Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2018 Nov;6(6):295-302. 10.4168/aard.2018.6.6.295.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children: Clinical characteristics and risk factors of refractory pneumonia by age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea. phj7294@hanmail.net
- 2Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2427488
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2018.6.6.295
Abstract
- PURPOSE
It is thought that Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is more prevalent and causes more severe pneumonia in school-age children and young adults than in preschool children; however, recent studies suggest that the infection may be underdiagnosed and more severe in preschool children. This study investigated the clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) and the risk factors of refractory MPP (RMPP) by age.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 353 children admitted due to MPP from January 2015 to December 2016. Demographics, clinical information, laboratory data and radiological findings were collected from all patients in this study. The patients were divided into 2 groups by the age of 6 years. Also, both preschool ( < 6 years old) and school-age (≥6 years old) children were divided into RMPP and non-RMPP patients.
RESULTS
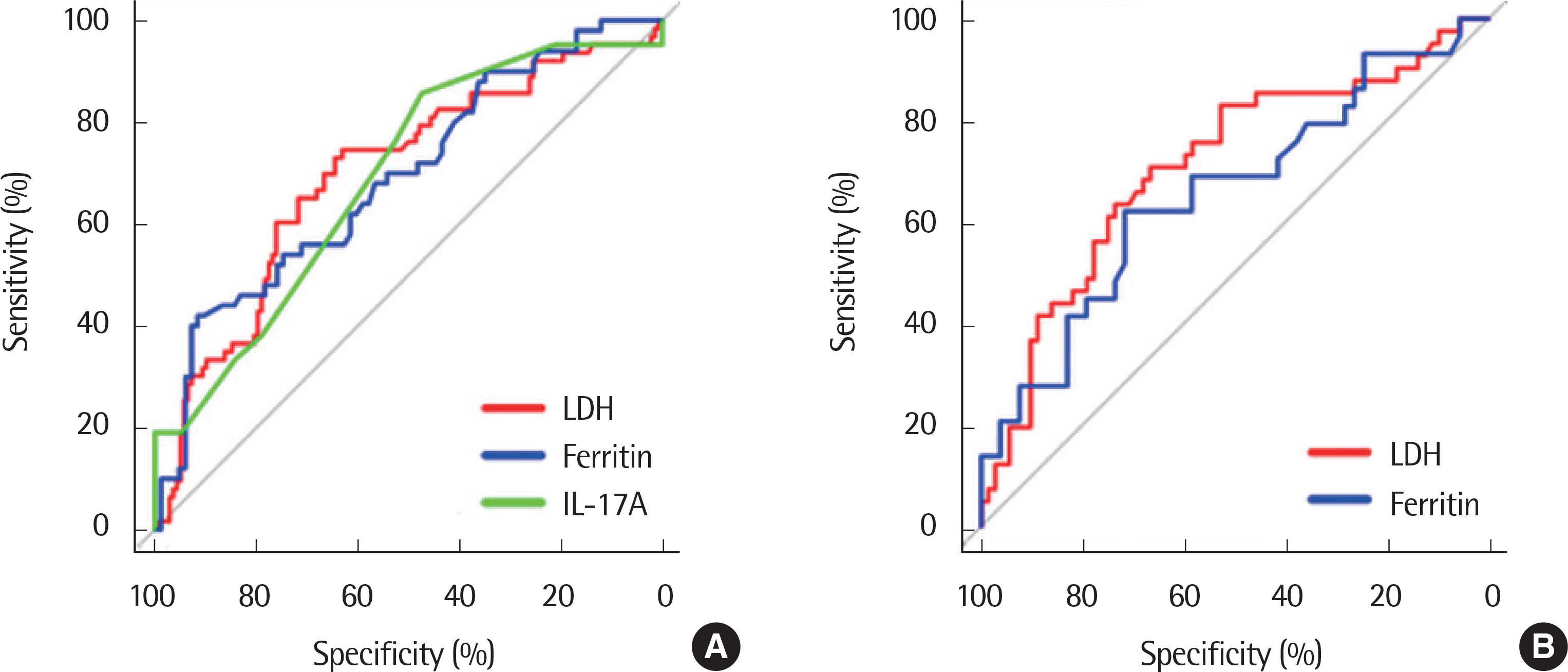
Total febrile days, febrile days before admission and the duration of macrolide antibiotic therapy were significantly longer in school-age children than in preschool children. School-age children had significantly greater risk of lobar consolidation (P=0.036), pleural effusion (P=0.001) and extrapulmonary complications (P=0.019). Necrotizing pneumonia and bronchiolitis obliterans tended to occur more frequently in preschool children than in school-age children. In both preschool and school-age children, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels were significantly higher in RMPP patients than in non-RMPP patients. In preschool children, LDH >722 IU/L (odds ratio [OR], 3.02; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.44-6.50) and ferritin >177 ng/mL (OR, 5.38; 95% CI, 1.61-19.49) were significant risk factors for RMPP, while LDH >645 IU/L (OR, 4.12; 95% CI, 1.64-10.97) and ferritin >166 ng/mL (OR, 5.51; 95% CI, 1.59-22.32) were so in school-age children.
