Hip Pelvis.
2018 Dec;30(4):202-209. 10.5371/hp.2018.30.4.202.
Surgical Treatment of the Atypical Femoral Fracture: Overcoming Femoral Bowing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Keimyung University Dongsan Hospital, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. oslee@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2427923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.4.202
Abstract
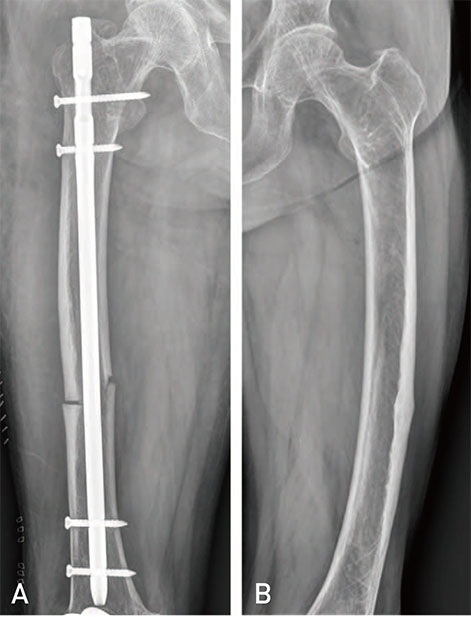
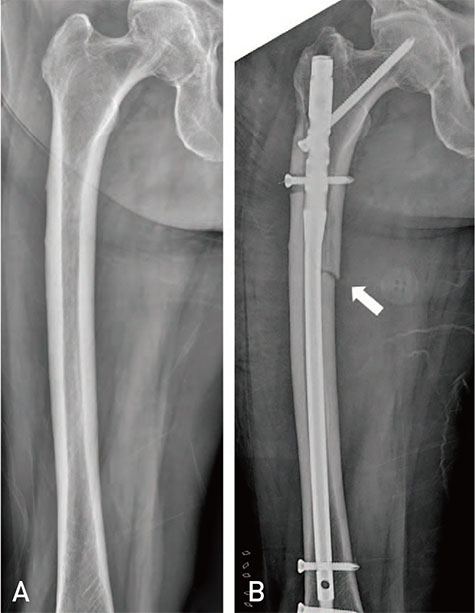
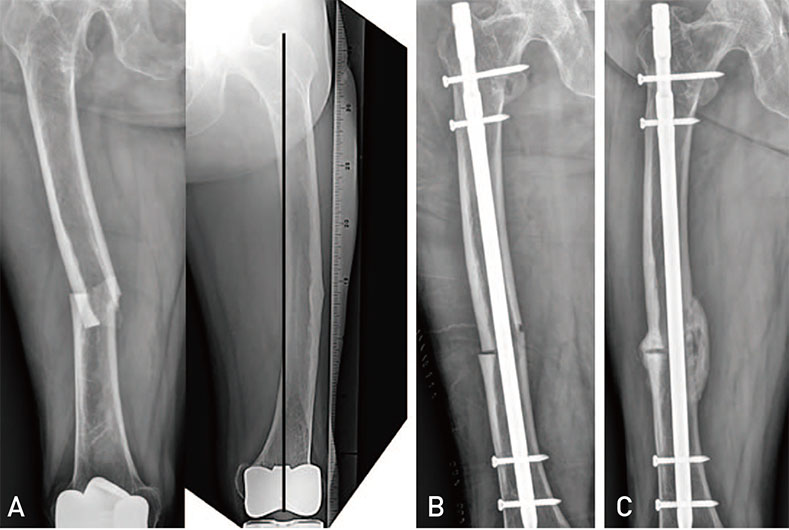
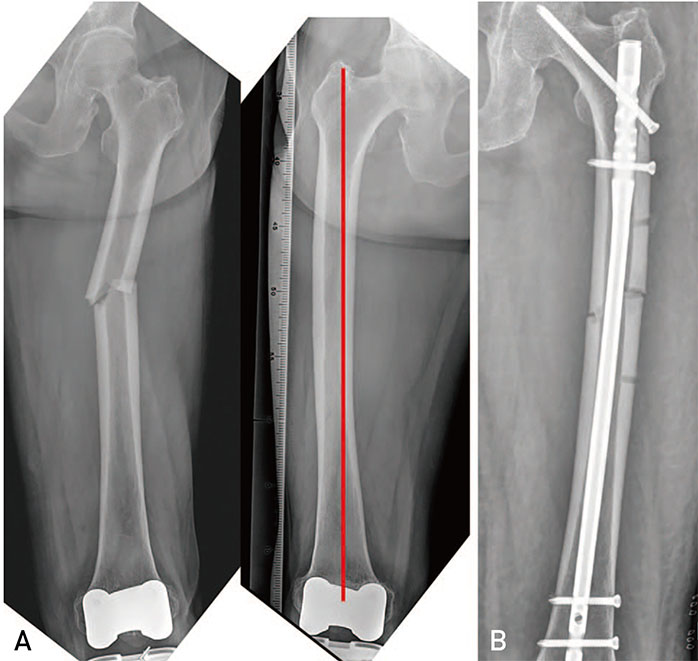
- Atypical femoral fractures differ from ordinary femoral diaphyseal or subtrochanteric fractures in several aspects. Although several authors have reported the results of surgical treatment for atypical femoral fractures, the rate of complications (e.g., delayed union, nonunion, fixation failure, and reoperation) is still high. Therefore, we reviewed principles of surgical treatment and describe useful methods for overcoming femoral bowing in these high-risk patients.
