Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Dec;32(6):478-482. 10.3341/kjo.2018.0040.
Horizontal Effects of 10-mm Inferior Oblique Recession versus 14-mm Inferior Oblique Recession
- Affiliations
-
- 1Kim's Eye Hospital, Seoul, Korea. ungsookim@kimeye.com
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2427962
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2018.0040
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to investigate the quantitative effect of inferior oblique (IO) 10- and 14-mm recession on postoperative horizontal deviation.
METHODS
Patients (22 men and 18 women) who underwent IO recession were divided into two groups for comparison studies: group 1 (10-mm IO recession, 15 patients) and group 2 (14-mm IO recession, 25 patients). Preoperative and postoperative horizontal deviations were measured, and the resulting horizontal deviations from the 10- and 14-mm IO recession surgeries were compared. The effects of superior oblique underaction, IO overaction, and combined exodeviation on postoperative horizontal deviation were analyzed.
RESULTS
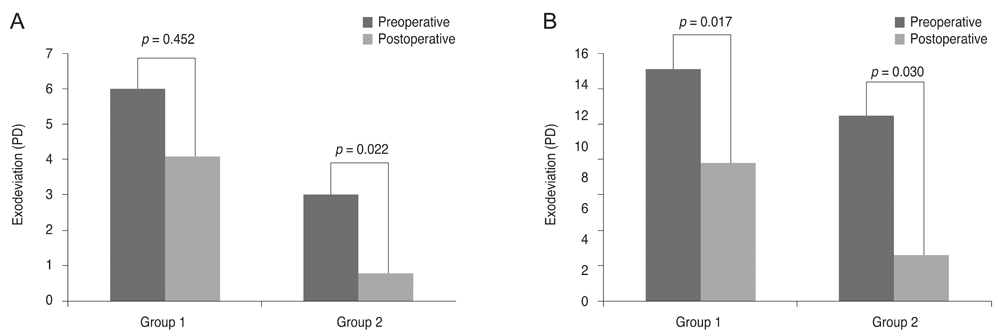
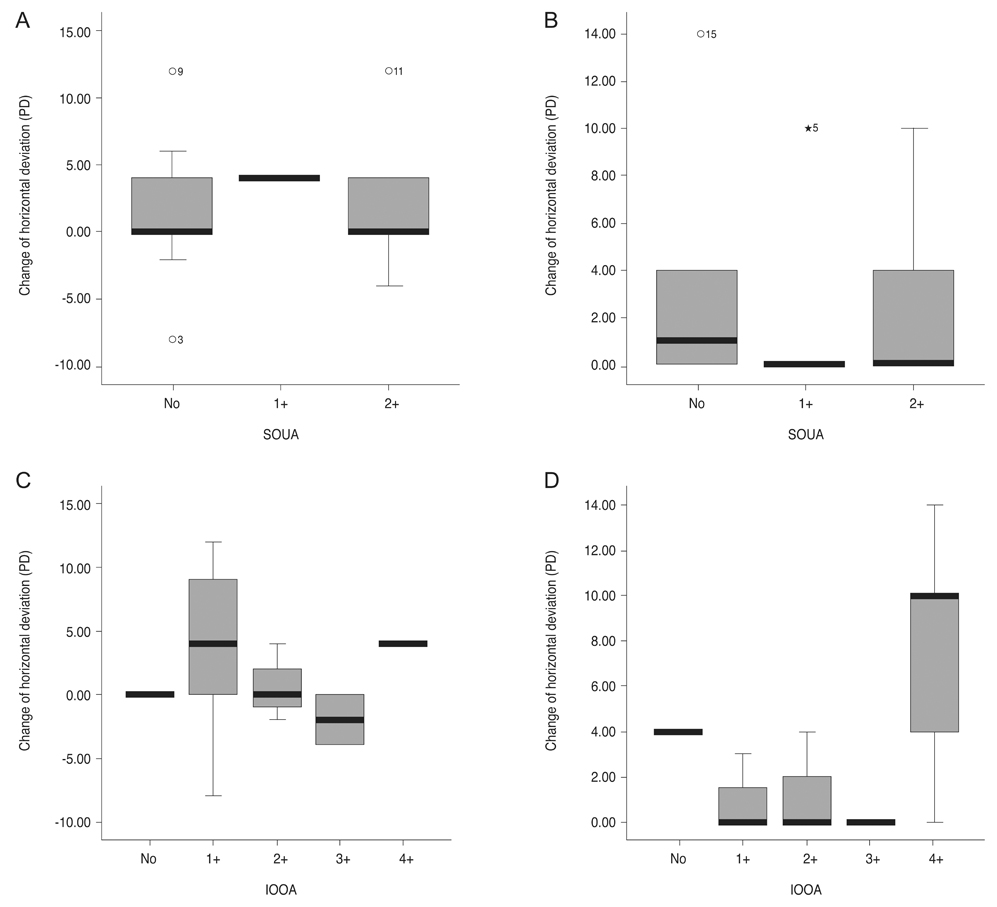
Although group 1 did not show a significant horizontal deviation change after surgery (1.9 ± 4.5 prism diopters [PD], p = 0.452), group 2 had a meaningful horizontal change after 14-mm recession (2.2 ± 3.8 PD, p = 0.022). Both groups showed a significant esodrift in horizontal deviation (group 1, p = 0.017; group 2, p = 0.030) in patients with exodeviation over 8 PD. The mean change in horizontal deviation was 6.0 ± 5.4 PD for group 1 and 9.0 ± 5.0 PD for group 2. Although the amount of superior oblique underaction did not affect the extent of change in horizontal deviation, patients with severe IO overaction showed a significant change in horizontal deviation after 14-mm IO recession.
CONCLUSIONS
