Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2018 Jan;10(1):34-42. 10.4168/aair.2018.10.1.34.
Chinese Herbal Medicine to Treat Allergic Rhinitis: Evidence From a Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery and Department of allergy, Beijing TongRen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China. dr.luozhang@139.com
- 2Beijing Key Laboratory of Nasal Diseases, Beijing Institute of Otolaryngology, Beijing, China.
- KMID: 2428848
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2018.10.1.34
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) has been widely used in China to treat allergic rhinitis (AR). However, several studies have produced conflicting data with regard to the efficacy of the medicine. Our aim was to perform a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to evaluate the relative efficacy of CHM.
METHODS
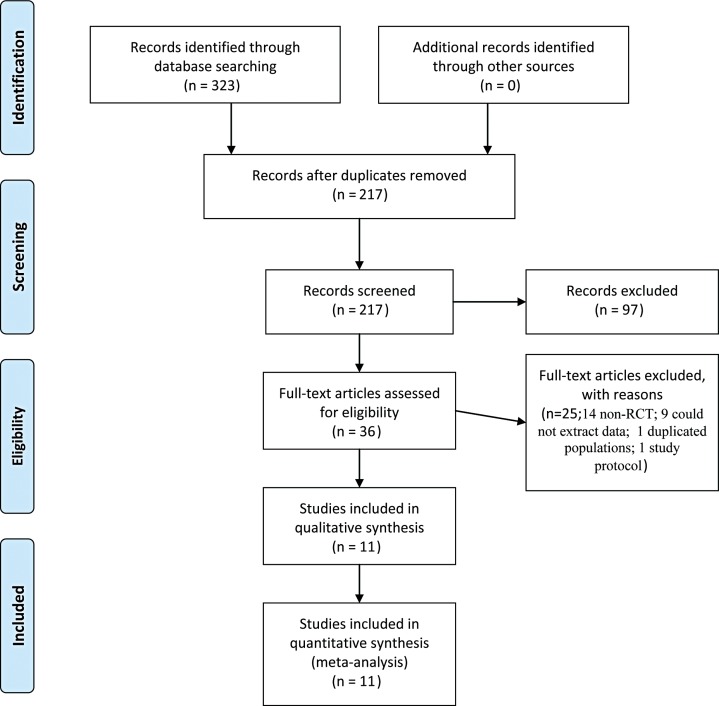
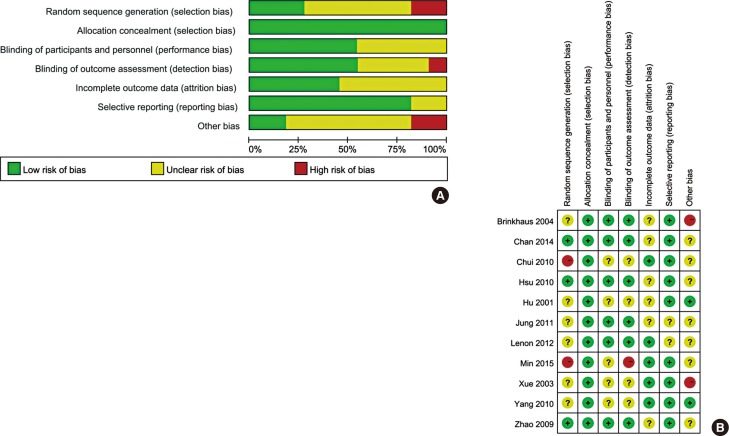
We systematically searched the PubMed, Medline, and Springer electronic databases up to March 2017 for RCTs comparing the efficacy of CHM versus placebo for the treatment of patients with AR. Total nasal symptoms and quality of life were assessed through pooling mean difference (MD) with its 95% confidence interval (CI). Moreover, sensitivity and subgroup analyses according to control design and quality of life assessment were performed to evaluate the source of heterogeneity.
