Korean J Sports Med.
2018 Jun;36(2):77-83. 10.5763/kjsm.2018.36.2.77.
Effect of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Maximal Exercise Tolerance in Young Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Sport Science, University of Seoul, Seoul, Korea. syjae@uos.ac.kr
- KMID: 2429180
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2018.36.2.77
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC), induced by repeated bouts of ischemia followed by reperfusion of the arm or leg is a noninvasive strategy to protect a target organ against oxidative stress and injury caused by ischemia and reperfusion. Interestingly, recent evidence suggests that RIPC may also improve exercise performance by increasing maximal oxygen consumption, but such finding remain equivocal. As such, the purpose of the study was to examine the effect of RIPC on exercise performance in healthy individuals.
METHODS
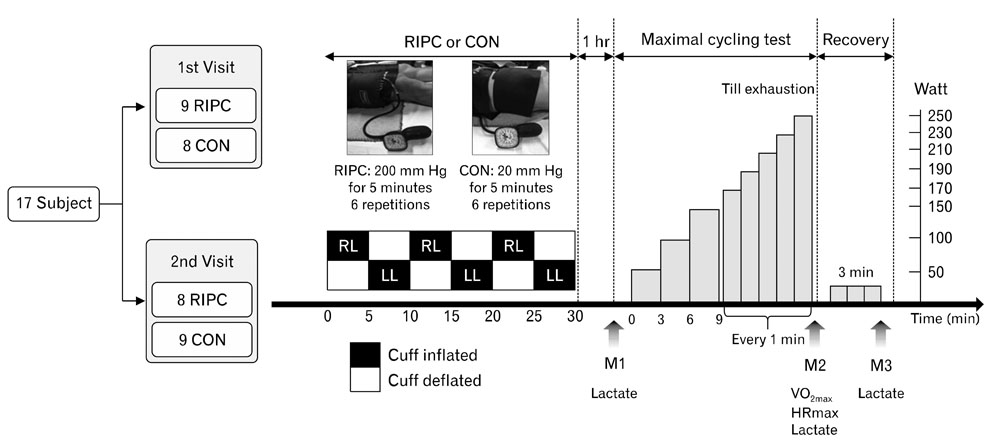
In a randomized cross-over design, 17 healthy male participants (age, 23±3 years) were exposed to either a sham control (six cycles of 5 minutes bilateral thigh cuff occlusion at 20 mm Hg) or RIPC (six cycles of 5 minutes bilateral thigh cuff occlusion at 180 mm Hg) an hour before a maximal exercise test. We measured maximal oxygen consumption, power output, heat rate, blood pressure, and blood lactate as exercise performance parameters during a maximal exercise test performed on an upright bicycle.
RESULTS
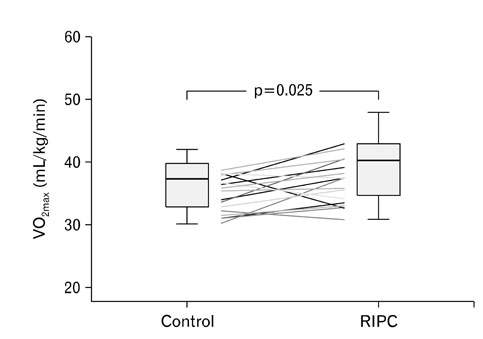
Compared with the sham control, RIPC improved maximal oxygen consumption (7.4%, p=0.025) and maximal power output (11.5%, p=0.010), whereas other exercise performance parameters remained unchanged with RIPC (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Taken together, the improvements in maximal oxygen consumption and maximal power output induced by RIPC may suggest that RIPC should be considered as a method for improving exercise performance.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of Prior Short-term Ischemic Preconditioning on Sitting-Induced Lower Limb Vascular Dysfunction in Healthy Men
Jong-Hwa Won, Sae Young Jae
Korean J Sports Med. 2022;40(4):252-258. doi: 10.5763/kjsm.2022.40.4.252.
Reference
-
1. Carden DL, Granger DN. Pathophysiology of ischaemiareperfusion injury. J Pathol. 2000; 190:255–266.
Article2. Eisen A, Fisman EZ, Rubenfire M, et al. Ischemic preconditioning: nearly two decades of research. A comprehensive review. Atherosclerosis. 2004; 172:201–210.
Article3. Laude K, Beauchamp P, Thuillez C, Richard V. Endothelial protective effects of preconditioning. Cardiovasc Res. 2002; 55:466–473.
Article4. de Groot PC, Thijssen DH, Sanchez M, Ellenkamp R, Hopman MT. Ischemic preconditioning improves maximal performance in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010; 108:141–146.
Article5. Salvador AF, De Aguiar RA, Lisboa FD, Pereira KL, Cruz RS, Caputo F. Ischemic preconditioning and exercise performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2016; 11:4–14.
Article6. Sharma V, Cunniffe B, Verma AP, Cardinale M, Yellon D. Characterization of acute ischemia-related physiological responses associated with remote ischemic preconditioning: a randomized controlled, crossover human study. Physiol Rep. 2014; 2:e12200.
