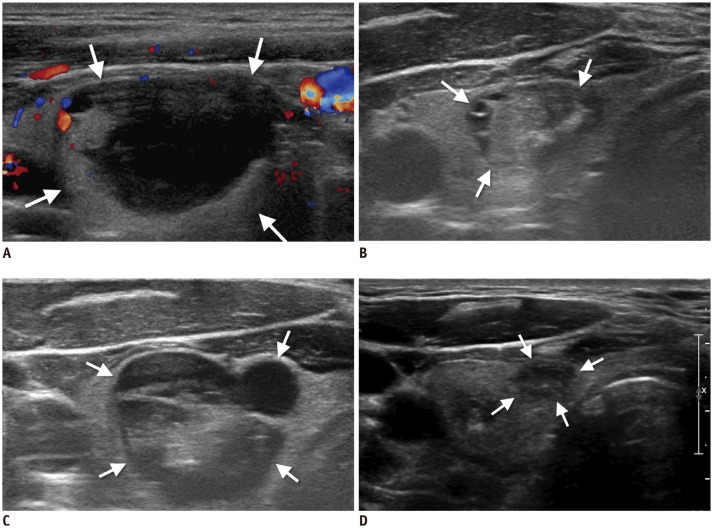
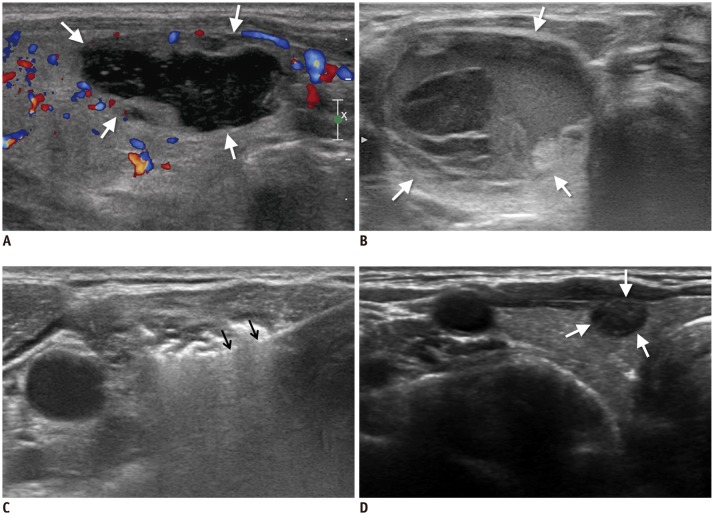
Innovative Techniques for Image-Guided Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules: Combined Ethanol and Radiofrequency Ablation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul 05505, Korea. radbaek@naver.com
- KMID: 2427301
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2017.18.3.461
Abstract
- In the treatment of benign thyroid nodules, ethanol ablation (EA), and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) have been suggested for cystic and solid thyroid nodules, respectively. Although combining these ablation techniques may be effective, no guidelines for or reviews of the combination have been published. Currently, there are three ways of combining EA and RFA: additional RFA is effective for treatment of incompletely resolved symptoms and solid residual portions of a thyroid nodule after EA. Additional EA can be performed for the residual unablated solid portion of a nodule after RFA if it is adjacent to critical structures (e.g., trachea, esophagus, and recurrent laryngeal nerve). In the concomitant procedure, ethanol is injected to control venous oozing after aspiration of cystic fluid prior to RFA of the remaining solid nodule.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
RE: Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Multicenter Study
Qi Di
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(3):542-543. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.3.542.Long-Term Outcomes Following Thermal Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules as an Alternative to Surgery: The Importance of Controlling Regrowth
Jung Suk Sim, Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):117-123. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.117.Does Radiofrequency Ablation Induce Neoplastic Changes in Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Preliminary Study
Su Min Ha, Jun Young Shin, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Eun Song, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):169-178. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.169.Revisiting Rupture of Benign Thyroid Nodules after Radiofrequency Ablation: Various Types and Imaging Features
Sae Rom Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji Hwa Ryu, So Lyung Jung
Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):415-421. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.415.2017 Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation Guideline: Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology
Ji-hoon Kim, Jung Hwan Baek, Hyun Kyung Lim, Hye Shin Ahn, Seon Mi Baek, Yoon Jung Choi, Young Jun Choi, Sae Rom Chung, Eun Ju Ha, Soo Yeon Hahn, So Lyung Jung, Dae Sik Kim, Soo Jin Kim, Yeo Koon Kim, Chang Yoon Lee, Jeong Hyun Lee, Kwang Hwi Lee, Young Hen Lee, Jeong Seon Park, Hyesun Park, Jung Hee Shin, Chong Hyun Suh, Jin Yong Sung, Jung Suk Sim, Inyoung Youn, Miyoung Choi, Dong Gyu Na,
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(4):632-655. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.632.Efficacy of Ethanol Ablation for Benign Thyroid Cysts and Predominantly Cystic Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Cheng-Chun Yang, Yung Hsu, Jyun-Yan Liou
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):81-95. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.833.