Fourteen-millimeter IO recession could make a statistically significant change in horizontal deviation after surgery. In addition, esodrift should be considered after IO recession in patients with a preoperative exodeviation greater than 8 PD or severe IO overaction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Engel JM. Treatment and diagnosis of congenital fourth nerve palsies: an update. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015; 26:353–356.2. Taylan Sekeroglu H, Dikmetas O, Sanac AS, et al. Inferior oblique muscle weakening: is it possible to quantify its effects on horizontal deviations? J Ophthalmol. 2012; 2012:813085.
Article3. Souza-Dias C. Horizontal effect of the surgical weakening of the oblique muscles. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2011; 74:382.
Article4. Diamond GR, Parks MM. The effect of superior oblique weakening procedures on primary position horizontal alignment. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1981; 18:35–38.
Article5. Jampel RS. The fundamental principle of the action of the oblique ocular muscles. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970; 69:623–638.
Article6. Stager DR, Parks MM. Inferior oblique weakening procedures. Effect on primary position horizontal alignment. Arch Ophthalmol. 1973; 90:15–16.7. Khawam E, Scott AB, Jampolsky A. Acquired superior oblique palsy. Diagnosis and management. Arch Ophthalmol. 1967; 77:761–768.8. Chang BL, Yang SW. Inferior oblique overaction. Korean J Ophthalmol. 1988; 2:77–81.
Article9. Tommila V, Valle O. Effect of inferior oblique muscle recession on horizontal deviation. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1968; 46:779–784.
Article10. Shin JH, Paik HJ. Effect of inferior oblique weakening procedures combined with surgery for intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:249–253.
Article11. Guzzinati GC. Effect of surgery of the inferior oblique muscle on horizontal heterotropia. Ann Ottalmol Clin Ocul. 1955; 81:447–454.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term Outcome of Graded Inferior Oblique Recession
- The Effect of Reoperation in Inferior Oblique Overaction
- Effect of Recession of Inferior Oblique: Analysis in the Primary Gaze and Adduction
- The Effect of Graded Recession and Anteriorization on Unilateral Superior Oblique Palsy
- The Correlations Between Landmark of Inferior Oblique Muscle Recession and Adjacent Globe Structures