J Korean Acad Nurs.
2017 Apr;47(2):222-232. 10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.222.
Development and Effects of a Children's Sex Education Program for the Parents of Lower Elementary Grade Students
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Songwon University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. hlkim5207@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2426348
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.222
Abstract
- PURPOSE
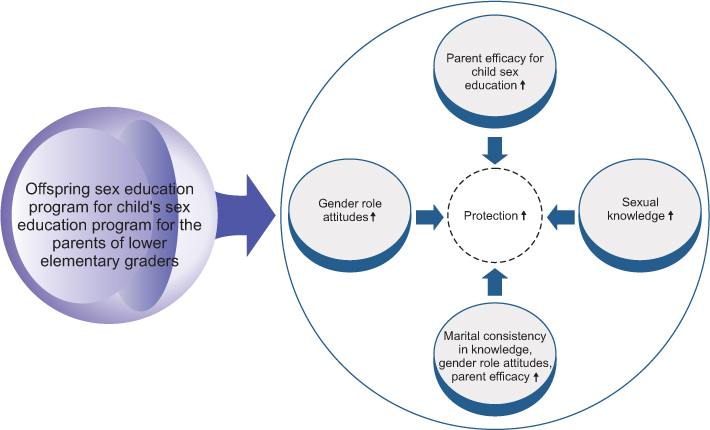
This study was done to develop a children's sex education program for the parents of lower elementary grade students and to evaluate its effects on sexual knowledge, gender role attitude, parent efficacy for child's sex education, and marital consistency.
METHODS
A quasi-experimental with a non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The participants were 29 couples (58 parents, experimental group=28, control group=30) from G city. The 5-week (5-session) program was developed based on "˜A theory of protection: parents as sex educators' and used the case-based small group learning method. Data were collected during July and August 2015. The characteristics of the program developed in the present study were a theoretical-based, client-centered, multi-method.
RESULTS
After the intervention, the experimental group showed a significant improvement in sexual knowledge, gender role attitudes, parent efficacy for child's sex education, and marital consistency, compared to the control group. The effect sizes of the program were .64 (knowledge), .65 (gender role attitudes), and .68 (parent efficacy).
CONCLUSION
The results of this study provided implications for the parents as effective sex educator and the role expansion of school health nurses.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ministry of Education, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The eleventh Korea youth risk behavior web-based survey. Seoul: Author;2015.2. Kim JY, Choi JH, Lee H, Kim SB. The influence of pornography use and social interaction on South Korean males'rape myth acceptance. Korean J Soc Welf Res. 2015; 46:55–80. DOI: 10.17997/SWRY.46.1.3.3. Cho YR, Kim JE, Park KM. Differences in the characteristics of sexual abuse victimization between low- and high-grade elementary school children and correlations among the characteristics. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2015; 26(2):119–127. DOI: 10.12799/jkachn.2015.26.2.119.4. Yoon IK, No SO, Park SY, Park SE, Song SK, Yu IK, et al. Sex education and sexual assault prevention materials research and development. Seoul: Ministry of Education Science and Technology;2007. p. 25–70.5. Jeong GH, Yang SO, Kim SJ. Teachers' needs analysis about contents of sexual education for the lower grades of primary school. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2007; 13(1):35–42.6. Jin HS, Park HR. Sexual knowledge and perception and current status of sex education among parents of first and second grade elementary schoolers. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2011; 17(3):198–205.7. Turnbull T, van Wersc A, van Schaik P. A review of parental involvement in sex education: The role for effective communication in British families. Health Educ J. 2008; 67(3):182–195. DOI: 10.1177/0017896908094636.8. Liavshina G. Parents' participation in sex education of children. Probl Sotsialnoi Gig Zdravookhranenniiai Istor Med. 2002; (3):22–24.9. Lee EM, Kweon YR. Effects of a maternal sexuality education program for mothers of preschoolers. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2013; 43(3):370–378. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.370.10. Guem SH, Kim MH, Kang IS. Research on sex education of young children's mothers. Korean Parent Child Health J. 2005; 8(1):49–63.11. Schuster EA, Kruger SF, Hebenstreit JJ. A theory of protection: Parents as sex educators. ANS Adv Nurs Sci. 1985; 7(3):70–77.12. Vieira I, Fernandes O, Vieira RX. Evaluation of parents as partners in sex education. Sexologies. 2008; 17:Suppl 1. S154. DOI: 10.1016/S1158-1360(08)72946-3.13. Youn G. Preventive suggestions of sexual violence through school- and community-based sexuality education. Korean J Sex Health. 