Reference
-
1. Kim YS, Rhim H, Tae K, Park DW, Kim ST. Radiofrequency ablation of benign cold thyroid nodules: initial clinical experience. Thyroid. 2006; 16:361–367. PMID: 16646682.
Article2. Jeong WK, Baek JH, Rhim H, Kim YS, Kwak MS, Jeong HJ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: safety and imaging follow-up in 236 patients. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:1244–1250. PMID: 18286289.
Article3. Spiezia S, Garberoglio R, Milone F, Ramundo V, Caiazzo C, Assanti AP, et al. Thyroid nodules and related symptoms are stably controlled two years after radiofrequency thermal ablation. Thyroid. 2009; 19:219–225. PMID: 19265492.
Article4. Faggiano A, Ramundo V, Assanti AP, Fonderico F, Macchia PE, Misso C, et al. Thyroid nodules treated with percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation: a comparative study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:4439–4445. PMID: 23019349.
Article5. Shin JH, Baek JH, Ha EJ, Lee JH. Radiofrequency ablation of thyroid nodules: basic principles and clinical application. Int J Endocrinol. 2012; 2012:919650. PMID: 23133449.
Article6. Lim HK, Lee JH, Ha EJ, Sung JY, Kim JK, Baek JH. Radiofrequency ablation of benign non-functioning thyroid nodules: 4-year follow-up results for 111 patients. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:1044–1049. PMID: 23096937.
Article7. Ha EJ, Baek JH. Advances in nonsurgical treatment of benign thyroid nodules. Future Oncol. 2014; 10:1399–1405. PMID: 25052750.
Article8. Gharib H, Papini E, Valcavi R, Baskin HJ, Crescenzi A, Dottorini ME, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and Associazione Medici Endocrinologi medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules. Endocr Pract. 2006; 12:63–102.9. Shin JE, Baek JH, Lee JH. Radiofrequency and ethanol ablation for the treatment of recurrent thyroid cancers: current status and challenges. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013; 25:14–19. PMID: 23079931.10. Sywak M, Cornford L, Roach P, Stalberg P, Sidhu S, Delbridge L. Routine ipsilateral level VI lymphadenectomy reduces postoperative thyroglobulin levels in papillary thyroid cancer. Surgery. 2006; 140:1000–1005. PMID: 17188149.
Article11. Hauch A, Al-Qurayshi Z, Randolph G, Kandil E. Total thyroidectomy is associated with increased risk of complications for low- and high-volume surgeons. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21:3844–3852. PMID: 24943236.
Article12. Zingrillo M, Torlontano M, Chiarella R, Ghiggi MR, Nirchio V, Bisceglia M, et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection may be a definitive treatment for symptomatic thyroid cystic nodules not treatable by surgery: five-year follow-up study. Thyroid. 1999; 9:763–767. PMID: 10482367.
Article13. Del Prete S, Caraglia M, Russo D, Vitale G, Giuberti G, Marra M, et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection efficacy in the treatment of large symptomatic thyroid cystic nodules: ten-year follow-up of a large series. Thyroid. 2002; 12:815–821. PMID: 12481948.
Article14. Kim JH, Lee HK, Lee JH, Ahn IM, Choi CG. Efficacy of sonographically guided percutaneous ethanol injection for treatment of thyroid cysts versus solid thyroid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:1723–1726. PMID: 12760950.
