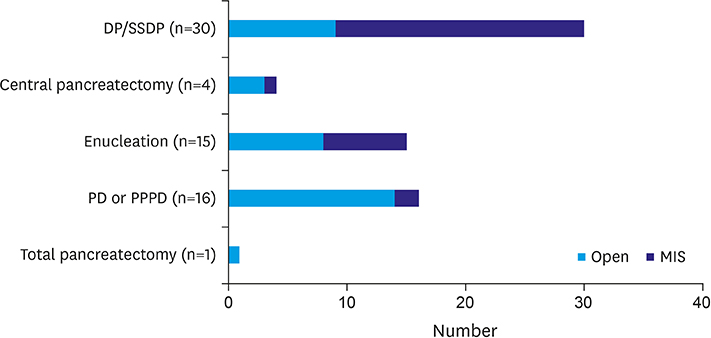Adv Pediatr Surg.
2018 Dec;24(2):76-85. 10.13029/aps.2018.24.2.76.
Perioperative Outcomes and Surgical Indications of Minimally Invasive Pancreatectomy for Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor in Pediatric Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Pediatric Surgery, Department of Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. namgoong2940@naver.com
- KMID: 2429804
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13029/aps.2018.24.2.76
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We evaluated perioperative and long-term outcomes of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) and established indications of MIS in solid pseudopapillary tumor (SPT) in pediatric patients.
METHODS
From October 1992 to April 2018, 66 patients (age, < 18 years) diagnosed with SPT underwent either open pancreatectomy (OP) or MIS. Variables including postoperative complications and recurrence rates were retrospectively analyzed.
RESULTS
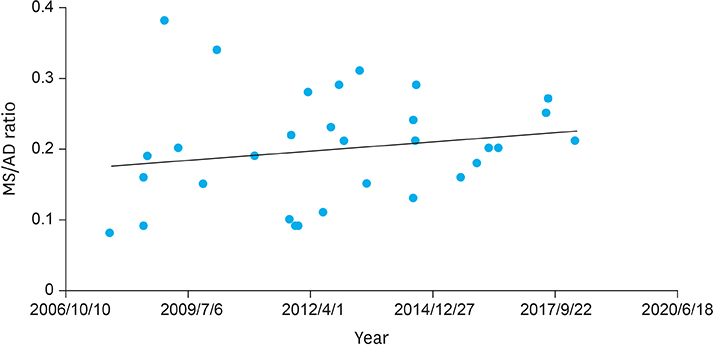
Thirty-five patients underwent open surgery and 31 underwent laparoscopic/robotic surgery. Mean tumor size in MIS was significantly smaller than that in OP (4.3±1.8 cm vs. 7.6±3.5 cm, p=0.005). There were 4 cases of open conversion from laparoscopic surgery because of vessel encasements (n=2), bleeding (n=1), and pancreatic ductal injury (n=1). Solitary pseudopapillary carcinoma was diagnosed in 6 patients. Recurrence was observed in 3 and 1 patients who underwent OP and MIS, respectively (p=0.634). Tumor size, mass size/abdominal diameter (MS/AD) ratio, and degree of the portal or superior mesenteric vein involvement were the most important indications for MIS.
CONCLUSION
MIS is being widely used in pediatric surgeries with increased expertise and safety, especially in pancreatic diseases. Careful patient selection for MIS in regards with parameters such as MS/AD ratio and vessel abutment might be a feasible choice.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kanter J, Wilson DB, Strasberg S. Downsizing to resectability of a large solid and cystic papillary tumor of the pancreas by single-agent chemotherapy. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:e23–e25.2. Yu DC, Kozakewich HP, Perez-Atayde AR, Shamberger RC, Weldon CB. Childhood pancreatic tumors: a single institution experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:2267–2272.
Article3. Law JK, Ahmed A, Singh VK, Akshintala VS, Olson MT, Raman SP, et al. A systematic review of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms: are these rare lesions? Pancreas. 2014; 43:331–337.4. Stewart CL, Meguid C, Chapman B, Schulick R, Edil BH. Evolving trends towards minimally invasive surgery for solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016; 23:4165–4168.
Article5. Scandavini C, Valente R, Rangelova E, Segersvärd R, Arnelo U, Permert J, et al. Pancreatectomies for pancreatic neoplasms in pediatric and adolescent age: A single institution experience. Pancreatology. 2018; 18:204–207.
