Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Multicenter Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul 05505, Korea. radbaek@naver.com
- 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul 05505, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Thyroid Center, Daerim St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul 07442, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Thyroid Center, Daerim St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul 07442, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea.
- 7Department of Radiology, Sharing and Happiness Hospital, Busan 48101, Korea.
- 8Department of Radiology, Withsim Clinic, Seongnam 13590, Korea.
- 9Department of Radiology, Human Medical Imaging & Intervention Center, Seoul 06524, Korea.
- KMID: 2425123
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.167
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To assess the efficacy and safety of thyroid radiofrequency (RF) ablation for benign thyroid nodules by trained radiologists according to a unified protocol in a multi-center study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
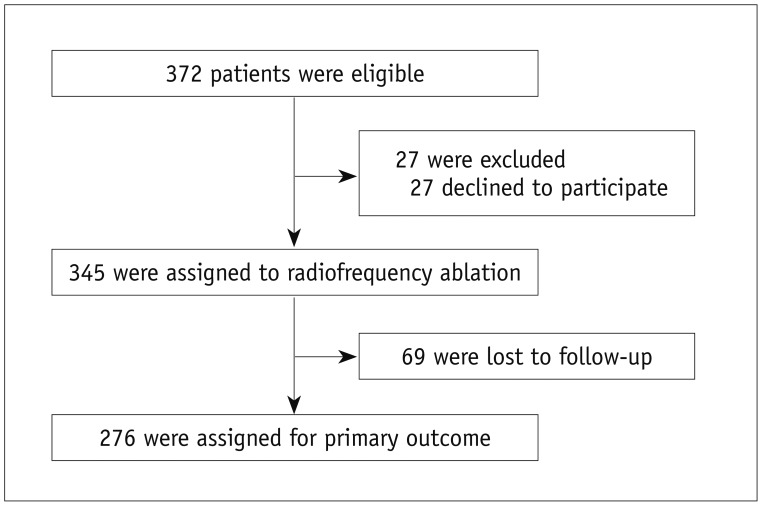
From 2010 to 2011, 345 nodules from 345 patients (M:F = 43:302; mean age ± SD = 46.0 ± 12.7 years, range = 15-79) who met eligibility criteria were enrolled from five institutions. At pre-ablation, the mean volume was 14.2 ± 13.2 mL (1.1-80.8 mL). For 12 months or longer after treatment, 276 lesions, consisting of 248 solid and 28 predominantly cystic nodules, were followed. All operators performed RF ablation with a cool-tip RF system and two standard techniques (a transisthmic approach and the moving-shot technique). Volume reduction at 12 months after RF ablation (the primary outcome), therapeutic success, improvement of symptoms as well as of cosmetic problems, and complications were evaluated. Multiple linear regression analysis was applied to identify factors that were independently predictive of volume reduction.
RESULTS
The mean volume reduction at 12 months was 80.3% (n = 276) and at the 24-, 36-, 48-, and 60-month follow-ups 84.3% (n = 198), 89.2% (n = 128), 91.9% (n = 57), and 95.3% (n = 6), respectively. Our therapeutic success was 97.8%. Both mean symptom and cosmetic scores showed significant improvements (p < 0.001). The rate of major complications was 1.0% (3/276). Solidity and applied energy were independent factors that predicted volume reduction.