Article15. Sung JY, Kim YS, Choi H, Lee JH, Baek JH. Optimum first-line treatment technique for benign cystic thyroid nodules: ethanol ablation or radiofrequency ablation? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:W210–W214. PMID: 21257865.
Article16. Sung JY, Baek JH, Kim KS, Lee D, Yoo H, Kim JK, et al. Single-session treatment of benign cystic thyroid nodules with ethanol versus radiofrequency ablation: a prospective randomized study. Radiology. 2013; 269:293–300. PMID: 23616630.
Article17. Ugurlu MU, Uprak K, Akpinar IN, Attaallah W, Yegen C, Gulluoglu BM. Radiofrequency ablation of benign symptomatic thyroid nodules: prospective safety and efficacy study. World J Surg. 2015; 39:961–968. PMID: 25446486.
Article18. Suh CH, Baek JH, Ha EJ, Choi YJ, Lee JH, Kim JK, et al. Ethanol ablation of predominantly cystic thyroid nodules: evaluation of recurrence rate and factors related to recurrence. Clin Radiol. 2015; 70:42–47. PMID: 25443776.
Article19. Garberoglio R, Aliberti C, Appetecchia M, Attard M, Boccuzzi G, Boraso F, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for thyroid nodules: which indications? The first Italian opinion statement. J Ultrasound. 2015; 18:423–443. PMID: 26550079.
Article20. Huang G, Lin M, Xie X, Liu B, Xu Z, Lencioni R, et al. Combined radiofrequency ablation and ethanol injection with a multipronged needle for the treatment of medium and large hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2014; 24:1565–1571. PMID: 24788036.
Article21. Na DG, Lee JH, Jung SL, Kim JH, Sung JY, Shin JH, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules and recurrent thyroid cancers: consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:117–125. PMID: 22438678.
Article22. Pacella CM, Mauri G, Achille G, Barbaro D, Bizzarri G, De Feo P, et al. Outcomes and risk factors for complications of laser ablation for thyroid nodules: a multicenter study on 1531 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:3903–3910. PMID: 26274342.
Article23. Papini E, Rago T, Gambelunghe G, Valcavi R, Bizzarri G, Vitti P, et al. Long-term efficacy of ultrasound-guided laser ablation for benign solid thyroid nodules. Results of a three-year multicenter prospective randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:3653–3659. PMID: 25050903.
Article24. Cho SH, Lee SH, Jung KY, Woo JS, Back SK, Choi JH, et al. Sonography-guided OK-432 sclerotherapy for benign thyroid cysts. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008; 128:597–600. PMID: 18421618.25. Baek JH, Ha EJ, Choi YJ, Sung JY, Kim JK, Shong YK. Radiofrequency versus ethanol ablation for treating predominantly cystic thyroid nodules: a randomized clinical trial. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:1332–1340. PMID: 26576124.
Article26. Kim JH. Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy for benign non-thyroid cystic mass in the neck. Ultrasonography. 2014; 33:83–90. PMID: 24936500.
Article27. Cesareo R, Pasqualini V, Simeoni C, Sacchi M, Saralli E, Campagna G, et al. Prospective study of effectiveness of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation versus control group in patients affected by benign thyroid nodules. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:460–466. PMID: 25387256.
Article28. Ha EJ, Baek JH, Kim KW, Pyo J, Lee JH, Baek SH, et al. Comparative efficacy of radiofrequency and laser ablation for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules: systematic review including traditional pooling and bayesian network meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:1903–1911. PMID: 25695887.
Article29. Chen L, Sun J, Yang X. Radiofrequency ablation-combined multimodel therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: current status. Cancer Lett. 2016; 370:78–84. PMID: 26472630.
Article30. Cha DI, Lee MW, Rhim H, Choi D, Kim YS, Lim HK. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of percutaneous ethanol injection with or without combined radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinomas in high risk locations. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:240–247. PMID: 23483664.
Article31. Huang G, Lin M, Xie X, Liu B, Xu Z, Lencioni R, et al. Combined radiofrequency ablation and ethanol injection with a multipronged needle for the treatment of medium and large hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2014; 24:1565–1571. PMID: 24788036.
