Arch Hand Microsurg.
2018 Dec;23(4):296-300. 10.12790/ahm.2018.23.4.296.
Reconstruction of a Circumferential Penile Shaft Defect Using Bilateral Superficial External Pudendal Artery Perforator Flaps
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Konkuk University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. 20150136@kuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 2427398
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.4.296
Abstract
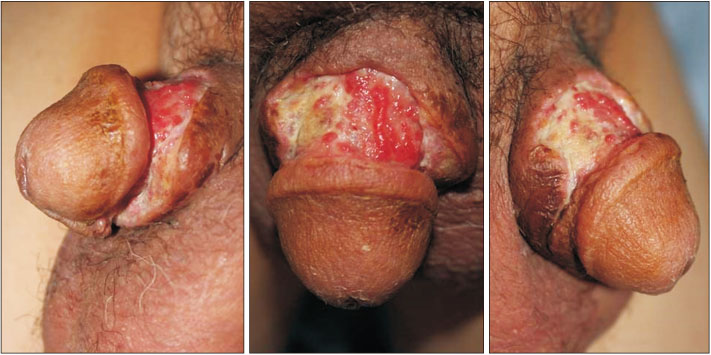
- Penile shaft reconstruction requires adequate soft tissue characteristics as well as constant vascular pedicles when considering a perforator flap. The free flap technique using various donor sites and regional conventional and perforator flaps have been utilized for penile shaft reconstruction. Still, the free flap techniques include challenging surgical procedures in addition to postoperative management. The regional flap can be applied to limited defects due to the size and shape. We performed the bilateral superficial external pudendal artery (SEPA) perforator flaps in order to reconstruct a circumferential penile shaft defect. The circumferential wound has noted necrotic tissue involving superficial (Dartos) fascia. We underwent debridement, preserving deep (Buck's) fascia and corpus spongiosum. Thereafter, the soft tissue defect was covered with bilateral SEPA perforator flaps. The patient has been observed for 27 months, showing penile resilience without deformity or wound-related problems.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garaffa G, Sansalone S, Ralph DJ. Penile reconstruction. Asian J Androl. 2013; 15:16–19.
Article2. Kim SW, Yoon BI, Ha US, Kim SW, Cho YH, Sohn DW. 2014. Treatment of paraffin-induced lipogranuloma of the penis by bipedicled scrotal flap with Y-V incision. Ann Plast Surg. 2014; 73:692–695.3. Guo L, Zhang M, Zeng J, Liang P, Zhang P, Huang X. Utilities of scrotal flap for reconstruction of penile skin defects after severe burn injury. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017; 49:1593–1603.
Article4. Doornaert M, Hoebeke P, Ceulemans P, T'Sjoen G, Heylens G, Monstrey S. Penile reconstruction with the radial forearm flap: an update. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2011; 43:208–214.
Article5. Garaffa G, Christopher N, Ralph DJ. The management of genital lymphedema. BJU Int. 2008; 102:480–484.6. Black PC, Friedrich JB, Engrav LH, Wessells H. Meshed unexpanded split-thickness skin grafting for reconstruction of penile skin loss. J Urol. 2004; 172:976–979.
Article7. Yao A, Ingargiola MJ, Lopez CD, et al. Total penile reconstruction: a systematic review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018; 71:788–806.
Article8. Seo BF, Choi JY, Han HH, et al. Perforators as recipients for free flap reconstruction of the inguinal and perineal region. Microsurgery. 2015; 35:627–633.
Article9. La Falce OL, Ambrosio JD, Souza RR. The anatomy of the superficial external pudendal artery: a quantitative study. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2006; 61:441–444.
Article10. Cormack GC, Lamberty BG. A classification of fasciocutaneous flaps according to their patterns of vascularisation. Br J Plast Surg. 1984; 37:80–87.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral Vulvar Reconstruction Using Two Different Types of Perforator Flap: A Case Report
- Reconstruction of the Defect in Perineum using Local Perforator Based Flap
- Reconstruction of the Soft Tissue Defect Using Thoracodorsal Artery Perforator Skin Flap
- Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery Perforator Free Flap for Reconstruction of Small or Medium Sized Defect on Lower Extremities
- One Staged Urethroplasty Using Bilateral Penile Pedicled Rotation Skin-flaps in the Proximal Penile Shaft Hypospadias with Insufficient Penile Skin