Korean J Gastroenterol.
2018 Nov;72(5):262-266. 10.4166/kjg.2018.72.5.262.
Covered Self-expandable Metallic Stent Insertion as a Rescue Procedure for Postoperative Leakage after Primary Repair of Perforated Duodenal Ulcer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. soon0925@nhimc.or.kr
- KMID: 2426868
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2018.72.5.262
Abstract
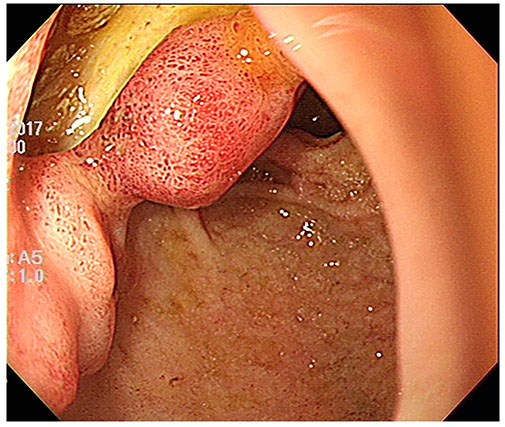
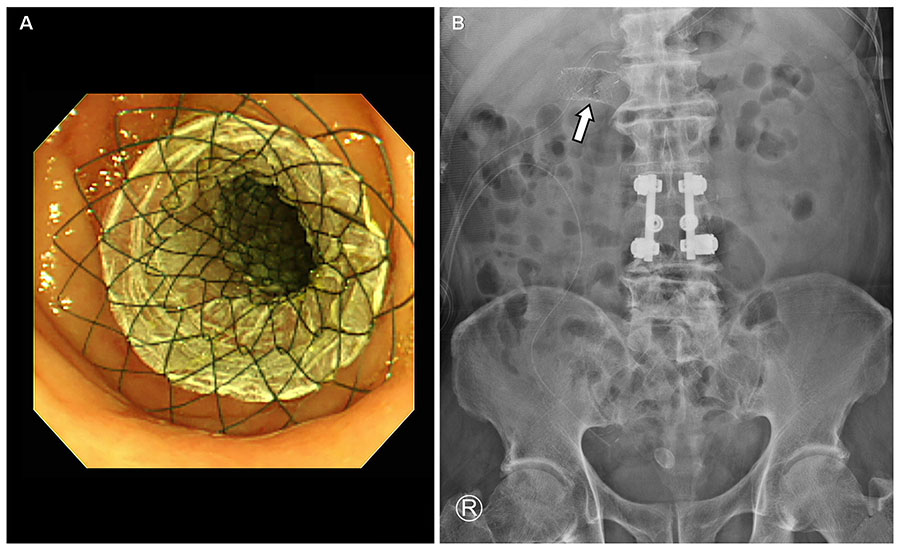
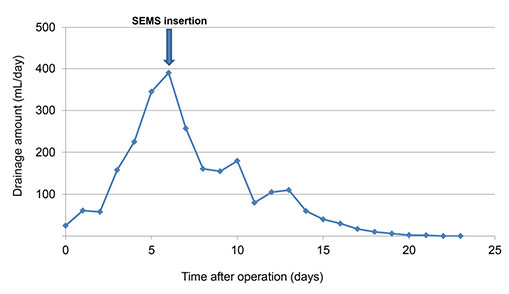
- Surgery has been the standard treatment for perforated duodenal ulcers, with mostly good results. However, the resolution of postoperative leakage after primary repair of perforated duodenal ulcer remains challenging. There are several choices for re-operation required in persistent leakage from perforated duodenal ulcers. However, many of these choices are complicated surgical procedures requiring prolonged general anesthesia that may increase the chances of morbidity and mortality. Several recent reports have demonstrated postoperative leakage after primary repair of a perforated duodenal ulcer treated with endoscopic insertion using a covered self-expandable metallic stent, with good clinical results. We report a case with postoperative leakage after primary repair of a perforated duodenal ulcer treated using a covered self-expandable metallic stent.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gupta S, Kaushik R, Sharma R, Attri A. The management of large perforations of duodenal ulcers. BMC Surg. 2005; 5:15.