Article32. Watanabe S, Kurokohchi K, Masaki T, Miyauchi Y, Funaki T, Inoue H, et al. Enlargement of thermal ablation zone by the combination of ethanol injection and radiofrequency ablation in excised bovine liver. Int J Oncol. 2004; 24:279–284. PMID: 14719103.33. Kurokohchi K, Watanabe S, Masaki T, Hosomi N, Miyauchi Y, Himoto T, et al. Comparison between combination therapy of percutaneous ethanol injection and radiofrequency ablation and radiofrequency ablation alone for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:1426–1432. PMID: 15770716.
Article34. Kim DW, Rho MH, Park HJ, Kwag HJ. Ultrasonography-guided ethanol ablation of predominantly solid thyroid nodules: a preliminary study for factors that predict the outcome. Br J Radiol. 2012; 85:930–936. PMID: 22167503.
Article35. Yasuda K, Ozaki O, Sugino K, Yamashita T, Toshima K, Ito K, et al. Treatment of cystic lesions of the thyroid by ethanol instillation. World J Surg. 1992; 16:958–961. PMID: 1462637.
Article36. Bennedbaek FN, Hegedüs L. Percutaneous ethanol injection therapy in benign solitary solid cold thyroid nodules: a randomized trial comparing one injection with three injections. Thyroid. 1999; 9:225–233. PMID: 10211597.
Article37. Kim DW. Sonography-guided ethanol ablation of a remnant solid component after radio-frequency ablation of benign solid thyroid nodules: a preliminary study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:1139–1143. PMID: 22268084.
Article38. Baek JH, Moon WJ, Kim YS, Lee JH, Lee D. Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of autonomously functioning thyroid nodules. World J Surg. 2009; 33:1971–1977. PMID: 19575141.
Article39. Ha EJ, Baek JH, Lee JH. Moving-shot versus fixed electrode techniques for radiofrequency ablation: comparison in an ex-vivo bovine liver tissue model. Korean J Radiol. 2014; 15:836–843. PMID: 25469097.40. Kim YJ, Baek JH, Ha EJ, Lim HK, Lee JH, Sung JY, et al. Cystic versus predominantly cystic thyroid nodules: efficacy of ethanol ablation and analysis of related factors. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22:1573–1578. PMID: 22437920.
Article41. Bennedbaek FN, Hegedüs L. Treatment of recurrent thyroid cysts with ethanol: a randomized double-blind controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 88:5773–5777. PMID: 14671167.42. Monzani F, Lippi F, Goletti O, Del Guerra P, Caraccio N, Lippolis PV, et al. Percutaneous aspiration and ethanol sclerotherapy for thyroid cysts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994; 78:800–802. PMID: 8126160.
Article43. Zingrillo M, Torlontano M, Ghiggi MR, D'Aloiso L, Nirchio V, Bisceglia M, et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection of large thyroid cystic nodules. Thyroid. 1996; 6:403–408. PMID: 8936663.
Article44. Cho YS, Lee HK, Ahn IM, Lim SM, Kim DH, Choi CG, et al. Sonographically guided ethanol sclerotherapy for benign thyroid cysts: results in 22 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 174:213–216. PMID: 10628481.45. Lee JH, Kim YS, Lee D, Choi H, Yoo H, Baek JH. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of benign thyroid nodules in patients with incompletely resolved clinical problems after ethanol ablation (EA). World J Surg. 2010; 34:1488–1493. PMID: 20376445.
Article46. Jang SW, Baek JH, Kim JK, Sung JY, Choi H, Lim HK, et al. How to manage the patients with unsatisfactory results after ethanol ablation for thyroid nodules: role of radiofrequency ablation. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:905–910. PMID: 21388767.
Article47. Kim DW. Usefulness of two-stage ethanol ablation in the treatment of benign predominantly cystic thyroid nodules. Endocr Pract. 2014; 20:548–555. PMID: 24449678.
Article48. Ha EJ, Baek JH, Lee JH. The efficacy and complications of radiofrequency ablation of thyroid nodules. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011; 18:310–314. PMID: 21841482.
Article49. Baek JH, Lee JH, Sung JY, Bae JI, Kim KT, Sim J, et al. Complications encountered in the treatment of benign thyroid nodules with US-guided radiofrequency ablation: a multicenter study. Radiology. 2012; 262:335–342. PMID: 21998044.
