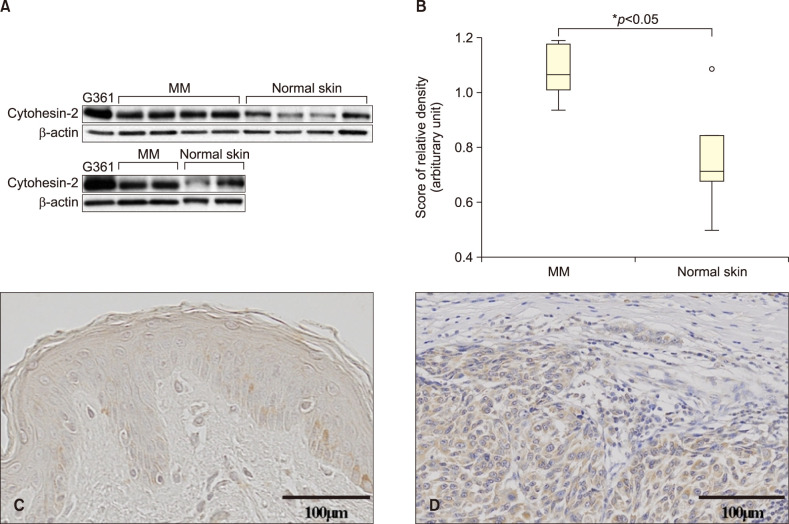
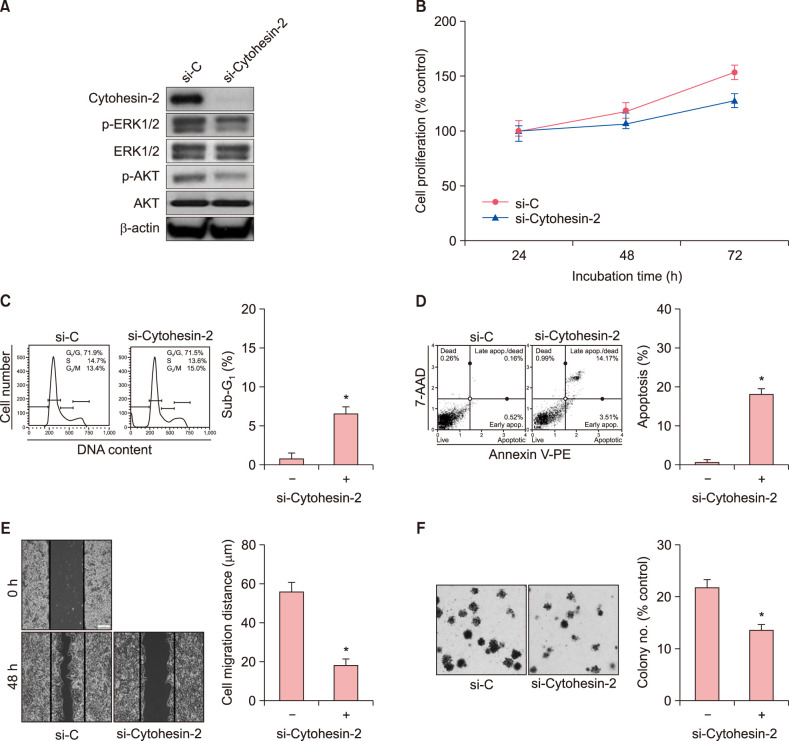
Ann Dermatol.
2019 Feb;31(1):93-96. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.1.93.
Cytohesin-2 Is Upregulated in Malignant Melanoma and Contributes to Tumor Growth
- Affiliations
-
- 1Molecular Cancer Research, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea. mkcho@schmc.ac.kr
- 3Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 4Department of Dermatology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2430811
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.1.93
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moss J, Vaughan M. Molecules in the ARF orbit. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:21431–21434. PMID: 9705267.
Article2. Kolanus W. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors of the cytohesin family and their roles in signal transduction. Immunol Rev. 2007; 218:102–113. PMID: 17624947.
Article3. Casanova JE. Regulation of Arf activation: the Sec7 family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Traffic. 2007; 8:1476–1485. PMID: 17850229.
Article4. Lim J, Zhou M, Veenstra TD, Morrison DK. The CNK1 scaffold binds cytohesins and promotes insulin pathway signaling. Genes Dev. 2010; 24:1496–1506. PMID: 20634316.
Article5. Pan T, Sun J, Hu J, Hu Y, Zhou J, Chen Z, et al. Cytohesins/ARNO: the function in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e90997. PMID: 24618737.
Article6. Xu K, Gao J, Yang X, Yao Y, Liu Q. Cytohesin-2 as a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2013; 29:2211–2218. PMID: 23545718.
Article7. Santy LC, Casanova JE. Activation of ARF6 by ARNO stimulates epithelial cell migration through downstream activation of both Rac1 and phospholipase D. J Cell Biol. 2001; 154:599–610. PMID: 11481345.
Article8. Muralidharan-Chari V, Hoover H, Clancy J, Schweitzer J, Suckow MA, Schroeder V, et al. ADP-ribosylation factor 6 regulates tumorigenic and invasive properties in vivo. Cancer Res. 2009; 69:2201–2209. PMID: 19276388.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Malignant Melanoma on Congenital Melanocytic Nevus
- A Case of Conjunctival Malignant Melanoma with Extensive Corneal Displacement
- A Case of Nodular Melanoma with a Family History of Difficult Clinical Diagnosis
- Three Cases of Malignant Melanoma Possibly Arising in a Long Standing Melanocytic Nevus
- A Case of Primary Malignant Leptomeningeal Melanoma of the Spinal Cord: Case Report