Article2. Bergström M, Arroyo Vázquez JA, Park PO. Self-expandable metal stents as a new treatment option for perforated duodenal ulcer. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:222–225.
Article3. Eubanks S, Edwards CA, Fearing NM, et al. Use of endoscopic stents to treat anastomotic complications after bariatric surgery. J Am Coll Surg. 2008; 206:935–938. discussion 938-939.
Article4. Puli SR, Spofford IS, Thompson CC. Use of self-expandable stents in the treatment of bariatric surgery leaks: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:287–293.
Article5. Schubert D, Scheidbach H, Kuhn R, et al. Endoscopic treatment of thoracic esophageal anastomotic leaks by using silicone-covered, self-expanding polyester stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:891–896.
Article6. Serra C, Baltasar A, Andreo L, et al. Treatment of gastric leaks with coated self-expanding stents after sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2007; 17:866–872.
Article7. Swinnen J, Eisendrath P, Rigaux J, et al. Self-expandable metal stents for the treatment of benign upper GI leaks and perforations. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:890–899.
Article8. Søreide K, Thorsen K, Harrison EM, et al. Perforated peptic ulcer. Lancet. 2015; 386:1288–1298.
Article9. Søreide K, Thorsen K, Søreide JA. Strategies to improve the outcome of emergency surgery for perforated peptic ulcer. Br J Surg. 2014; 101:e51–e64.
Article10. Lunevicius R, Morkevicius M. Management strategies, early results, benefits, and risk factors of laparoscopic repair of perforated peptic ulcer. World J Surg. 2005; 29:1299–1310.
Article11. Kim KY, Tsauo J, Song HY, Kim PH, Park JH. Self-expandable metallic stent placement for the palliation of esophageal cancer. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:1062–1071.
Article12. Johnsson E, Lundell L, Liedman B. Sealing of esophageal perforation or ruptures with expandable metallic stents: a prospective controlled study on treatment efficacy and limitations. Dis Esophagus. 2005; 18:262–266.
Article13. Reintam Blaser A, Starkopf J, Alhazzani W, et al. Early enteral nutrition in critically ill patients: ESICM clinical practice guidelines. Intensive Care Med. 2017; 43:380–398.
Article14. Chertoff J, Khullar V, Burke L. Duodenal perforation following esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) with cautery and epinephrine injection for peptic ulcer disease: an interesting case of nonoperative management in the medical intensive care unit (MICU). Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 10:121–125.
Article15. Wai CT, Khor C, Lim SE, Ho KY. Post-metallic stent placement bleeding caused by stent-induced ulcers. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11:5739–5741.
Article16. Holm TE, Rosseland AR, Lundin KA, et al. Endoscopic stent treatment of a duodenal ulcer perforation. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:Suppl 2 UCTN. E60.
Article17. Mouly C, Chati R, Scotté M, Regimbeau JM. Therapeutic management of perforated gastro-duodenal ulcer: literature review. J Visc Surg. 2013; 150:333–340.
Article18. Babor R, Talbot M, Tyndal A. Treatment of upper gastrointestinal leaks with a removable, covered, self-expanding metallic stent. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2009; 19:e1–e4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Obstructive Jaundice after Insertion of Metallic Stent for Duodenal Obstruction by Recurrent Duodenal Ulcer
- A Case of Esophageal Perforation Cured by Conservative Management after Stent Insertion
- The use of self expandable metallic stent in the management of malignant biliary obstruction
- A Case of Endoscopic Stenting for Anastomotic Leakage after Total Gastrectomy
- Laparoscopic Repair with Omental Patch for Perforated Duodenal Ulcer