CONCLUSION
Clinical features of MPP were significantly different between preschool and school-age children. LDH and ferritin may be significant factors of RMPP in preschool and school-age children.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee KY. Pediatric respiratory infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008; 6:509–21.2. Atkinson TP, Balish MF, Waites KB. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis and laboratory detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008; 32:956–73.3. Ferwerda A, Moll HA, de Groot R. Respiratory tract infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: a review of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Eur J Pediatr. 2001; 160:483–91.
Article4. Almasri M, Diza E, Papa A, Eboriadou M, Souliou E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory tract infections among Greek children. Hippokratia. 2011; 15:147–52.5. Chalker V, Stocki T, Litt D, Bermingham A, Watson J, Fleming D, et al. Increased detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in children in England and Wales, October 2011 to January 2012. Euro Surveill. 2012; 17.
Article6. Kim JW, Seo HK, Yoo EG, Park SJ, Yoon SH, Jung HY, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children, from 1979 to 2006-a metaanalysis. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:315–23.
Article7. Wy HH, Min DH, Kim DS, Park MS, Shim JW, Jung HL, et al. Clinical characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children during the recent 3 epidemics. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017; 5:8–14.8. S⊘rensen CM, Sch⊘nning K, Rosenfeldt V. Clinical characteristics of children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection hospitalized during the Danish 2010-2012 epidemic. Dan Med J. 2013; 60:A4632.9. Inchley CS, Berg AS, Vahdani Benam A, Kvissel AK, Leegaard TM, Naks-tad B. Mycoplasma pneumoniae: a cross-sectional population-based comparison of disease severity in preschool and school-age children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2017; 36:930–6.
Article10. Tamura A, Matsubara K, Tanaka T, Nigami H, Yura K, Fukaya T. Methylprednisolone pulse therapy for refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. J Infect. 2008; 57:223–8.
Article11. Lu A, Wang L, Zhang X, Zhang M. Combined treatment for child refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia with ciprofloxacin and glucocorticoid. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2011; 46:1093–7.
Article12. Inamura N, Miyashita N, Hasegawa S, Kato A, Fukuda Y, Saitoh A, et al. Management of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: utility of measuring serum lactate dehydrogenase level. J Infect Chemother. 2014; 20:270–3.
Article13. Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Li S, Yang D, Wu X, Chen Z. The clinical characteristics and predictors of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0156465.
Article14. Lu A, Wang C, Zhang X, Wang L, Qian L. Lactate dehydrogenase as a biomarker for prediction of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Respir Care. 2015; 60:1469–75.
Article15. Kawamata R, Yokoyama K, Sato M, Goto M, Nozaki Y, Takagi T, et al. Utility of serum ferritin and lactate dehydrogenase as surrogate markers for steroid therapy for Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2015; 21:783–9.
Article16. Zhang Y, Mei S, Zhou Y, Huang M, Dong G, Chen Z. Cytokines as the good predictors of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in school-aged children. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:37037.
Article17. Waris ME, Toikka P, Saarinen T, Nikkari S, Meurman O, Vainionpää R, et al. Diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:3155–9.18. Yang J, Hooper WC, Phillips DJ, Talkington DF. Cytokines in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004; 15:157–68.
Article19. Shin JE, Cheon BR, Shim JW, Kim DS, Jung HL, Park MS, et al. Increased risk of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children with atopic sensitization and asthma. Korean J Pediatr. 2014; 57:271–7.20. Skakni L, Sardet A, Just J, Landman-Parker J, Costil J, Moniot-Ville N, et al. Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in clinical samples from pediatric patients by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992; 30:2638–43.
Article21. Loens K, Goossens H, Ieven M. Acute respiratory infection due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae: current status of diagnostic methods. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010; 29:1055–69.
Article22. Wang M, Wang Y, Yan Y, Zhu C, Huang L, Shao X, et al. Clinical and laboratory profiles of refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children. Int J Infect Dis. 2014; 18–23.
Article23. Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Sheng Y, Zhang L, Shen Z, Chen Z. More complications occur in macrolide-resistant than in macrolide-sensitive Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014; 58:1034–8.
Article24. Yamazaki T, Kenri T. Epidemiology of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in Japan and therapeutic strategies for macrolide-resistant M. pneumoniae. Front Microbiol. 2016; 7:693.
Article25. Hong KB, Choi EH, Lee HJ, Lee SY, Cho EY, Choi JH, et al. Macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, South Korea, 2000-2011. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:1281–4.26. Guo H, He Z, Li M, Wang T, Zhang L. Imbalance of peripheral blood Th17 and Treg responses in children with refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2016; 22:162–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Observation on Pneumonia due to Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children
- A clinical study of mycoplasma pneumonia in children during recent 5 years
- Clinical Study of Patients with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children
- Clinical Consideration on Pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Children