2015; 2(1):31–40.14. Wakley G. Helping parents with sex education. J Fam Health Care. 2011; 21(2):30–33.15. Lee GY, Song SH. Influencing factors on sexual knowledge among elementary, middle, and high school students. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2015; 21(3):406–416. DOI: 10.5977/jkasne.2015.21.3.406.16. Sulak PJ, Herbelin SJ, Fix DD, Kuehl TJ. Impact of an adolescent sex education program that was implemented by an academic medical center. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006; 195(1):78–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2005.12.011.17. Fisher CM, Telljohann SK, Price JH, Dake JA, Glassman T. Perceptions of elementary school children's parents regarding sexuality education. Am J Sex Educ. 2015; 10(1):1–20. DOI: 10.1080/15546128.2015.1009595.18. Eum JS. Effects of a parent-involvement sex education program for high primary-school graders. J Korean Public Health Nurs. 2004; 18(1):143–153.19. Kim YS. Effects of parents sex education program to elementary school students in higher grade [master's thesis]. Seoul: Korea University;2008. 1–60.20. Park SR. The effect analysis of parents sex education program to puberty [master's thesis]. Busan: Dong Eui University;2009. 1–83.21. Yang SO, Jeong GH, Kim SJ, Lee QY, Baek SS. Development and application of evaluation tool for sexuality education in elementary school. Korean J Child Health Nurs. 2002; 8(3):334–343.22. Ahn SS, Kim YS, Park KS, Lee SH, Kim JI. Development and validation of a South Korean multifaceted gender perception test. Seoul: Korean Institute for Gender Equality Promotion and Education;2008.23. Ministry of Education, Science and Technology. Sexual education guideline. Seoul: Author;2001. p. 25–111.24. Aoosung. Sexual education for parents and teachers of elementary school students [Internet]. Seoul: Author;2009. cited 2015 September 10. Available from: http://www.aoosung.com/edu/package/list.php?Index=271.25. Yoon IK, Roh SO, Park SY, Park SE, Song SK, Yu IY, et al. Research and development of sex education and sexual assault prevention materials. Seoul: Ministry of Education, Busan Metropolitan City Office of Education;2008.26. Demetriadis SN, Papadopoulos PM, Stamelos IG, Fischer F. The effect of scaffolding students'context-generating cognitive activity in technology-enhanced case-based learning. Comput Educ. 2008; 51(2):939–954. DOI: 10.1016/j.compedu.2007.09.012.27. Michaelsen LK, Parmelee DX, McMahon KK, Levine RE, Billings DM. Team-based learning for health professions education: A guide to using small groups for improving learning. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing;2007. p. 169–170.28. Choi IS, Kim JI. The effects of sexual violence myths, interpersonal violence acceptance and sex role related attitudes on aggressive sexual behavior. Korean J Woman Psychol. 2015; 20(3):277–300. DOI: 10.19158/kjwp.2015.09.20.3.277.29. Crosby RA, Hanson A, Rager K. The protective value of parental sex education: A clinic-based exploratory study of adolescent females. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2009; 22(3):189–192. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpag.2008.08.006.30. Somers CL, Anagurthi C. Parents'attitudes about adolescents' premarital sexual activity: The role of inter-parent consistency/inconsistency in sexual outcomes. Health Educ J. 2014; 73(5):545–553. DOI: 10.1177/0017896913506702.31. Wight D, Fullerton D. A review of interventions with parents to promote the sexual health of their children. J Adolesc Health. 2013; 52(1):4–27. DOI: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2012.04.014.32. Kim MW, Kang MJ. The effects of double-income couples' gender role attitudes and recognition of social support on parenting stress. J Korean Home Econ Assoc. 2011; 49(8):25–35. DOI: 10.6115/khea.2011.49.8.025.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Application of a Practical Nutrition Education Program, KHIDIKIDS, for the Improvement of Dietary Attitudes and Habits of Elementary Students
- The Effects of Sex Education on the Knowledge and Attitude toward Sex in Sixth Grade Elementary School Students
- Development and Evaluation of an Elementary School Nutrition Education Program to Prevent Breakfast Skipping
- Development and Evaluation of a Safety Education Program for Injury Prevention in Elementary School Students
- Influencing Factors on Sexual Knowledge among Elementary, Middle, and High School Students