MeSH Terms
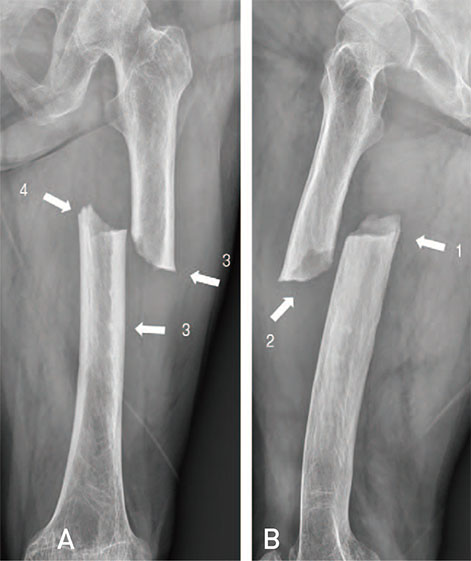
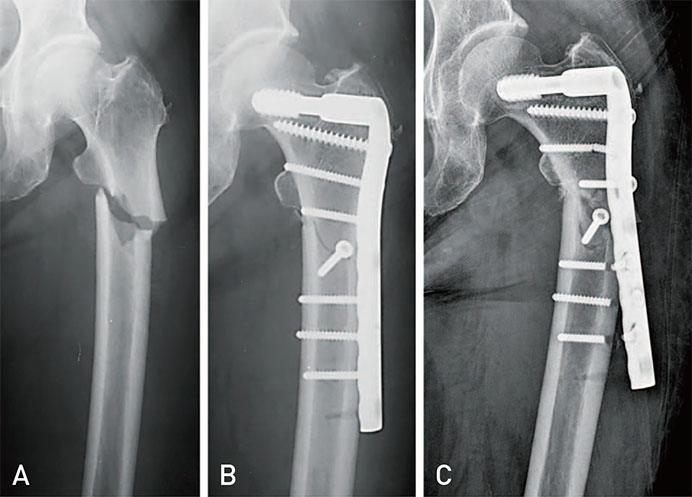
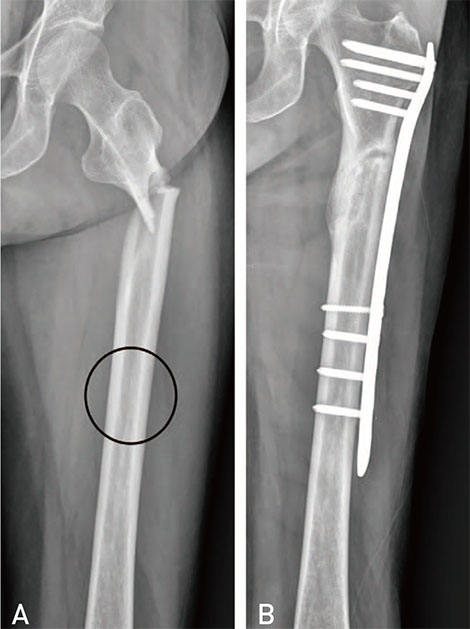
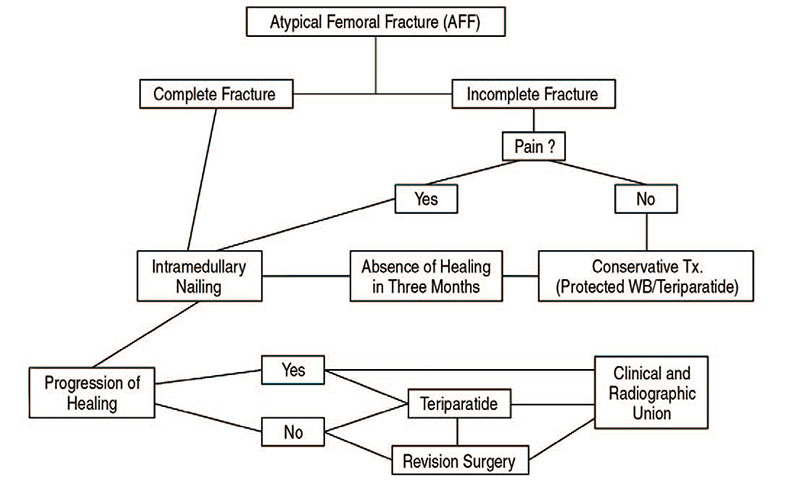
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2014; 29:1–23.
