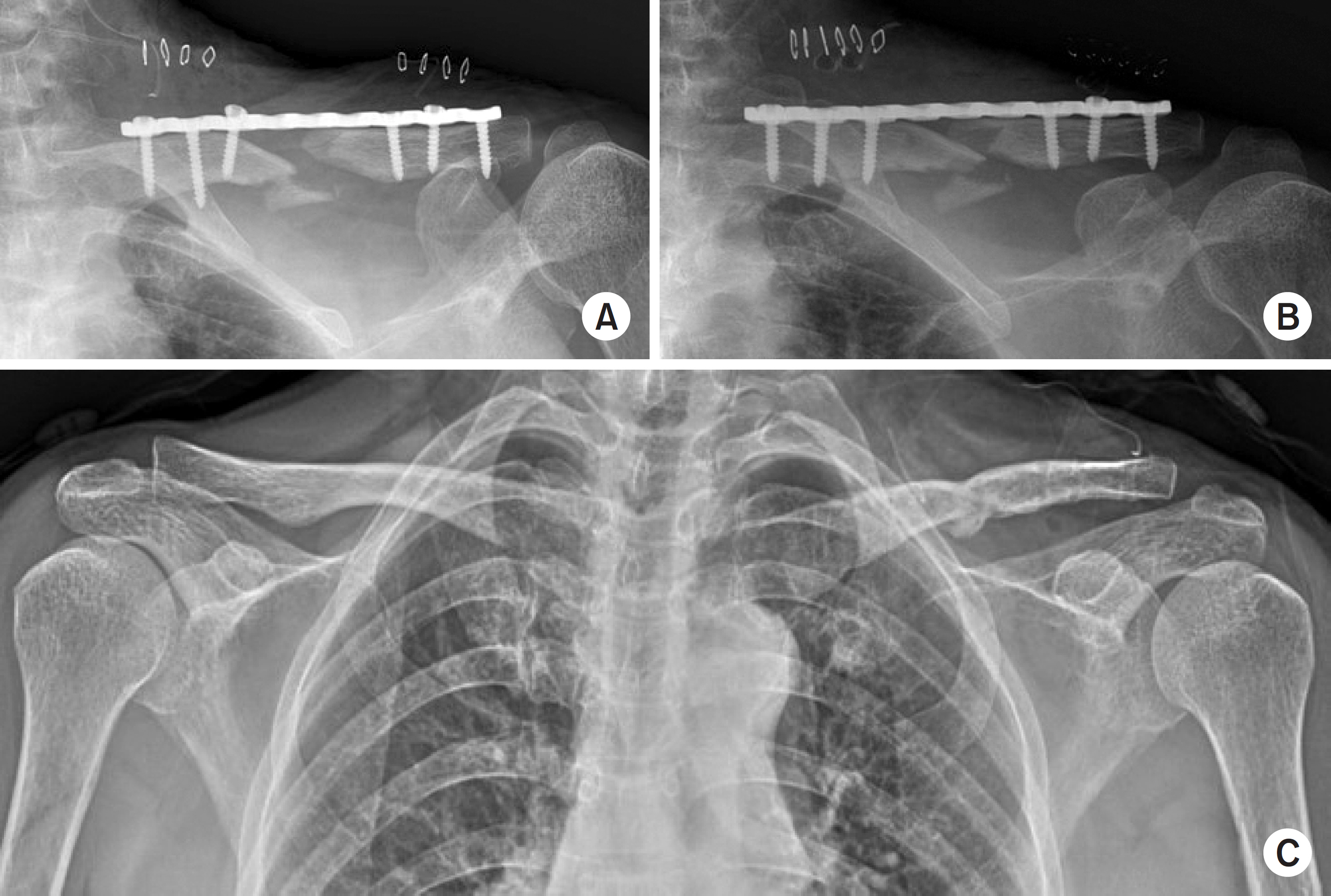
Surgical Results of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Fixation in the Treatment of Clavicle Shaft Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Busan Daedong Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea. redmaniak@naver.com
- KMID: 2432494
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.21
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study analyzed the results of the midclavicle fracture treatment using the minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique in a retrospective manner.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2013 and March 2017, this study analyzed 40 patients who received MIPO surgery. Excluding 1 patient who underwent surgery on another body part injury, and 4 patients who were lost to follow-up over 1 year, 40 patients were analyzed for their operation time, bone union, functional American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score, scar lengths, pain relief (visual analogue scale), and complications.