Article7. Crisafulli A, Tangianu F, Tocco F, et al. Ischemic preconditioning of the muscle improves maximal exercise performance but not maximal oxygen uptake in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011; 111:530–536.
Article8. Beaven CM, Cook CJ, Kilduff L, Drawer S, Gill N. Intermittent lower-limb occlusion enhances recovery after strenuous exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012; 37:1132–1139.
Article9. Paixao RC, da Mota GR, Marocolo M. Acute effect of ischemic preconditioning is detrimental to anaerobic performance in cyclists. Int J Sports Med. 2014; 35:912–915.
Article10. Jean-St-Michel E, Manlhiot C, Li J, et al. Remote preconditioning improves maximal performance in highly trained athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011; 43:1280–1286.
Article11. Bailey TG, Jones H, Gregson W, Atkinson G, Cable NT, Thijssen DH. Effect of ischemic preconditioning on lactate accumulation and running performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012; 44:2084–2089.
Article12. Bailey TG, Jones H, Gregson W, Atkinson G, Cable NT, Thijssen DH. Effect of ischemic preconditioning on lactate accumulation and running performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012; 44:2084–2089.
Article13. Kaur G, Binger M, Evans C, Trachte T, Van Guilder GP. No influence of ischemic preconditioning on running economy. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017; 117:225–235.
Article14. Patterson SD, Bezodis NE, Glaister M, Pattison JR. The effect of ischemic preconditioning on repeated sprint cycling performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015; 47:1652–1658.
Article15. Hausenloy DJ, Tsang A, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM. Ischemic preconditioning protects by activating prosurvival kinases at reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005; 288:H971–H976.
Article16. Hopkins WG, Hawley JA, Burke LM. Design and analysis of research on sport performance enhancement. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999; 31:472–485.
Article17. Kjeld T, Rasmussen MR, Jattu T, Nielsen HB, Secher NH. Ischemic preconditioning of one forearm enhances static and dynamic apnea. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014; 46:151–155.
Article18. Clevidence MW, Mowery RE, Kushnick MR. The effects of ischemic preconditioning on aerobic and anaerobic variables associated with submaximal cycling performance. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012; 112:3649–3654.
Article19. Gibson N, White J, Neish M, Murray A. Effect of ischemic preconditioning on land-based sprinting in team-sport athletes. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2013; 8:671–676.
Article20. Riksen NP, Smits P, Rongen GA. Ischaemic preconditioning: from molecular characterisation to clinical application: part I. Neth J Med. 2004; 62:353–363.21. Vander Heide RS, Reimer KA, Jennings RB. Adenosine slows ischaemic metabolism in canine myocardium in vitro: relationship to ischaemic preconditioning. Cardiovasc Res. 1993; 27:669–673.22. Maldonado C, Pushpakumar SB, Perez-Abadia G, Arumugam S, Lane AN. Administration of exogenous adenosine triphosphate to ischemic skeletal muscle induces an energy-sparing effect: role of adenosine receptors. J Surg Res. 2013; 181:e15–e22.
Article23. Pan SJ, Li LR. Adenosine A2 receptors are involved in the activation of ATP-sensitive K+ currents during metabolic inhibition in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011; 89:187–196.
Article24. Keller DM, Ogoh S, Greene S, Olivencia-Yurvati A, Raven PB. Inhibition of KATP channel activity augments baroreflex-mediated vasoconstriction in exercising human skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2004; 561(Pt 1):273–282.25. Horiuchi M, Endo J, Thijssen DH. Impact of ischemic preconditioning on functional sympatholysis during handgrip exercise in humans. Physiol Rep. 2015; 3:e12304.
Article26. Rubio R, Ceballos G, Balcells E. Intravascular adenosine: the endothelial mediators of its negative dromotropic effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999; 370:27–37.
Article27. Kimura M, Ueda K, Goto C, et al. Repetition of ischemic preconditioning augments endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans: role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide and endothelial progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007; 27:1403–1410.28. Bailey TG, Birk GK, Cable NT, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning prevents reduction in brachial artery flow-mediated dilation after strenuous exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012; 303:H533–H538.
Article29. Baldari C, Bonavolonta V, Emerenziani GP, Gallotta MC, Silva AJ, Guidetti L. Accuracy, reliability, linearity of Accutrend and Lactate Pro versus EBIO plus analyzer. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2009; 107:105–111.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mechanisms and Prospects of Ischemic Tolerance Induced by Cerebral Preconditioning
- Neurogenic pathways in remote ischemic preconditioning induced cardioprotection: Evidences and possible mechanisms
- Expression of Bcl-2 Protein in the Gerbil Hippocampus Following Transient Forebrain Ischemia and Its Modification by Ischemic Preconditioning
- Protective effect of combination therapy with ischemic preconditioning and rapamycin in fibrotic rat livers
- The Effects of Acute Resistance Exercise on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury-Induced Macro and Microvascular Dysfunction in Healthy Young Adults