RESULTS
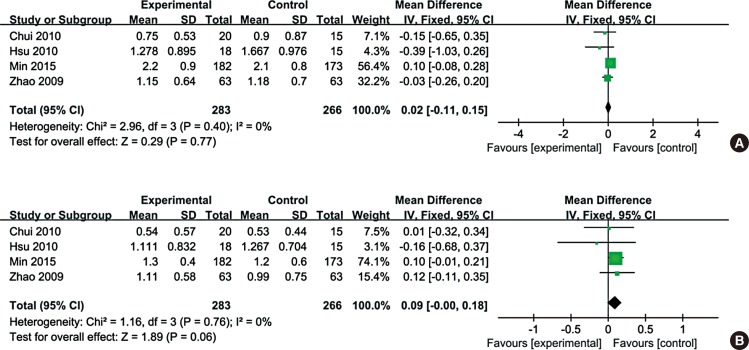
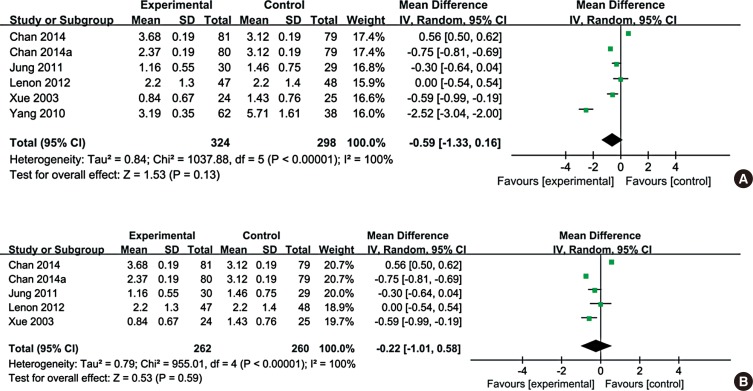
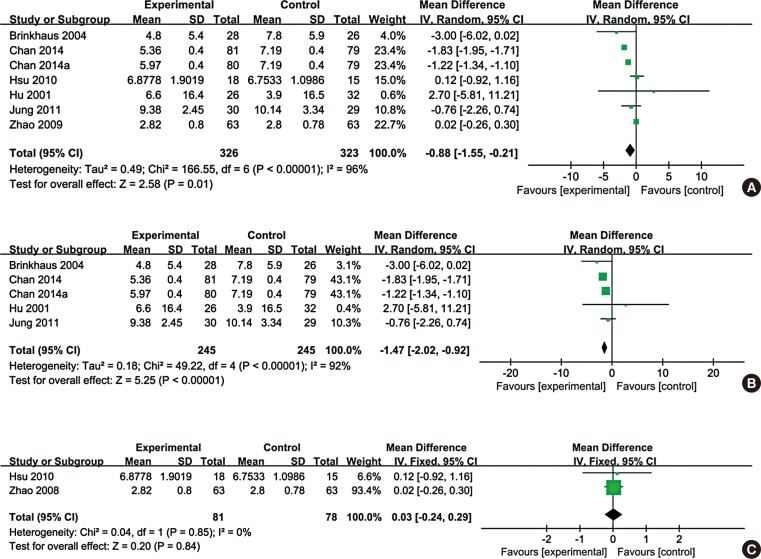
Eleven RCTs were enrolled in the meta-analysis. Assessment of overall heterogeneity indicated significant heterogeneity among the individual studies (I 2=100%, P<0.00001), and thus ransomed effects model was used to pool data. CHM was found to significantly enhance quality of life compared with placebo (MD=-0.88, (95% CI: -1.55, -0.21); P=0.01). The symptom of itchy nose, sneezing or total nasal symptoms scores were not significantly improved after CHM treatment, although the improvement in itchy nose just failed to reach significance (MD=0.09, (95% CI: 0.00, 0.18); P=0.06).
