Kosin Med J.
2018 Dec;33(2):257-262. 10.7180/kmj.2018.33.2.257.
Acute combined central and peripheral nervous system demyelination: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. pink2129@naver.com
- KMID: 2430744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2018.33.2.257
Abstract
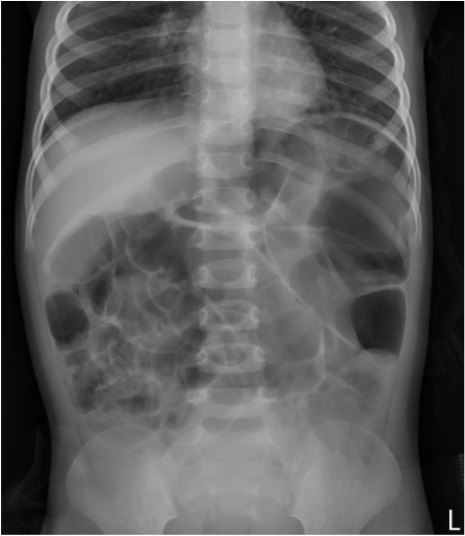
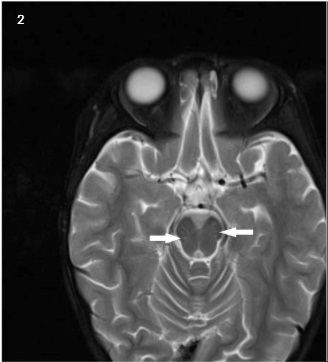
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) are demyelinating neurologic disorders with different target organs. Although they share similar pathogenetic mechanism, reports of simultaneous occurrence of the 2 disorders are rare. A 2 year 6 month old girl visited our hospital for fever, cough, and general weakness. Although the muscle power of extremities showed mild weakness and voiding difficulty, initial deep tendon reflex of both knees and ankles was normal. A nerve conduction study to evaluate the weakness revealed the absence of F waves. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis demonstrated pleocytosis with lymphocyte predominance and elevated protein levels. Magnetic resonance imaging showed abnormal T2 hyperintensity in pons, medulla and spinal cord. Serum anti-GD1b antibody was positive. Based on clinical findings, laboratory findings, nerve conduction study, and neuroimaging, the diagnosis of GBS and ADEM was made. This is the first case of GBS accompanied by ADEM in Korea.
MeSH Terms
-
Ankle
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cough
Demyelinating Diseases*
Diagnosis
Encephalomyelitis
Encephalomyelitis, Acute Disseminated
Extremities
Female
Fever
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Humans
Knee
Korea
Leukocytosis
Lymphocytes
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Nervous System Diseases
Neural Conduction
Neuroimaging
Peripheral Nervous System*
Pons
Reflex, Stretch
Spinal Cord
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jones HR Jr. Guillain-Barré syndrome: Perspectives with infants and children. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 2000; 7:91–102.
Article2. van Doorn PA. Diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of Guillain-barré syndrome (GBS). Presse Med. 2013; 42:e193–e201.
Article3. Leake JA, Albani S, Kao AS, Senac MO, Billman GF, Nespeca MP, et al. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in childhood: Epidemiologic, clinical and laboratory features. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004; 23:756–764.
Article4. Tenembaum S, Chitnis T, Ness J, Hahn JS. International Pediatric MS Study Group. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neurology. 2007; 68:S23–S36.
Article5. Fokke C, van den Berg B, Drenthen J, Walgaard C, van Doorn PA, Jacobs BC. Diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome and validation of brighton criteria. Brain. 2014; 137:33–43.
Article6. Okumura A, Ushida H, Maruyama K, Itomi K, Ishiguro Y, Takahashi M, et al. Guillain- Barré syndrome associated with central nervous system lesions. Arch Dis Child. 2002; 86:304–306.7. Amit R, Shapira Y, Blank A, Aker M. Acute, severe, central and peripheral nervous system combined demyelination. Pediatr Neurol. 1986; 2:47–50.
Article8. Bernard G, Riou E, Rosenblatt B, Dilenge ME, Poulin C. Simultaneous Guillain-Barré syndrome and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in the pediatric population. J Child Neurol. 2008; 23:752–757.
Article9. Mohammed RR, Jan MM. Co-morbid Guillainbarré syndrome and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2013; 18:166–168.10. Rauschka H, Jellinger K, Lassmann H, Braier F, Schmidbauer M. Guillain–Barré syndrome with marked pleocytosis or a significant proportion of polymorphonuclear granulocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid: Neuropathological investigation of five cases and review of differential diagnoses. Eur J Neurol. 2003; 10:479–486.
Article11. Spudich SS, Nilsson AC, Lollo ND, Liegler TJ, Petropoulos CJ, Deeks SG, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid HIV infection and pleocytosis: Relation to systemic infection and antiretroviral treatment. BMC Infect Dis. 2005; 5:98.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Combined Peripheral and Central Demyelinating Disease Associated with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Acute Combined Central and Peripheral Demyelination in Children: in Comparison with Isolated Demyelinating Disease
- A Case of Multiple Sclerosis Presenting as Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
- Immune mechanisms of Theiler's virus-induced demyelination
- The Changes of the Visual Evoked Potential for Aconitine Induced Visual Pathway Demyelination in Rabbit Model