Korean Lepr Bull.
2018 Dec;51(1):23-28. 10.33161/klb.2018.51.1.23.
New patient of Hansen's disease in young Korean man
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Leprosy Research, Korean Hansen Welfare Association, Korea. hafler@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2429660
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.33161/klb.2018.51.1.23
Abstract
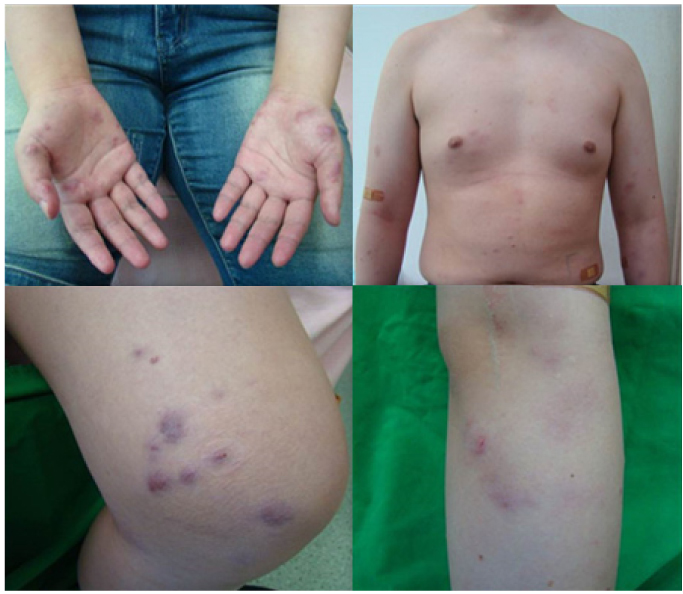
- Hansen's disease (leprosy) is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium leprae which affect mainly skin and nerve systems. Currently the incidence of leprosy reached the goals set by WHO in the year 2000. In recent 10 years, only 47 new patients were found in Koreans and their average age was over 70. A 21 year-old young man showed multiple erythematous papules, macules and plaque at face, extremities and trunk. In family history, his grandfather was diagnosed with leprosy at young age and leprosy was recurred when the patient was 7 years old. The patient lived with grandfather from birth to 7 years old. Clinico-pathologically he was diagnosed with a lepromatous leprosy. We performed VNTR both at the skin tissue of grandfather and patient to find out the infection pathway of the patient and found some consistent. Herein, we report a new case of young Korean male transmitted from grandfather.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Relapsed Leprosy with Multiple Ulcerative Skin Lesions: A Case Report
Han Him Jeong, Seung Gi Hong, Jin-Mo Park, Jong-Pill Kim, Eun Phil Heo, Jae Wan Go
Korean Lepr Bull. 2019;52(1):55-61. doi: 10.33161/klb.2019.52.1.55.
Reference
-
1. Meyers WM, Walsh GP, Brown HL, Binford CH, Imes GD Jr, Hadfield TL, et al. Leprosy in a mangabey monkey-naturally acquired infection. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1985; 53:1–14.2. Leininger JR, Donham KJ, Meyers WM. Leprosy in a chimpanzee. Postmortem lesions. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1980; 48:414–442.3. Truman RW, Singh P, Sharma R, Busso P, Rougemont J, Paniz-Mondolfia , et al. Probable zoonotic leprosy in the southern United States. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:1626–1633.
Article4. Kim JP. Leprosy on Korea. 2001-2015: Situation, International Migration and Perspectives. Korean Leprosy bullet. 2016; 49:37–34.5. Reibel F, Cambau E, Aubry A. Update on the epidemiology, diagnosis, and the treatment of leprosy. Med Mal Infect. 2015; 45:383–393.6. KHWA. Current situation and major indicator of Hansen's service program in Korea. Uiwang, Korea: KHWA;2009.7. Lee DJ, Rea TH, Modlin RL. Leprosy. In : Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2012. p. 2253–2263.8. Ridley DS, Jopling WH. A classification of leprosy for research purposes. Lepr Rev. 1962; 33:119–128.
Article9. Pedley JC. The nasal mucus in leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1973; 44:33–35.
Article10. Morgado de Abreu MA, Roselino AM, Enokihara M, Nonogaki S, Prestes-Carneiro LE, Weckx LL, et al. Mycobacterium leprae is identified in the oral mucosa from paucibacillary and multibacillary leprosy patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014; 20:59–64.
Article11. Baohong J. Does there exist a subgroup of MB patients at greater risk of relapse after MDT. Lepr Rev. 2001; 72:3–7.
Article12. Gelber RH, Balagon VF, Cellona RV. The relapse rate in MB leprosy patients treated with 2-years of WHO-MDT is not low. Int J Lepr other Mycobact Dis. 2004; 72:493–500.
Article13. Hughes CR, Queller DC. Detection of highly polymorphic microsatellite loci in a species with little allozyme polymorphism. Mol Ecol. 1993; 2:131–137.
Article14. Hall BG, Salipante SJ. Molecular epidemiology of Mycobacterium leprae as determined by structure-neighbor clustering. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:1997–2008.
Article15. Suzuki K, Udono T, Fujisawa M, Tanigawa K, Idani G, Ishii N. Infection during infancy and long incubation period of leprosy suggested in a case of a chimpanzee used for medical research. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:3432–3434.
Article16. Gaschignard J, Scurr E, Alcais A. Leprosy, a pillar of human genetics of infectious diseases. Pathol Biol. 2013; 61:120–128.17. Saucr MED, Salomao H, Ramos GB, D'Espindula HRS, Rodrigues RSA, Macedo Wc, et al. Genetics of leprosy: expected-and unexpected-developments and perspectives. Clin Dermatol. 2016; 34:96–104.
Article18. Cambri G, Mira MT. Genetic Susceptibility to Leprosy-From Classic Immune-Related Candidate Genes to Hypothesis-Free, Whole Genome Approaches. Front Immunol. 2018; 9:1674.
Article