CONCLUSIONS
This study suggests that CHM appears to improve the quality of life of AR patients. However, these findings, as well as the findings for the effect of CHM on sneezing, total nasal symptoms, and the symptom of itchy nose, need to be substantiated in larger cohorts of AR patients by further well-designed studies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Chinese Society of Allergy Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis
Lei Cheng, Jianjun Chen, Qingling Fu, Shaoheng He, Huabin Li, Zheng Liu, Guolin Tan, Zezhang Tao, Dehui Wang, Weiping Wen, Rui Xu, Yu Xu, Qintai Yang, Chonghua Zhang, Gehua Zhang, Ruxin Zhang, Yuan Zhang, Bing Zhou, Dongdong Zhu, Luquan Chen, Xinyan Cui, Yuqin Deng, Zhiqiang Guo, Zhenxiao Huang, Zizhen Huang, Houyong Li, Jingyun Li, Wenting Li, Yanqing Li, Lin Xi, Hongfei Lou, Meiping Lu, Yuhui Ouyang, Wendan Shi, Xiaoyao Tao, Huiqin Tian, Chengshuo Wang, Min Wang, Nan Wang, Xiangdong Wang, Hui Xie, Shaoqing Yu, Renwu Zhao, Ming Zheng, Han Zhou, Luping Zhu, Luo Zhang
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(4):300-353. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.4.300.
Reference
-
1. Bernstein DI, Schwartz G, Bernstein JA. Allergic rhinitis: mechanisms and treatment. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2016; 36:261–278. PMID: 27083101.2. Zhang Y, Zhang L. Prevalence of allergic rhinitis in China. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:105–113. PMID: 24587945.
Article3. Zheng M, Wang X, Bo M, Wang K, Zhao Y, He F, et al. Prevalence of allergic rhinitis among adults in urban and rural areas of china: a population-based cross-sectional survey. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015; 7:148–157. PMID: 25729622.
Article4. Canonica GW, Bousquet J, Mullol J, Scadding GK, Virchow JC. A survey of the burden of allergic rhinitis in Europe. Allergy. 2007; 62(Suppl 85):17–25.
Article5. Thompson A, Sardana N, Craig TJ. Sleep impairment and daytime sleepiness in patients with allergic rhinitis: the role of congestion and inflammation. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013; 111:446–451. PMID: 24267356.
Article6. Kirstein MM, Vogel A. Epidemiology and risk factors of cholangiocarcinoma. Visc Med. 2016; 32:395–400. PMID: 28229073.
Article7. Feng CH, Miller MD, Simon RA. The united allergic airway: connections between allergic rhinitis, asthma, and chronic sinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2012; 26:187–190. PMID: 22643942.
Article8. Chan RY, Chien WT. The effects of two Chinese herbal medicinal formulae vs. placebo controls for treatment of allergic rhinitis: a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2014; 15:261. PMID: 24986270.
Article9. Jung JW, Kang HR, Ji GE, Park MS, Song WJ, Kim MH, et al. Therapeutic effects of fermented red ginseng in allergic rhinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:103–110. PMID: 21461249.
Article10. Wang S, Tang Q, Qian W, Fan Y. Meta-analysis of clinical trials on traditional Chinese herbal medicine for treatment of persistent allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 2012; 67:583–592. PMID: 22435619.
Article11. Peacock WF, Chandra A, Char D, Collins S, Der Sahakian G, Ding L, et al. Clevidipine in acute heart failure: results of the a study of blood pressure control in acute heart failure-a pilot study (PRONTO). Am Heart J. 2014; 167:529–536. PMID: 24655702.
Article12. Min C, Peng C, Wei G, Huang X, Fu T, Du Y, et al. Moxibustion with Chinese herbal has good effect on allergic rhinitis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8:16480–16487. PMID: 26629174.13. Pfaar O, Raap U, Holz M, Hörmann K, Klimek L. Pathophysiology of itching and sneezing in allergic rhinitis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2009; 139:35–40. PMID: 19169901.14. Gu H, Jiang Z, Jiang H, Jiang Y, Zhao F, Zhang Z, et al. Review on the investigation of protective function on nervous system of compound Chinese herbal and active ingredient. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med. 2011; 10:36–38.15. Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: vol. 5. Hoboken (NJ): Wiley Online Library;2008.16. Huedo-Medina TB, Sánchez-Meca J, Marín-Martínez F, Botella J. Assessing heterogeneity in meta-analysis: Q statistic or I2 index? Psychol Methods. 2006; 11:193–206. PMID: 16784338.17. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–560. PMID: 12958120.