Article2. Lee KJ, Min BW, Song KS, Bae KC, Cho CH, Lee SW. T-Score discordance of bone mineral density in patients with atypical femoral fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017; 99:1683–1688.
Article3. Al-Ashqar M, Panteli M, Chakrabarty G, Giannoudis PV. Atypical fractures: an issue of concern or a myth? Injury. 2018; 49:649–655.
Article4. Weil YA, Rivkin G, Safran O, Liebergall M, Foldes AJ. The outcome of surgically treated femur fractures associated with long-term bisphosphonate use. J Trauma. 2011; 71:186–190.
Article5. Teo BJ, Koh JS, Goh SK, Png MA, Chua DT, Howe TS. Post-operative outcomes of atypical femoral subtrochanteric fracture in patients on bisphosphonate therapy. Bone Joint J. 2014; 96-B:658–664.
Article6. Prasarn ML, Ahn J, Helfet DL, Lane JM, Lorich DG. Bisphosphonate-associated femur fractures have high complication rates with operative fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470:2295–2301.
Article7. Lee KJ, Yoo JJ, Oh KJ, et al. Surgical outcome of intramedullary nailing in patients with complete atypical femoral fracture: a multicenter retrospective study. Injury. 2017; 48:941–945.
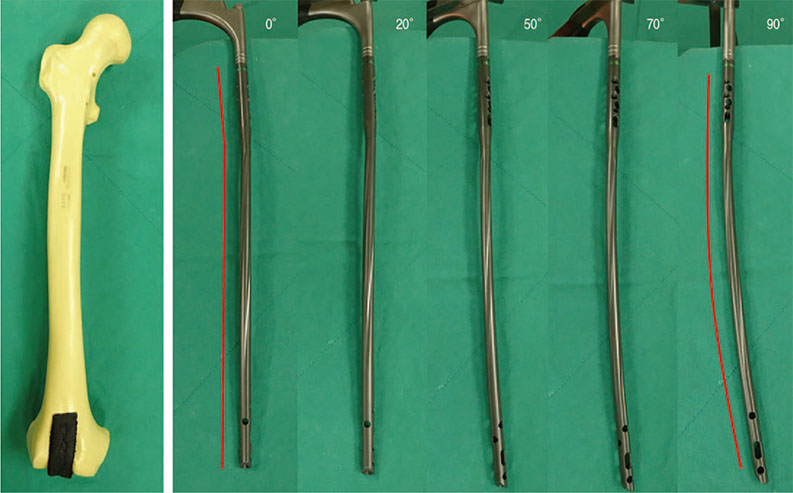
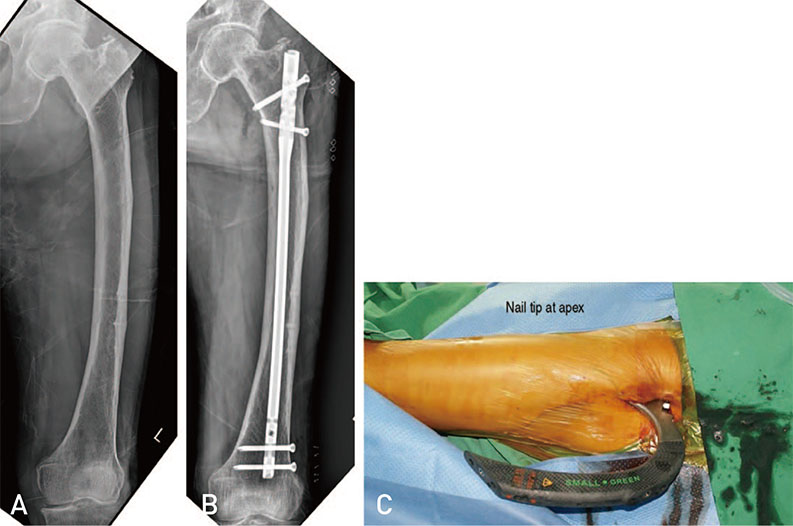
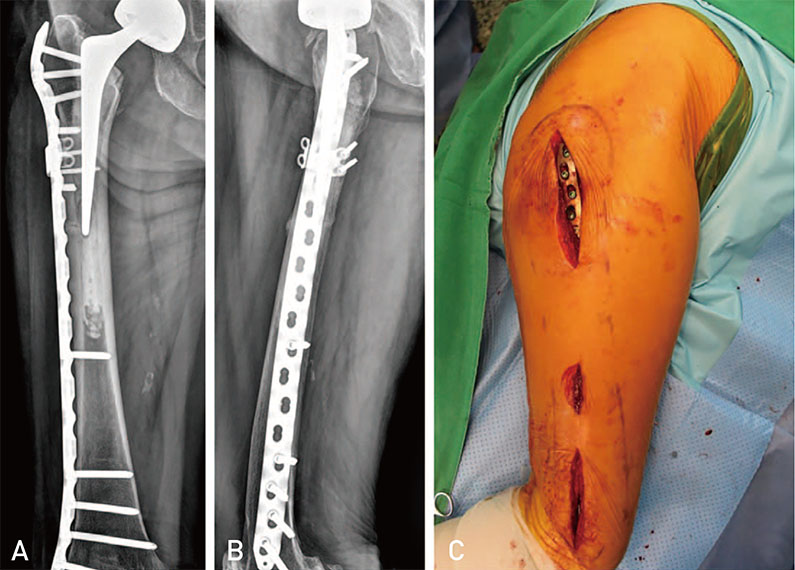
Article8. Park JH, Lee Y, Shon OJ, Shon HC, Kim JW. Surgical tips of intramedullary nailing in severely bowed femurs in atypical femur fractures: simulation with 3D printed model. Injury. 2016; 47:1318–1324.
Article9. Hauser M, Siegrist M, Keller I, Hofstetter W. Healing of fractures in osteoporotic bones in mice treated with bisphosphonates - a transcriptome analysis. Bone. 2018; 112:107–119.
Article10. Cao Y, Mori S, Mashiba T, et al. Raloxifene, estrogen, and alendronate affect the processes of fracture repair differently in ovariectomized rats. J Bone Miner Res. 2002; 17:2237–2246.