Article6. Namgoong JM, Kim DY, Kim SC, Kim SC, Hwang JH, Song KB. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy to treat solid pseudopapillary tumors in children: transition from open to laparoscopic approaches in suitable cases. Pediatr Surg Int. 2014; 30:259–266.
Article7. Rebhandl W, Felberbauer FX, Puig S, Paya K, Hochschorner S, Barlan M, et al. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas (Frantz tumor) in children: report of four cases and review of the literature. J Surg Oncol. 2001; 76:289–296.
Article8. Speer AL, Barthel ER, Patel MM, Grikscheit TC. Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a single-institution 20-year series of pediatric patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2012; 47:1217–1222.
Article9. Song H, Dong M, Zhou J, Sheng W, Zhong B, Gao W. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: Clinicopathologic feature, risk factors of malignancy, and survival analysis of 53 cases from a single center. BioMed Res Int. 2017; 2017:5465261.
Article10. Laje P, Bhatti TR, Adzick NS. Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas in children: a 15-year experience and the identification of a unique immunohistochemical marker. J Pediatr Surg. 2013; 48:2054–2060.
Article11. Zampieri N, Schiavo N, Capelli P, Scarpa A, Bassi C, Camoglio FS. Pseudopapillary tumor in pediatric age: clinical and surgical management. Pediatr Surg Int. 2011; 27:1271–1275.
Article12. Choi SH, Kim SM, Oh JT, Park JY, Seo JM, Lee SK. Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a multicenter study of 23 pediatric cases. J Pediatr Surg. 2006; 41:1992–1995.
Article13. Morita K, Urushihara N, Fukumoto K, Miyano G, Yamoto M, Nouso H, et al. Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas in children: surgical intervention strategies based on pathological findings. Pediatr Surg Int. 2014; 30:253–257.
Article14. Abu Hilal M, Hamdan M, Di Fabio F, Pearce NW, Johnson CD. Laparoscopic versus open distal pancreatectomy: a clinical and cost-effectiveness study. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:1670–1674.
Article15. Kim SC, Park KT, Hwang JW, Shin HC, Lee SS, Seo DW, et al. Comparative analysis of clinical outcomes for laparoscopic distal pancreatic resection and open distal pancreatic resection at a single institution. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:2261–2268.
Article16. Kang CM, Choi SH, Hwang HK, Lee WJ, Chi HS. Minimally invasive (laparoscopic and robot-assisted) approach for solid pseudopapillary tumor of the distal pancreas: a single-center experience. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011; 18:87–93.
Article17. Venkat R, Edil BH, Schulick RD, Lidor AO, Makary MA, Wolfgang CL. Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy is associated with significantly less overall morbidity compared to the open technique: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2012; 255:1048–1059.18. Lee SE, Jang JY, Hwang DW, Park KW, Kim SW. Clinical features and outcome of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm: differences between adults and children. Arch Surg. 2008; 143:1218–1221.19. van den Akker M, Angelini P, Taylor G, Chami R, Gerstle JT, Gupta A. Malignant pancreatic tumors in children: a single-institution series. J Pediatr Surg. 2012; 47:681–687.
Article20. Hwang J, Kim DY, Kim SC, Namgoong JM, Hong SM. Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas in children: can we predict malignancy? J Pediatr Surg. 2014; 49:1730–1733.
Article21. Gagner M, Pomp A. Laparoscopic pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy. Surg Endosc. 1994; 8:408–410.
Article22. Zureikat AH, Breaux JA, Steel JL, Hughes SJ. Can laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy be safely implemented? J Gastrointest Surg. 2011; 15:1151–1157.
Article23. Kim SC, Song KB, Jung YS, Kim YH, Park DH, Lee SS, et al. Short-term clinical outcomes for 100 consecutive cases of laparoscopic pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy: improvement with surgical experience. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:95–103.
Article24. Stauffer JA, Coppola A, Villacreses D, Mody K, Johnson E, Li Z, et al. Laparoscopic versus open pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: long-term results at a single institution. Surg Endosc. 2017; 31:2233–2241.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Robotic Central Pancreatectomy with Pancreaticojejunostomy for Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm
- Spleen Preservation in Laparoscopic Distal Pancreatectomy for Solitary Pseudopapillary Tumors Is Oncologic Safe
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas: a report of three cases
- Robotic central pancreatectomy: a surgical technique
- Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor of the Pancreas with Liver Metastasis in Children