RESULTS
All patients over a 1 year of follow-up achieved bone union, and American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score 97.6 (94-100) on their shoulder functional scores. Their average operation time was 42.7 minutes, and the average scar length was 6.1 cm. Eighteen patients successfully received metal removal using the previous scar without additional incision. The clavicle length was similar in the normal and operated group.
CONCLUSION
Despite its small sample size, clavicle fixation using the MIPO technique can be considered an effective treatment because of its limited number of complications, such as nonunion and rotational angulations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Robinson CM, Goudie EB, Murray IR, et al. Open reduction and plate fixation versus nonoperative treatment for displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 95:156–184. 2013.2. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, radomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 89:1–10. 2007.3. Böstman O, Manninen M, Pihlajamäki H. Complications of plate fixation in fresh displaced midclavicular fractures. J Trauma. 43:778–783. 1997.4. Wijdicks FJ, Van der Meijden OA, Millett PJ, Verleisdonk EJ, Houwert RM. Systematic review of the complications of plate fixation of clavicle fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 132:617–625. 2012.
Article5. Der Tavitian J, Davison JN, Dias JJ. Clavicular fracture nonunion surgical outcome and complications. Injury. 33:135–143. 2002.
Article6. Millett PJ, Hurst JM, Horan MP, Hawkins RJ. Complications of clavicle fractures treated with intramedullary fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 20:86–91. 2011.
Article7. Strauss EJ, Egol KA, France MA, Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD. Complications of intramedullary Hagie pin fixation for acute midshaft clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 16:280–284. 2007.
Article8. Babst R, Hehli M, Regazzoni P. LISS tractor. Combination of the “less invasive stabilization system” (LISS) with the AO distractor for distal femur and proximal tibial fractures. Unfallchirurg. 104:530–535. 2001.9. Krettek C, Müller M, Miclau T. Evolution of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in the femur. Injury. 32(Suppl 3):SC14–23. 2001.
Article10. Kang TW, Hwang HJ, Lee DK, Han SB, Jeong WK. The usefulness of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis to manage comminuted mid-clavicle fracture: a comparison with conventional open plating. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 52:403–410. 2017.
Article11. Bang JY, Park BO, Seo YM, et al. Surgical treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression plate: conventional open reduction and plating with internal fixation versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 52:529–536. 2017.
Article12. Zhang T, Chen W, Sun J, Zhang Q, Zhang Y. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis technique for displaced midshaft clavicular fracture using the clavicle reductor. Int Orthop. 41:1679–1683. 2017.
Article13. Sohn HS, Kim WJ, Shon MS. Comparison between open plating versus minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for acute displaced clavicular shaft fractures. Injury. 46:1577–1584. 2015.
Article14. Nathe T, Tseng S, Yoo B. The anatomy of the supraclavicular nerve during surgical approach to the clavicular shaft. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 469:890–894. 2011.
Article15. Jiang H, Qu W. Operative treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression plate: comparison between mini-invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) technique and conventional open reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 98:666–671. 2012.
Article16. Yoo SH, Kang SW, Kim BH, et al. A comparison between minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis and plate fixation in the treatment of clavicle midshaft fracture. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 52:1–6. 2017.
Article17. VanBeek C, Boselli KJ, Cadet ER, Ahmad CS, Levine WN. Precontoured plating of clavicle fractures: decreased hardware-related complication? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 469:3337–3343. 2011.18. Jeong HS, Park KJ, Kil KM, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using 3D printing for shaft fractures of clavicle: technical note. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 134:1551–1555. 2014.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Infected Nonunion of Clavicle Shaft after Operation: A Case Report
- Periprosthetic Clavicle Shaft Fracture After Treatment of Type V Distal Clavicle Fracture Using a Hook Plate: A Report of Two Cases
- Surgical Techniques for Percutaneous Reduction by Towel Clips and Percutaneous Intramedullary Fixation with Steinmann Pins for Clavicle Shaft Fractures
- Treatment of Clavicle Medial End Fracture Using Double-plate Fixation
- Clinical Outcomes of Locking Compression Plate Fixation through Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Distal Tibia Fracture