Article18. O’Rourke K, Altman DG. Bayesian random effects meta-analysis of trials with binary outcomes: methods for the absolute risk difference and relative risk scales. Stat Med. 2005; 24:2733–2742. PMID: 16118810.19. Xue CC, Thien FC, Zhang JJ, Da Costa C, Li CG. Treatment for seasonal allergic rhinitis by Chinese herbal medicine: a randomized placebo controlled trial. Altern Ther Health Med. 2003; 9:80–87.20. Xue CC, Thien FC, Zhang JJ, Yang W, Da Costa C, Li CG. Effect of adding a Chinese herbal preparation to acupuncture for seasonal allergic rhinitis: randomised double-blind controlled trial. Hong Kong Med J. 2003; 9:427–434. PMID: 14660810.21. Zhao Y, Woo KS, Ma KH, van Hansselt CA, Wong KC, Cheng KF, et al. Treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis using Shi-Bi-Lin, a Chinese herbal formula. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009; 122:100–105. PMID: 19118617.
Article22. Chui SH, Shek SL, Fong MY, Szeto YT, Chan K. A panel study to evaluate quality of life assessments in patients suffering from allergic rhinitis after treatment with a Chinese herbal nasal drop. Phytother Res. 2010; 24:609–613. PMID: 20014162.
Article23. Hsu WH, Ho TJ, Huang CY, Ho HC, Liu YL, Liu HJ, et al. Chinese medicine acupoint herbal patching for allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Chin Med. 2010; 38:661–673. PMID: 20626052.
Article24. Hu G, Walls RS, Bass D, Ramon B, Grayson D, Jones M, et al. The Chinese herbal formulation biminne in management of perennial allergic rhinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 12-week clinical trial. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002; 88:478–487. PMID: 12027069.
Article25. Lenon GB, Li CG, Da Costa C, Thien FC, Shen Y, Xue CC. Lack of efficacy of a herbal preparation (RCM-102) for seasonal allergic rhinitis: a double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Asia Pac Allergy. 2012; 2:187–194. PMID: 22872821.
Article26. Yang SH, Yu CL, Chen YL, Chiao SL, Chen ML. Traditional Chinese medicine, Xin-yi-san, reduces nasal symptoms of patients with perennial allergic rhinitis by its diverse immunomodulatory effects. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010; 10:951–958. PMID: 20546945.
Article27. Brinkhaus B, Hummelsberger J, Kohnen R, Seufert J, Hempen CH, Leonhardy H, et al. Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis: a randomized-controlled clinical trial. Allergy. 2004; 59:953–960. PMID: 15291903.
Article28. Juniper EF. Measuring health-related quality of life in rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:S742–S749. PMID: 9042066.
Article29. Yuan R, Lin Y. Traditional Chinese medicine: an approach to scientific proof and clinical validation. Pharmacol Ther. 2000; 86:191–198. PMID: 10799714.
Article30. Xie Z. Clinical trials in traditional Chinese medicine. J Clin Ethics. 2004; 15:51–54. PMID: 15202358.31. Krouse JH. Allergic rhinitis--current pharmacotherapy. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2008; 41:347–358. viiPMID: 18328373.
Article32. Ridolo E, Montagni M, Melli V, Braido F, Incorvaia C, Canonica GW. Pharmacotherapy of allergic rhinitis: current options and future perspectives. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014; 15:73–83. PMID: 24219793.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Present State of Korean Traditional Medicine and Alternative Medicine in Nasal Disease
- Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis
- Allergic Rhinitis Mouse Model
- Traditional herbal medicine, Rikkunshito, for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
- Lack of efficacy of a herbal preparation (RCM-102) for seasonal allergic rhinitis: a double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial