J Breast Cancer.
2018 Dec;21(4):447-452. 10.4048/jbc.2018.21.e50.
Patterns of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer: A Prospective Single-Center Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. seokwon1.kim@samsung.com
- KMID: 2429824
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2018.21.e50
Abstract
- PURPOSE
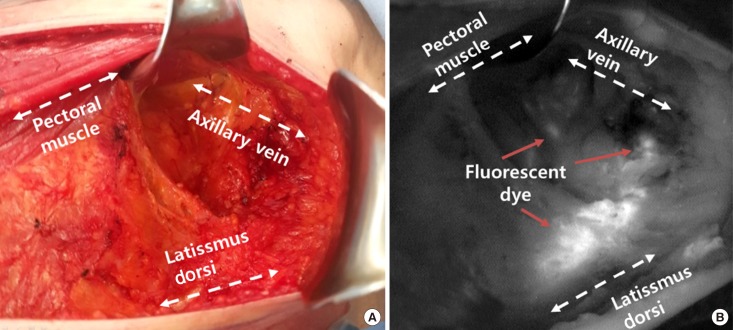
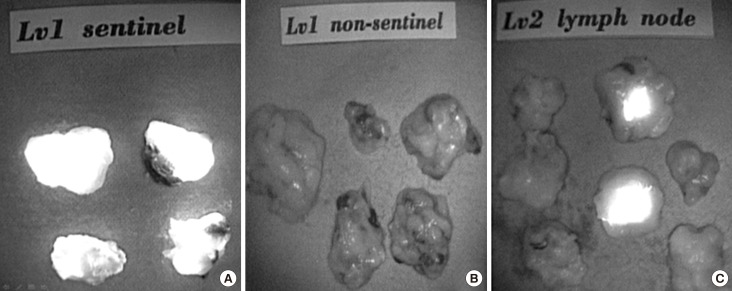
The recent trend in breast cancer treatment is to minimize axillary dissection. However, no pattern of axillary metastasis has been precisely established. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the metastatic lymphatic pattern using near-infrared fluorescence imaging with indocyanine green (ICG) in breast cancer with cytologically proven axillary metastasis.
METHODS
This was a prospective single-center study. We evaluated 147 patients with breast cancer involving cytologically proven axillary metastasis, and compared physiological and nonphysiological lymphatic metastasis.
RESULTS
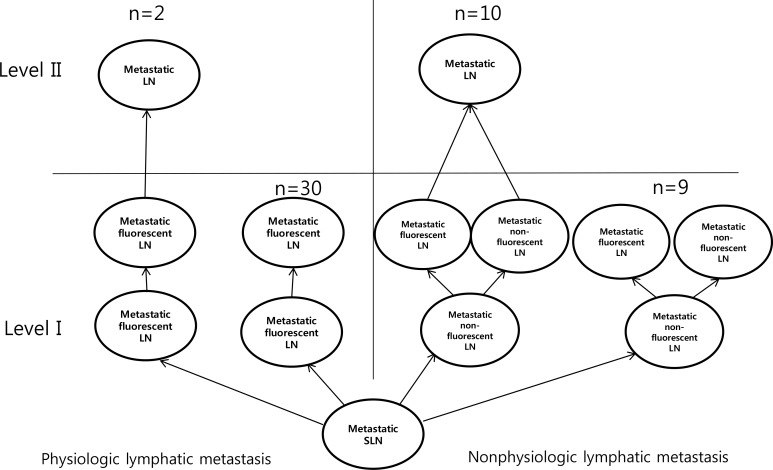
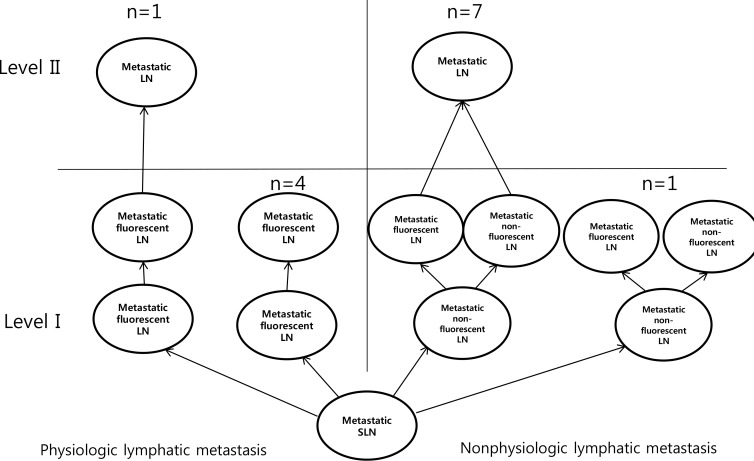
We performed lymphatic mapping for 64 patients who exhibited level II lymphatic flow on near-infrared fluorescence imaging with ICG, and found that all had axillary metastasis: 51 patients who did not receive neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and 13 patients post-NAC. Of patients who did not receive NAC, 32 had physiological lymphatic metastasis and 19 had nonphysiological lymphatic metastasis. The risk factors for nonphysiological lymphatic metastasis were age ≥55 years, high Ki-67 index (>20%), and perinodal extension in both univariate and multivariate analysis (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
Patients with identified risk factors in cytologically-proven axillary metastasis who did not receive NAC may have nonphysiological lymphatic metastasis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dewis R, Gribbin J. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: guidance. In : Dewis R, Gribbin J, editors. Breast Cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment: An Assessment of Need. Cardiff: National Collaborating Centre for Cancer;2009. p. 13–35.2. Donker M, van Tienhoven G, Straver ME, Meijnen P, van de Velde C, Mansel RE, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:1303–1310. PMID: 25439688.
