Yonsei Med J.
2018 Sep;59(7):904-907. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.904.
Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage in a Two-Month-Old Infant with Inspissated Bile Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea. smlee@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2428918
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.7.904
Abstract
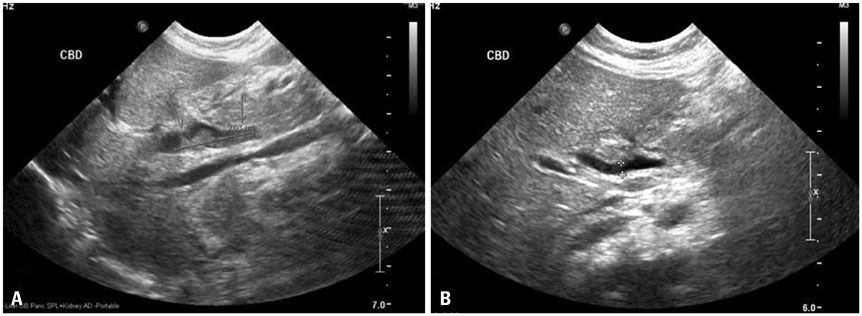
- Inspissated bile syndrome (IBS) is a relatively rare condition. Many treatment options are available, including medication, surgery, and surgical interventions, such as insertion of cholecystostomy drain, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, internal biliary drainage, and percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD). We herein report the first case of IBS that was successfully treated with PTBD in a two-month-old infant in Korea. PTBD was initiated on postnatal day 72. On postnatal day 105, we confirmed complete improvement and successfully removed the catheters. This report suggests that PTBD is a viable and safe treatment option for obstructive jaundice in very young infants.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bernstein J, Braylan R, Brough AJ. Bile-plug syndrome: a correct-able cause of obstructive jaundice in infants. Pediatrics. 1969; 43:273–276.
Article2. Davenport M, Betalli P, D'Antiga L, Cheeseman P, Mieli-Vergani G, Howard ER. The spectrum of surgical jaundice in infancy. J Pediatr Surg. 2003; 38:1471–1479.
Article3. Lightwood R, Bodian M. Biliary obstruction associated with icterus gravis neonatorum. Arch Dis Child. 1946; 21:209–217.
Article4. Bollu BK, Dawrant MJ, Thacker K, Thomas G, Chenapragadda M, Gaskin K, et al. Inspissated bile syndrome; safe and effective minimally invasive treatment with percutaneous cholecystostomy in neonates and infants. J Pediatr Surg. 2016; 51:2119–2122.
Article5. Helin R, Bhat R, Rao B. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous cholecystostomy for acute neonatal biliary obstruction. Neonatology. 2007; 91:266–270.
Article6. Duman L, Büyükyavuz BI, Akcam M, Koroglu M, Tepeli H. Percutaneous management of bile-plug syndrome: a case report. J Pediatr Surg. 2011; 46:e37–e41.
Article7. Gunnarsdóttir A, Holmqvist P, Arnbjörnsson E, Kullendorff CM. Laparoscopic aided cholecystostomy as a treatment of inspissated bile syndrome. J Pediatr Surg. 2008; 43:e33–e35.
Article8. Brownschidle S, Sullivan J, Sartorelli K, Potenta S, Zenali M. Neonatal cholestasis due to biliary sludge-review and report of a case associated with use of diflucan. Ann Clin Path. 2014; 2:1018.9. Fawaz R, Baumann U, Ekong U, Fischler B, Hadzic N, Mack CL, et al. Guideline for the evaluation of cholestatic jaundice in infants: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017; 64:154–168.
Article10. Suchy FJ. Neonatal cholestasis. Pediatr Rev. 2004; 25:388–396.
Article11. Doty JE, Pitt HA, Porter-Fink V, DenBesten L. The effect of intravenous fat and total parenteral nutrition on biliary physiology. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1984; 8:263–268.
Article12. Soysal A, Eras¸ov K, Akpinar I, Bakir M. Biliary precipitation during ceftriaxone therapy: frequency and risk factors. Turk J Pediatr. 2007; 49:404–407.13. Lang EV, Pinckney LE. Spontaneous resolution of bile-plug syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991; 156:1225–1226.
Article14. Jee KB, Song JY, You KY, Min KS, Kim DH, Lee KS. A case of spontaneous resolution of bile plug syndrome in a 4-year-old girl. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999; 2:262–266.
Article15. Jun WY, Cho MJ, Han HS, Bae SH. Use of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids to treat inspissated bile syndrome: a case report. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2016; 19:286–290.
Article16. Berger S, Schibli S, Stranzinger E, Cholewa D. One-stage laparoscopic surgery for inspissated bile syndrome: case report and review of surgical techniques. Springerplus. 2013; 2:648.
Article17. Park JS, Baek JG, Yeom JS, Park ES, Seo JH, Lim JY, et al. A case of obstructive jaundice secondary to traumatic pancreatitis treated with percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2010; 13:204–209.
Article18. Saettini F, Agazzi R, Giraldi E, Foglia C, Cavalleri L, Morali L, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage in an infant with obstructive jaundice caused by neuroblastoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2015; 32:223–228.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Percutaneous biliary drainage in acute suppurative cholangitis with biliary sepsis
- De novo hepatico-gastric stent placement for biliary stricture via percutaneous transhepatic biliary approach
- Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage
- Percutaneous transhepatic removal of common bile duct stone: a case report
- Subcutaneous Implantation Metastasis of a Cholangiocarcinoma of the Bile Duct after Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage (PTBD)