CONCLUSION
Radiofrequency ablation performed by trained radiologists from multiple institutions using a unified protocol and similar devices was effective and safe for treating benign thyroid nodules.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 10 articles
-
Long-Term Results of Thermal Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Se Jin Cho, Jung Hwan Baek, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):339-350. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.339.Effectiveness of Injecting Cold 5% Dextrose into Patients with Nerve Damage Symptoms during Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation
Min Kyoung Lee, Jung Hwan Baek, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):407-415. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.407.RE: Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Multicenter Study
Qi Di
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(3):542-543. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.3.542.RE: Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Multicenter Study
Qi Di
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(3):542-543. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.3.542.Feasibility of Adjustable Electrodes for Radiofrequency Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules
Jiyeong Lee, Jung Hee Shin, Soo Yeon Hahn, Ko Woon Park, Ji Soo Choi
Korean J Radiol. 2020;21(3):377-383. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0724.2017 Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation Guideline: Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology
Ji-hoon Kim, Jung Hwan Baek, Hyun Kyung Lim, Hye Shin Ahn, Seon Mi Baek, Yoon Jung Choi, Young Jun Choi, Sae Rom Chung, Eun Ju Ha, Soo Yeon Hahn, So Lyung Jung, Dae Sik Kim, Soo Jin Kim, Yeo Koon Kim, Chang Yoon Lee, Jeong Hyun Lee, Kwang Hwi Lee, Young Hen Lee, Jeong Seon Park, Hyesun Park, Jung Hee Shin, Chong Hyun Suh, Jin Yong Sung, Jung Suk Sim, Inyoung Youn, Miyoung Choi, Dong Gyu Na,
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(4):632-655. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.632.US-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Efficacy and Safety in a Large Population
Hyun Kyung Lim, Se Jin Cho, Jung Hwan Baek, Kang Dae Lee, Chang Woo Son, Jung Min Son, Seon Mi Baek
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(12):1653-1661. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0192.Ultrasound (US)-Guided Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
Byung Seup Kim
J Surg Ultrasound. 2023;10(1):14-23. doi: 10.46268/jsu.2023.10.1.14.2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung, Yoon Young Cho, Yun Jae Chung, Won Bae Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Ho-Cheol Kang, Do Joon Park
Int J Thyroidol. 2023;16(1):1-31. doi: 10.11106/ijt.2023.16.1.1.Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules 2024
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Su Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung, Yoon Young Cho, Yun Jae Chung, Won Bae Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Ho-Cheol Kang, Do Joon Park
Int J Thyroidol. 2024;17(1):208-244. doi: 10.11106/ijt.2024.17.1.208.
Reference
-
1. Na DG, Lee JH, Jung SL, Kim JH, Sung JY, Shin JH, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules and recurrent thyroid cancers: consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:117–125. PMID: 22438678.
Article2. Garberoglio R, Aliberti C, Appetecchia M, Attard M, Boccuzzi G, Boraso F, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for thyroid nodules: which indications? The first Italian opinion statement. J Ultrasound. 2015; 18:423–430. PMID: 26550079.
Article3. Fuller CW, Nguyen SA, Lohia S, Gillespie MB. Radiofrequency ablation for treatment of benign thyroid nodules: systematic review. Laryngoscope. 2014; 124:346–353. PMID: 24122763.
Article4. Gharib H, Hegedüs L, Pacella CM, Baek JH, Papini E. Clinical review: Nonsurgical, image-guided, minimally invasive therapy for thyroid nodules. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98:3949–3957. PMID: 23956350.5. Jeong WK, Baek JH, Rhim H, Kim YS, Kwak MS, Jeong HJ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: safety and imaging follow-up in 236 patients. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:1244–1250. PMID: 18286289.
Article6. Spiezia S, Garberoglio R, Milone F, Ramundo V, Caiazzo C, Assanti AP, et al. Thyroid nodules and related symptoms are stably controlled two years after radiofrequency thermal ablation. Thyroid. 2009; 19:219–225. PMID: 19265492.
Article7. Deandrea M, Limone P, Basso E, Mormile A, Ragazzoni F, Gamarra E, et al. US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation for the treatment of solid benign hyperfunctioning or compressive thyroid nodules. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008; 34:784–791. PMID: 18207307.
Article8. Lee JH, Kim YS, Lee D, Choi H, Yoo H, Baek JH. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of benign thyroid nodules in patients with incompletely resolved clinical problems after ethanol ablation (EA). World J Surg. 2010; 34:1488–1493. PMID: 20376445.
Article9. Faggiano A, Ramundo V, Assanti AP, Fonderico F, Macchia PE, Misso C, et al. Thyroid nodules treated with percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation: a comparative study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:4439–4445. PMID: 23019349.
Article10. Lim HK, Lee JH, Ha EJ, Sung JY, Kim JK, Baek JH. Radiofrequency ablation of benign non-functioning thyroid nodules: 4-year follow-up results for 111 patients. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:1044–1049. PMID: 23096937.
Article11. Baek JH, Lee JH, Valcavi R, Pacella CM, Rhim H, Na DG. Thermal ablation for benign thyroid nodules: radiofrequency and laser. Korean J Radiol. 2011; 12:525–540. PMID: 21927553.
Article12. Huh JY, Baek JH, Choi H, Kim JK, Lee JH. Symptomatic benign thyroid nodules: efficacy of additional radiofrequency ablation treatment session--prospective randomized study. Radiology. 2012; 263:909–916. PMID: 22438360.
Article13. Deandrea M, Sung JY, Limone P, Mormile A, Garino F, Ragazzoni F, et al. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation versus observation for nonfunctioning benign thyroid nodules: a randomized controlled international collaborative trial. Thyroid. 2015; 25:890–896. PMID: 26061686.
