J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2018 Dec;22(4):161-165. 10.14193/jkfas.2018.22.4.161.
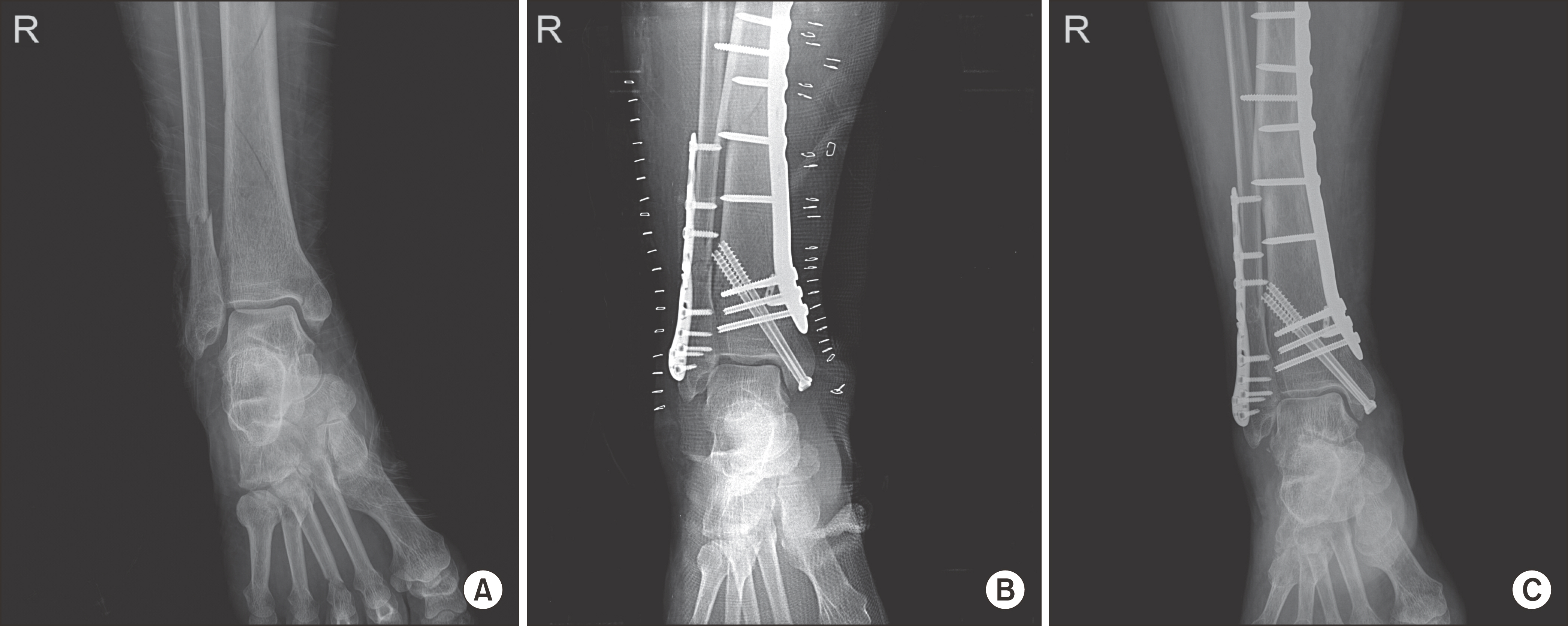
Comparision between Syndesmotic Screw Fixation and Knotless Tightrope® Fixation on Ankle Fractures with Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kiga9@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2428656
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2018.22.4.161
Abstract
- PURPOSE
A distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury with an ankle fracture is usually fixed with syndesmotic screws. Knotless Tightrope® has been used as an alternative procedure because of the fewer reported complications. Therefore, this study compared the two surgeries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Forty-two patients, who underwent syndesmotic screw fixation, and 34 patients, who underwent Knotless Tightrope® fixation for distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury from February 2014 to February 2016, were analyzed retrospectively. The visual analogue scale (VAS) score, American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) score, range of motion of ankle at 1 year after surgery, tibiofibular clear space, and tibiofibular interval at preoperative, postoperative and 1 year after surgery were investigated.
RESULTS
The VAS score, AOFAS score and radiographs were similar in the two groups. Knotless Tightrope® showed better results in complications and plantarflexion.
CONCLUSION
Knotless Tightrope® fixation is a useful treatment that does not show a difference in fixation strength and clinical outcome. Knotless Tightrope® fixation also has an advantage in the range of motion and complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Lin CF., Gross ML., Weinhold P. Ankle syndesmosis injuries: anatomy, biomechanics, mechanism of injury, and clinical guidelines for diagnosis and intervention. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006. 36:372–84.
Article2.Snedden MH., Shea JP. Diastasis with low distal fibula fractures: an anatomic rationale. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001. 382:197–205.3.Ogilvie-Harris DJ., Reed SC., Hedman TP. Disruption of the ankle syndesmosis: biomechanical study of the ligamentous restraints. Arthroscopy. 1994. 10:558–60.
Article4.Sman AD., Hiller CE., Refshauge KM. Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for diagnosis of ankle syndesmosis injury: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2013. 47:620–8.
Article5.Porter DA. Evaluation and treatment of ankle syndesmosis injuries. Instr Course Lect. 2009. 58:575–81.6.Plessis GN., Griesel LD., Lourens D., Gräbe RP. Incidence of syndesmotic injuries in all different types of ankle fractures. SA Or-thop J. 2008. 7:28–32.7.Park JC., McLaurin TM. Acute syndesmosis injuries associated with ankle fractures: current perspectives in management. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009. 67:39–44.8.van den Bekerom MP., Kloen P., Luitse JS., Raaymakers EL. Complications of distal tibiofibular syndesmotic screw stabilization: analysis of 236 patients. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013. 52:456–9.
Article9.Naqvi GA., Cunningham P., Lynch B., Galvin R., Awan N. Fixation of ankle syndesmotic injuries: comparison of tightrope fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy of syndesmotic reduction. Am J Sports Med. 2012. 40:2828–35.10.Thornes B., Walsh A., Hislop M., Murray P., O’Brien M. Suture-endobutton fixation of ankle tibio-fibular diastasis: a cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int. 2003. 24:142–6.
Article11.Coetzee JC., Ebeling P. Treatment of syndesmoses disruptions: a prospective, randomized study comparing conventional screw fixation vs TightRope® fiber wire fixation: medium term results. SA Orthop J. 2009. 8:32–7.12.Storey P., Gadd RJ., Blundell C., Davies MB. Complications of suture button ankle syndesmosis stabilization with modifications of surgical technique. Foot Ankle Int. 2012. 33:717–21.
Article13.Hong CC., Lee WT., Tan KJ. Osteomyelitis after TightRope(®) fixation of the ankle syndesmosis: a case report and review of the literature. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2015. 54:130–4.
Article14.Willmott HJ., Singh B., David LA. Outcome and complications of treatment of ankle diastasis with tightrope fixation. Injury. 2009. 40:1204–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Syndesmotic Screw of Ankle Fracture with Distal Tibiofibular Diastasis
- Comparative Analysis of Trans-syndesmotic Versus Non-syndesmotic Screw Fixation in Surgical Treatment of Ankle Fracture with Diastasis
- Ankle Syndesmotic Injury
- Injury of Distal Tibio-Fibular Syndesmosis Treated with Trans-Syndesmotic Screw Fixation
- Syndesmotic Injury