Article11. Martinez MD, Schmid GJ, McKenzie JA, Ornitz DM, Silva MJ. Healing of non-displaced fractures produced by fatigue loading of the mouse ulna. Bone. 2010; 46:1604–1612.
Article12. Shane E, Burr D, Ebeling PR, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2010; 25:2267–2294.
Article13. Ha YC, Cho MR, Park KH, Kim SY, Koo KH. Is surgery necessary for femoral insufficiency fractures after long-term bisphosphonate therapy? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:3393–3398.
Article14. Demiralp B, Ilgan S, Ozgur Karacalioglu A, Cicek EI, Yildrim D, Erler K. Bilateral femoral insuffiency fractures treated with inflatable intramedullary nails: a case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007; 127:597–601.
Article15. Crossley K, Bennell KL, Wrigley T, Oakes BW. Ground reaction forces, bone characteristics, and tibial stress fracture in male runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999; 31:1088–1093.
Article16. Sasaki S, Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, Kasukawa Y, Shimada Y. Low-energy diaphyseal femoral fractures associated with bisphosphonate use and severe curved femur: a case series. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012; 30:561–567.
Article17. Kim JW, Kim H, Oh CW, et al. Surgical outcomes of intramedullary nailing for diaphyseal atypical femur fractures: is it safe to modify a nail entry in bowed femur? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017; 137:1515–1522.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Outcomes of Atypical Femoral Fracture
- Lateral Femoral Bowing and the Location of Atypical Femoral Fractures
- Surgical Treatment in Atypical Diaphyseal Femoral Fracture with Anterior and Lateral Bowing
- Localization of Atypical Femoral Fracture on Straight and Bowed Femurs
- Rendezvous Surgery for Peri-Implant Fractures around Locking Compression Plate on Anterolateral Bowed Femur - A Case Report -