Article50. Baek JH, Jeong HJ, Kim YS, Kwak MS, Lee D. Radiofrequency ablation for an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. Thyroid. 2008; 18:675–676. PMID: 18578625.
Article51. Deandrea M, Limone P, Basso E, Mormile A, Ragazzoni F, Gamarra E, et al. US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation for the treatment of solid benign hyperfunctioning or compressive thyroid nodules. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008; 34:784–791. PMID: 18207307.
Article52. Huh JY, Baek JH, Choi H, Kim JK, Lee JH. Symptomatic benign thyroid nodules: efficacy of additional radiofrequency ablation treatment session--prospective randomized study. Radiology. 2012; 263:909–916. PMID: 22438360.
Article53. Ha EJ, Baek JH, Lee JH. Ultrasonography-based thyroidal and perithyroidal anatomy and its clinical significance. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:749–766. PMID: 26175574.
Article54. Shi F, Tan Z, An H, Wang X, Xu Y, Wang S. Hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 4 cm treated with radiofrequency ablation with or without percutaneous ethanol injection. Ann Hepatol. 2016; 15:61–70. PMID: 26626642.
Article55. Wong SN, Lin CJ, Lin CC, Chen WT, Cua IH, Lin SM. Combined percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma in high-risk locations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:W187–W195. PMID: 18287411.
Article56. Zhang YJ, Liang HH, Chen MS, Guo RP, Li JQ, Zheng Y, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with radiofrequency ablation with or without ethanol injection: a prospective randomized trial. Radiology. 2007; 244:599–607. PMID: 17641378.
Article57. Fotiadis NI, Sabharwal T, Morales JP, Hodgson DJ, O'Brien TS, Adam A. Combined percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and ethanol injection of renal tumours: midterm results. Eur Urol. 2007; 52:777–784. PMID: 17400364.
Article58. Sakr AA, Saleh AA, Moeaty AA, Moeaty AA. The combined effect of radiofrequency and ethanol ablation in the management of large hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol. 2005; 54:418–425. PMID: 15899345.
Article59. Kurokohchi K, Watanabe S, Masaki T, Hosomi N, Funaki T, Arima K, et al. Combination therapy of percutaneous ethanol injection and radiofrequency ablation against hepatocellular carcinomas difficult to treat. Int J Oncol. 2002; 21:611–615. PMID: 12168107.
Article60. Kurokohchi K, Watanabe S, Masaki T, Hosomi N, Funaki T, Arima K, et al. Combined use of percutaneous ethanol injection and radiofrequency ablation for the effective treatment of hepatocelluar carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2002; 21:841–846. PMID: 12239624.
Article61. Shiina S, Tagawa K, Unuma T, Takanashi R, Yoshiura K, Komatsu Y, et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. A histopathologic study. Cancer. 1991; 68:1524–1530. PMID: 1654196.
Article62. Døssing H, Bennedbaek FN, Hegedüs L. Beneficial effect of combined aspiration and interstitial laser therapy in patients with benign cystic thyroid nodules: a pilot study. Br J Radiol. 2006; 79:943–947. PMID: 16822801.
Article63. Lee YH, Baek JH, Jung SL, Kwak JY, Kim JH, Shin JH, et al. Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: a consensus statement by the Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:391–401. PMID: 25741201.
Article64. Shin JH, Baek JH, Chung J, Ha EJ, Kim JH, Lee YH, et al. Ultrasonography diagnosis and imaging-based management of thyroid nodules: revised Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol. 2016; 17:370–395. PMID: 27134526.
Article65. Yoon HM, Baek JH, Lee JH, Ha EJ, Kim JK, Yoon JH, et al. Combination therapy consisting of ethanol and radiofrequency ablation for predominantly cystic thyroid nodules. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 35:582–586. PMID: 23969340.
Article66. Larijani B, Pajouhi M, Ghanaati H, Bastanhagh MH, Abbasvandi F, Firooznia K, et al. Treatment of hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules by percutaneous ethanol injection. BMC Endocr Disord. 2002; 2:3. PMID: 12470301.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Non-surgical, Image-guided Management of Benign Thyroid Nodules
- Ultrasound (US)-Guided Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
- Effective and Safe Application of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules
- The Effect of Ethanol Ablation for the Treatment of Benign Cystic Thyroid Nodules
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodule