J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2018 Dec;53(6):459-465. 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.6.459.
Robotic Surgery in the Orthopedic Field
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wsleeos@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2430052
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.6.459
Abstract
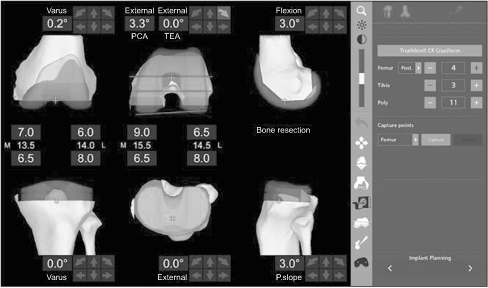
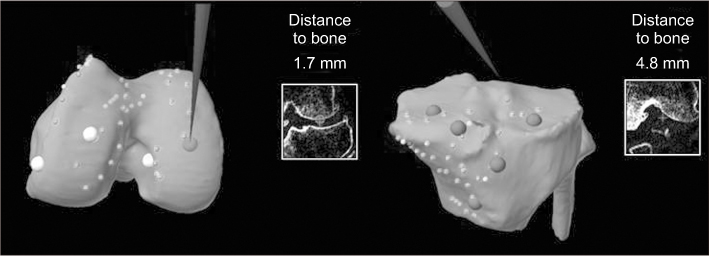
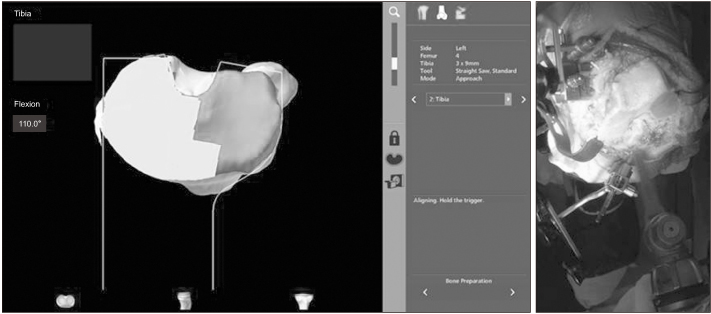
- Of the many factors that affect the clinical outcomes of orthopedic surgery, the surgical procedure is the most important. Robotics have been developed to perform the surgical procedures more accurately and consistently. Robotic surgical procedures in the orthopedic field were developed 20 years ago. Some designs of surgical robots have disappeared due to practical problems and complications, and an another design of surgical robots is emerging. To date, the use of robot surgery in arthroplasty is still controversial in terms of the clinical outcomes, practicality, and cost-effectiveness, even though it has been reported to be effective in the alignment and positioning of components in the field of artificial joints. Early robotic surgery was based mainly on active robot surgery according to the scheduled operation without the intervention of the operator. Recently the semi-active system of robotic surgery has been introduced. In a semi-active system, the robot constrains the surgeon to a haptic boundary defined by the computer based on the 3-dimensional imaging preoperative plan, and the operator can change the preoperative plan through real-time feedback during operation.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zheng G, Nolte LP. Computer-assisted orthopedic surgery: current state and future perspective. Front Surg. 2015; 2:66.
Article2. Urish KL, Conditt M, Roche M, Rubash HE. Robotic total knee arthroplasty: surgical assistant for a customized normal kinematic knee. Orthopedics. 2016; 39:e822–e827.
Article3. Keeney JA. Innovations in total knee arthroplasty: improved technical precision, but unclear clinical benefits. Orthopedics. 2016; 39:217–220.
Article4. Waddell BS, Carroll K, Jerabek S. Technology in arthroplasty: are we improving value? Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017; 10:378–387.
Article5. Hill C, El-Bash R, Johnson L, Coustasse A. Robotic joint replacement surgery: does technology improve outcomes? Health Care Manag (Frederick). 2015; 34:128–136.6. Goradia VK. Computer-assisted and robotic surgery in orthopedics: where we are in 2014. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2014; 22:202–205.7. Jacofsky DJ, Allen M. Robotics in arthroplasty: a comprehensive review. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31:2353–2363.
