Ann Lab Med.
2019 May;39(3):245-251. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.245.
Analytical and Clinical Performance of the Nanopia Krebs von den Lungen 6 Assay in Korean Patients With Interstitial Lung Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wkmin@amc.seoul.kr
- 4Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2431601
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.3.245
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Krebs von den Lungen 6 (KL-6) is a sensitive marker for diagnosing, monitoring, and predicting the prognoses of interstitial lung diseases (ILDs). This study aimed to evaluate the performance of the Nanopia KL-6 assay (Sekisui Medical, Tokyo, Japan) and to test the relationship between KL-6 concentrations and clinical results.
METHODS
In total, 230 patients diagnosed as having ILDs were enrolled. All underwent high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) followed by the pulmonary function test (PFT). We also enrolled 116 disease controls and 200 healthy controls. Evaluation of the Nanopia KL-6 assay involved determination of precision, linearity, and limit of quantification (LOQ). Results from the Nanopia KL-6 assay were compared with those from ELISA and correlated with the HRCT and PFT results.
RESULTS
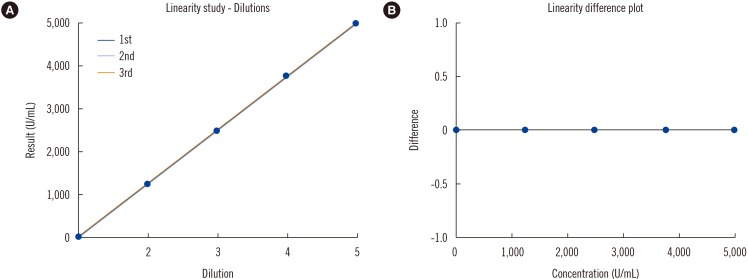
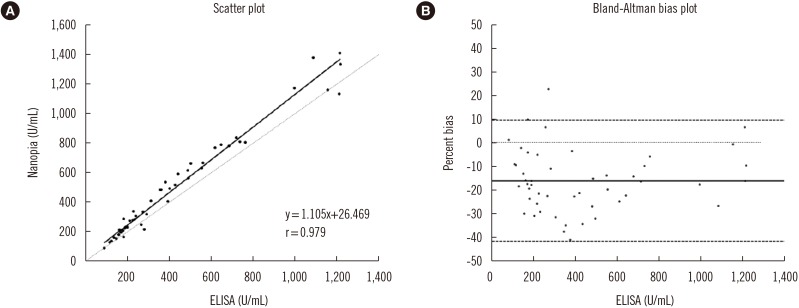
The within-laboratory precisions were < 2% of CV, and linearity was acceptable between 52.2 and 4,966.5 U/mL. The LOQ was 45.2 U/mL. Nanopia and ELISA results were strongly correlated (r=0.979). The average concentration of KL-6 was greater in ILD patients (711.5 U/mL) than in the disease (168.4 U/mL) and healthy (209.4 U/mL) controls. Serum KL-6 concentrations were strongly and moderately correlated with the extent of lung involvement and presence of typical HRCT abnormalities, respectively, and moderately correlated with PFT parameters.
CONCLUSIONS
The overall analytical and clinical performance of the Nanopia KL-6 assay was acceptable. Our study is the first to compare assay platforms and show correlations between KL-6 concentrations and HRCT or PFT results in Korean ILD patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kohno N, Awaya Y, Oyama T, Yamakido M, Akiyama M, Inoue Y, et al. KL-6, a mucin-like glycoprotein, in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993; 148:637–642. PMID: 8368634.2. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 165:277–304. PMID: 11790668.3. National Clinical Guideline C. National institute for health and care excellence: Clinical guidelines. Diagnosis and management of suspected idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. London: Royal College of Physicians (UK) National Clinical Guideline Centre;2013. p. 44–51.4. Meyer KC. Diagnosis and management of interstitial lung disease. Transl Respir Med. 2014; 2:4. PMID: 25505696.5. Huang H, Peng X, Nakajima J. Advances in the study of biomarkers of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Japan. Biosci Trends. 2013; 7:172–177. PMID: 24056167.6. Ishikawa N, Hattori N, Yokoyama A, Kohno N. Utility of KL-6/MUC1 in the clinical management of interstitial lung diseases. Respir Investig. 2012; 50:3–13.7. Ichiyasu H, Ichikado K, Yamashita A, Iyonaga K, Sakamoto O, Suga M, et al. Pneumocyte biomarkers KL-6 and surfactant protein D reflect the distinct findings of high-resolution computed tomography in nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Respiration. 2012; 83:190–197. PMID: 21555868.8. Wakamatsu K, Nagata N, Kumazoe H, Oda K, Ishimoto H, Yoshimi M, et al. Prognostic value of serial serum KL-6 measurements in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Investig. 2017; 55:16–23.9. Ishii H, Mukae H, Kadota J, Kaida H, Nagata T, Abe K, et al. High serum concentrations of surfactant protein A in usual interstitial pneumonia compared with non-specific interstitial pneumonia. Thorax. 2003; 58:52–57. PMID: 12511721.10. du Bois RM, Weycker D, Albera C, Bradford WZ, Costabel U, Kartashov A, et al. Forced vital capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: test properties and minimal clinically important difference. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011; 184:1382–1389. PMID: 21940789.11. Hamai K, Iwamoto H, Ishikawa N, Horimasu Y, Masuda T, Miyamoto S, et al. Comparative study of circulating MMP-7, CCL18, KL-6, SP-A, and SP-D as disease markers of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Dis Markers. 