Article14. Cesareo R, Pasqualini V, Simeoni C, Sacchi M, Saralli E, Campagna G, et al. Prospective study of effectiveness of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation versus control group in patients affected by benign thyroid nodules. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:460–466. PMID: 25387256.
Article15. Turtulici G, Orlandi D, Corazza A, Sartoris R, Derchi LE, Silvestri E, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules assisted by a virtual needle tracking system. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014; 40:1447–1452. PMID: 24785443.
Article16. Ugurlu MU, Uprak K, Akpinar IN, Attaallah W, Yegen C, Gulluoglu BM. Radiofrequency ablation of benign symptomatic thyroid nodules: prospective safety and efficacy study. World J Surg. 2015; 39:961–968. PMID: 25446486.
Article17. Baek JH, Lee JH, Sung JY, Bae JI, Kim KT, Sim J, et al. Complications encountered in the treatment of benign thyroid nodules with US-guided radiofrequency ablation: a multicenter study. Radiology. 2012; 262:335–342. PMID: 21998044.
Article18. Sung JY, Baek JH, Jung SL, Kim JH, Kim KS, Lee D, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for autonomously functioning thyroid nodules: a multicenter study. Thyroid. 2015; 25:112–117. PMID: 25320840.
Article19. Lee YH, Baek JH, Jung SL, Kwak JY, Kim JH, Shin JH. Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology (KSThR). Korean Society of Radiology. Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of thyroid nodules: A Consensus Statement by the Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:391–401. PMID: 25741201.
Article20. Sung JY, Baek JH, Kim KS, Lee D, Yoo H, Kim JK, et al. Single-session treatment of benign cystic thyroid nodules with ethanol versus radiofrequency ablation: a prospective randomized study. Radiology. 2013; 269:293–300. PMID: 23616630.
Article21. Ha EJ, Baek JH, Lee JH. Moving-shot versus fixed electrode techniques for radiofrequency ablation: comparison in an ex-vivo bovine liver tissue model. Korean J Radiol. 2014; 15:836–843. PMID: 25469097.22. Burke DR, Lewis CA, Cardella JF, Citron SJ, Drooz AT, Haskal ZJ, et al. Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography and biliary drainage. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14(9 Pt 2):S243–S246. PMID: 14514826.
Article23. Baek JH, Kim YS, Lee D, Huh JY, Lee JH. Benign predominantly solid thyroid nodules: prospective study of efficacy of sonographically guided radiofrequency ablation versus control condition. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:1137–1142. PMID: 20308523.
Article24. Baek JH, Ha EJ, Choi YJ, Sung JY, Kim JK, Shong YK. Radiofrequency versus ethanol ablation for treating predominantly cystic thyroid nodules: a randomized clinical trial. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:1332–1340. PMID: 26576124.
Article25. Wong KP, Lang BH. Use of radiofrequency ablation in benign thyroid nodules: a literature review and updates. Int J Endocrinol. 2013; 2013:428363. PMID: 24298282.
Article26. Ha EJ, Baek JH. Advances in nonsurgical treatment of benign thyroid nodules. Future Oncol. 2014; 10:1399–1405. PMID: 25052750.
Article27. Ha EJ, Baek JH, Kim KW, Pyo J, Lee JH, Baek SH, et al. Comparative efficacy of radiofrequency and laser ablation for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules: systematic review including traditional pooling and bayesian network meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 100:1903–1911. PMID: 25695887.
Article28. Baek JH, Moon WJ, Kim YS, Lee JH, Lee D. Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of autonomously functioning thyroid nodules. World J Surg. 2009; 33:1971–1977. PMID: 19575141.
Article29. Papini E, Rago T, Gambelunghe G, Valcavi R, Bizzarri G, Vitti P, et al. Long-term efficacy of ultrasound-guided laser ablation for benign solid thyroid nodules. Results of a three-year multicenter prospective randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:3653–3659. PMID: 25050903.
Article30. Kim YS, Rhim H, Tae K, Park DW, Kim ST. Radiofrequency ablation of benign cold thyroid nodules: initial clinical experience. Thyroid. 2006; 16:361–367. PMID: 16646682.
Article31. Jang SW, Baek JH, Kim JK, Sung JY, Choi H, Lim HK, et al. How to manage the patients with unsatisfactory results after ethanol ablation for thyroid nodules: role of radiofrequency ablation. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:905–910. PMID: 21388767.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- RE: Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Multicenter Study
- Effective and Safe Application of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules
- Non-surgical, Image-guided Management of Benign Thyroid Nodules
- Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Nodules of the Thyroid Gland
- Ultrasound (US)-Guided Ablation of Thyroid Nodules