Article8. Karthik K, Colegate-Stone T, Dasgupta P, Tavakkolizadeh A, Sinha J. Robotic surgery in trauma and orthopaedics: a systematic review. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97:292–299.9. Lang JE, Mannava S, Floyd AJ, et al. Robotic systems in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93:1296–1299.
Article10. Ng AT, Tam PC. Current status of robot-assisted surgery. Hong Kong Med J. 2014; 20:241–250.
Article11. Singh I. Robotics in urological surgery: review of current status and maneuverability, and comparison of robot-assisted and traditional laparoscopy. Comput Aided Surg. 2011; 16:38–45.
Article12. Hepinstall MS. Robotic total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014; 45:443–456.
Article13. Sugano N. Computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery and robotic surgery in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2013; 5:1–9.
Article14. Netravali NA, Shen F, Park Y, Bargar WL. A perspective on robotic assistance for knee arthroplasty. Adv Orthop. 2013; 2013:970703.
Article15. Park SE, Lee CT. Comparison of robotic-assisted and conventional manual implantation of a primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22:1054–1059.
Article16. Cobb J, Henckel J, Gomes P, et al. Hands-on robotic unicompartmental knee replacement: a prospective, randomised controlled study of the acrobot system. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88:188–197.17. Lonner JH, Moretti VM. The evolution of image-free robotic assistance in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2016; 45:249–254.18. Lonner JH. Robotically assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with a handheld image-free sculpting tool. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016; 47:29–40.
Article19. Lonner JH, John TK, Conditt MA. Robotic arm-assisted UKA improves tibial component alignment: a pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:141–146.
Article20. Roche M. Robotic-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: the MAKO experience. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015; 46:125–131.21. Overley SC, Cho SK, Mehta AI, Arnold PM. Navigation and robotics in spinal surgery: where are we now? Neurosurgery. 2017; 80:S86–S99.
Article22. van der List JP, Chawla H, Joskowicz L, Pearle AD. Current state of computer navigation and robotics in unicompartmental and total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24:3482–3495.
Article23. Citak M, Suero EM, Citak M, et al. Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: is robotic technology more accurate than conventional technique? Knee. 2013; 20:268–271.
Article24. Pearle AD, O'Loughlin PF, Kendoff DO. Robot-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25:230–237.
Article25. Bell SW, Anthony I, Jones B, MacLean A, Rowe P, Blyth M. Improved accuracy of component positioning with robotic-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: data from a prospective, randomized controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016; 98:627–635.26. Song EK, Seon JK, Park SJ, Jung WB, Park HW, Lee GW. Simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty with robotic and conventional techniques: a prospective, randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19:1069–1076.
Article27. Koulalis D, O'Loughlin PF, Plaskos C, Kendoff D, Cross MB, Pearle AD. Sequential versus automated cutting guides in computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2011; 18:436–442.
Article28. Bargar WL, Bauer A, Börner M. Primary and revision total hip replacement using the Robodoc system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; (354):82–91.
Article29. Honl M, Dierk O, Gauck C, et al. Comparison of robotic-assisted and manual implantation of a primary total hip replacement. A prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85:1470–1478.30. Schulz AP, Seide K, Queitsch C, et al. Results of total hip replacement using the robodoc surgical assistant system: clinical outcome and evaluation of complications for 97 procedures. Int J Med Robot. 2007; 3:301–306.
Article31. Elson L, Dounchis J, Illgen R, et al. Precision of acetabular cup placement in robotic integrated total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2015; 25:531–536.
Article32. Domb BG, Redmond JM, Louis SS, et al. Accuracy of component positioning in 1980 total hip arthroplasties: a comparative analysis by surgical technique and mode of guidance. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30:2208–2218.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The impact of robotic surgery on gynecologic oncology
- Totally Robotic Esophagectomy
- Current status of robotic surgery for pancreatic tumors
- Totally robotic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in a morbidly obese patient in Korea: a case report
- Methodology in Conventional Head and Neck Reconstruction Following Robotic Cancer Surgery: A Bridgehead Robotic Head and Neck Reconstruction