2016; 2016:4759040. PMID: 27293304.12. Chiba S, Ohta H, Abe K, Hisata S, Ohkouchi S, Hoshikawa Y, et al. The diagnostic value of the interstitial biomarkers KL-6 and SP-D for the degree of fibrosis in combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema. Pulm Med. 2012; 2012:492960. PMID: 22530118.13. CLSI. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; Approved guideline. 2nd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2014. CLSI document EP5-A3.14. CLSI. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; Approved guideline. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2003. CLSI document EP6-A.15. CLSI. Measurement procedure comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; Approved guideline. 3rd ed. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2013. CLSI document EP09-A3.16. Ichikado K, Johkoh T, Ikezoe J, Takeuchi N, Kohno N, Arisawa J, et al. Acute interstitial pneumonia: high-resolution CT findings correlated with pathology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:333–338. PMID: 9016201.17. Romei C, Tavanti L, Sbragia P, De Liperi A, Carrozzi L, Aquilini F, et al. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: do HRCT criteria established by ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT in 2011 predict disease progression and prognosis? Radiol Med. 2015; 120:930–940. PMID: 25743239.18. Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Brusasco V, Crapo RO, Burgos F, Casaburi R, et al. Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J. 2005; 26:948–968. PMID: 16264058.19. ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:111–117. PMID: 12091180.20. Ishikawa N, Hattori N, Yokoyama A, Tanaka S, Nishino R, Yoshioka K, et al. Usefulness of monitoring the circulating Krebs von den Lungen-6 levels to predict the clinical outcome of patients with advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer treated with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Int J Cancer. 2008; 122:2612–2620. PMID: 18324627.21. Matsuno Y, Satoh H, Ishikawa H, Kodama T, Ohtsuka M, Sekizawa K. Simultaneous measurements of KL-6 and SP-D in patients undergoing thoracic radiotherapy. Med Oncol. 2006; 23:75–82. PMID: 16645232.22. Fraser CG, Hyltoft Petersen P, Libeer JC, Ricos C. Proposals for setting generally applicable quality goals solely based on biology. Ann Clin Biochem. 1997; 34(Pt 1):8–12. PMID: 9022883.23. Tate J, Ward G. Interferences in immunoassay. Clin Biochem Rev. 2004; 25:105–120. PMID: 18458713.24. Sakamoto K, Taniguchi H, Kondoh Y, Johkoh T, Sumikawa H, Kimura T, et al. Serum KL-6 in fibrotic NSIP: correlations with physiologic and radiologic parameters. Respir Med. 2010; 104:127–133. PMID: 19811899.25. Zhu C, Zhao YB, Kong LF, Li ZH, Kang J. The expression and clinical role of KL-6 in serum and BALF of patients with different diffuse interstitial lung diseases. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2016; 39:93–97. PMID: 26879611.26. Bonella F, Volpe A, Caramaschi P, Nava C, Ferrari P, Schenk K, et al. Surfactant protein D and KL-6 serum levels in systemic sclerosis: correlation with lung and systemic involvement. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2011; 28:27–33. PMID: 21796888.27. Kuwana M, Shirai Y, Takeuchi T. E Elevated serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 in early disease predicts subsequent deterioration of pulmonary function in patients with systemic sclerosis and interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 2016; 43:1825–1831. PMID: 27481907.28. Raghu G, Selman M. Nintedanib and pirfenidone. New antifibrotic treatments indicated for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis offer hopes and raises questions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 191:252–254. PMID: 25635489.29. Yokoyama A, Kohno N, Hamada H, Sakatani M, Ueda E, Kondo K, et al. Circulating KL-6 predicts the outcome of rapidly progressive idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 158:1680–1684. PMID: 9817725.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association of Serum Biomarkers With Pulmonary Involvement of Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung Disease: From KORAIL Cohort Baseline Data
- Role of Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) in Assessing Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Initial and peak serum levels of Krebs von den Lungen-6 for predicting the prognosis of patients with COVID-19
- Subclinical interstitial lung damage in workers exposed to indium compounds
- Interstitial Lung Diseases: Respiratory Review of 2013