Ann Dermatol.
2018 Dec;30(6):725-727. 10.5021/ad.2018.30.6.725.
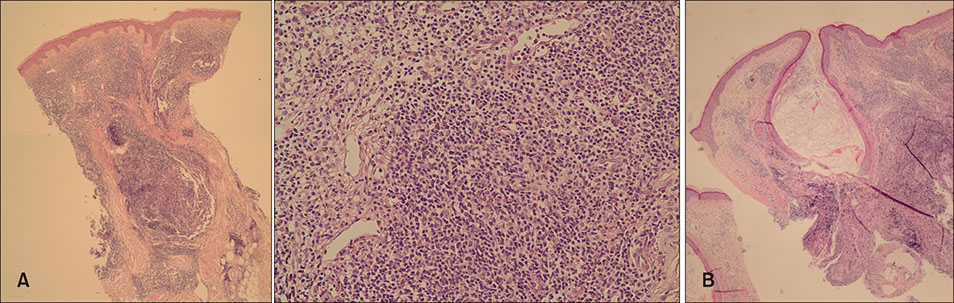
Cutaneous Pseudolymphoma Derived from Ruptured Milia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Severance Hospital, Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dykim@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2428932
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2018.30.6.725
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bergman R. Pseudolymphoma and cutaneous lymphoma: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010; 28:568–574.
Article2. Cristaudo A, Forte G, Bocca B, Petrucci F, Muscardin L, Trento E, et al. Permanent tattoos: evidence of pseudolymphoma in three patients and metal composition of the dyes. Eur J Dermatol. 2012; 22:776–780.
Article3. Imafuku S, Ito K, Nakayama J. Cutaneous pseudolymphoma induced by adalimumab and reproduced by infliximab in a patient with arthropathic psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2012; 166:675–678.
Article4. Nihal M, Mikkola D, Horvath N, Gilliam AC, Stevens SR, Spiro TP, et al. Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia: a lymphoproliferative continuum with lymphomatous potential. Hum Pathol. 2003; 34:617–622.
Article5. Burg G, Dummer R, Haeffner A, Kempf W, Kadin M. From inflammation to neoplasia: mycosis fungoides evolves from reactive inflammatory conditions (lymphoid infiltrates) transforming into neoplastic plaques and tumors. Arch Dermatol. 2001; 137:949–952.