Article3. Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, Beitsch PD, Brennan MB, Kelemen PR, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017; 318:918–926. PMID: 28898379.4. Guo J, Yang H, Wang S, Cao Y, Liu M, Xie F, et al. Comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy guided by indocyanine green, blue dye, and their combination in breast cancer patients: a prospective cohort study. World J Surg Oncol. 2017; 15:196. PMID: 29096643.
Article5. Schaafsma BE, Mieog JS, Hutteman M, van der Vorst JR, Kuppen PJ, Löwik CW, et al. The clinical use of indocyanine green as a near-infrared fluorescent contrast agent for image-guided oncologic surgery. J Surg Oncol. 2011; 104:323–332. PMID: 21495033.
Article6. Jung SY, Kim SK, Kim SW, Kwon Y, Lee ES, Kang HS, et al. Comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy guided by the multimodal method of indocyanine green fluorescence, radioisotope, and blue dye versus the radioisotope method in breast cancer: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21:1254–1259. PMID: 24356798.
Article7. Hirche C, Murawa D, Mohr Z, Kneif S, Hünerbein M. ICG fluorescence-guided sentinel node biopsy for axillary nodal staging in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010; 121:373–378. PMID: 20140704.
Article8. Sugie T, Kassim KA, Takeuchi M, Hashimoto T, Yamagami K, Masai Y, et al. A novel method for sentinel lymph node biopsy by indocyanine green fluorescence technique in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2010; 2:713–720. PMID: 24281090.
Article9. Wishart GC, Loh SW, Jones L, Benson JR. A feasibility study (ICG-10) of indocyanine green (ICG) fluorescence mapping for sentinel lymph node detection in early breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012; 38:651–656. PMID: 22704050.
Article10. Alford R, Simpson HM, Duberman J, Hill GC, Ogawa M, Regino C, et al. Toxicity of organic fluorophores used in molecular imaging: literature review. Mol Imaging. 2009; 8:341–354. PMID: 20003892.
Article11. Gilmore DM, Khullar OV, Gioux S, Stockdale A, Frangioni JV, Colson YL, et al. Effective low-dose escalation of indocyanine green for near-infrared fluorescent sentinel lymph node mapping in melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:2357–2363. PMID: 23440551.
Article12. Hokimoto N, Sugimoto T, Namikawa T, Funakoshi T, Oki T, Ogawa M, et al. A novel color fluorescence navigation system for intraoperative transcutaneous lymphatic mapping and resection of sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer: comparison with the combination of gamma probe scanning and visible dye methods. Oncology. 2018; 94:99–106. PMID: 29131021.
Article13. Zhang X, Li Y, Zhou Y, Mao F, Lin Y, Guan J, et al. Diagnostic performance of indocyanine green-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0155597. PMID: 27280407.
Article14. Chi C, Ye J, Ding H, He D, Huang W, Zhang GJ, et al. Use of indocyanine green for detecting the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer patients: from preclinical evaluation to clinical validation. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e83927. PMID: 24358319.
Article15. Pitsinis V, Provenzano E, Kaklamanis L, Wishart GC, Benson JR. Indocyanine green fluorescence mapping for sentinel lymph node biopsy in early breast cancer. Surg Oncol. 2015; 24:375–379. PMID: 26555151.
Article16. Kim I, Ryu JM, Kim JM, Choi HJ, Lee SK, Yu JH, et al. Development of a nomogram to predict N2 or N3 stage in T1-2 invasive breast cancer patients with no palpable lymphadenopathy. J Breast Cancer. 2017; 20:270–278. PMID: 28970853.
Article17. van der Loo EM, Sastrowijoto SH, Bril H, van Krimpen C, de Graaf PW, Eulderink F. Less operations required due to perioperative frozen section examination of sentinel nodes in 275 breast cancer patients. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2001; 145:1986–1991. PMID: 11680071.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ipsilateral Breast Tumor Recurrence with Metachronous Contralateral Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis after Breast-Conserving Surgery with Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
- Ultrasonography for Staging Axillary Lymph Node in Breast Cancer Patients
- Comparison of Early Postoperative Axillary Morbidity Following the Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy or Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
- Metachronous Contralateral Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis from Invasive Breast Carcinoma: A Case Report with Imaging Findings
- A Recurrence of Ovarian Carcinoma Presenting as Only Axillary Lymphatic Metastasis: A Case Report