Cancer Res Treat.
2018 Oct;50(4):1149-1163. 10.4143/crt.2017.194.
Effect of Adjuvant Chemotherapy on Stage II Colon Cancer: Analysis of Korean National Data
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. cmcgslee@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- 3Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2424788
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2017.194
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Debates exist regarding the effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. This study aimed to investigate the current status of adjuvant chemotherapy and its impact on survival for Korean stage II colon cancer patients by analyzing the National Quality Assessment data.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 7,880 patientswho underwent curative resection for stage II colon adenocarcinoma between January 2011 andDecember 2014 in Koreawere selected randomly as evaluation subjects for the quality assessment. The factors that influenced overall survival were identified. The high-risk group was defined as having at least one of the following: perforation/obstruction, lymph node harvest less than 12, lymphovascular/perineural invasion, positive resection margin, poor differentiation, or pathologic T4 stage.
RESULTS
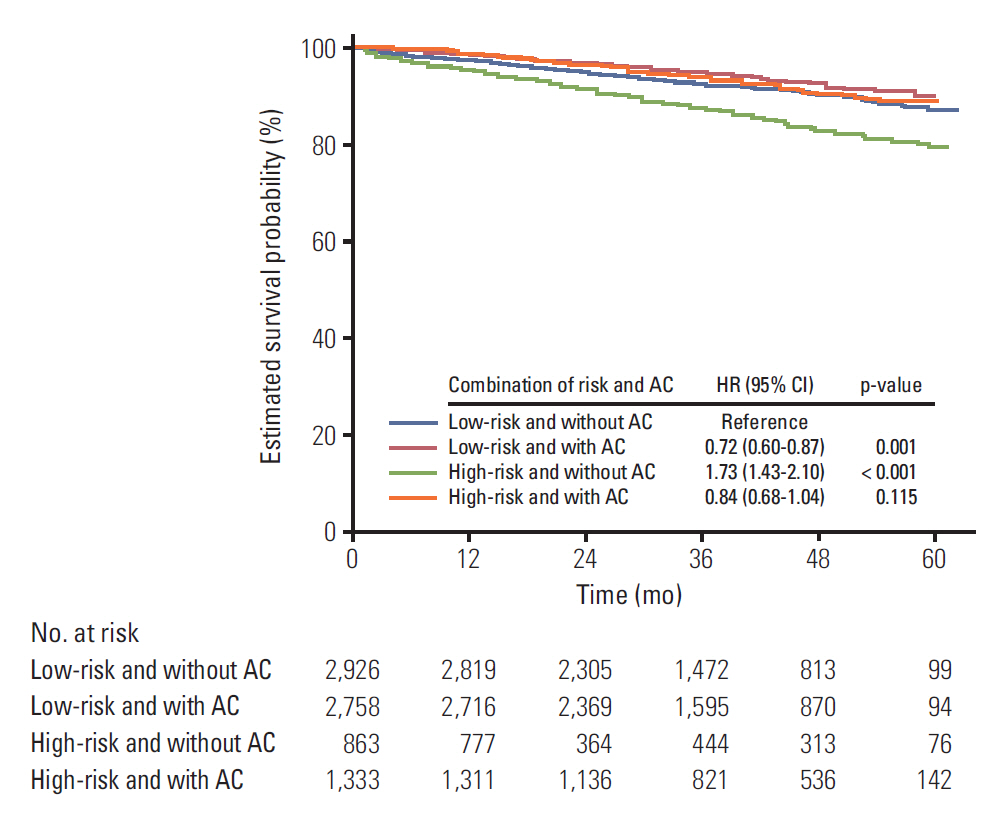
The median follow-up period was 38 months (range, 1 to 63 months). Chemotherapy was a favorable prognostic factor for either the high- (hazard ratio [HR], 0.76; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.38 to 0.59; p < 0.001) or low-risk group (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.61 to 0.89; p=0.002) in multivariate analysis. This was also the case in patients over 70 years of age. The hazard ratio was significantly increased as the number of involved risk factors was increased in patients who didn't receive chemotherapy. Adding oxaliplatin showed no difference in survival (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, 0.91 to 2.03; p=0.132).
CONCLUSION
Adjuvant chemotherapy can be recommended for stage II colon cancer patients, but the addition of oxaliplatin to the regimen must be selective.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wolmark N, Rockette H, Fisher B, Wickerham DL, Redmond C, Fisher ER, et al. The benefit of leucovorin-modulated fluorouracil as postoperative adjuvant therapy for primary colon cancer: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project protocol C-03. J Clin Oncol. 1993; 11:1879–87.
Article2. Quasar Collaborative Group, Gray R, Barnwell J, McConkey C, Hills RK, Williams NS, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy versus observation in patients with colorectal cancer: a randomised study. Lancet. 2007; 370:2020–9.3. Wilkinson NW, Yothers G, Lopa S, Costantino JP, Petrelli NJ, Wolmark N. Long-term survival results of surgery alone versus surgery plus 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin for stage II and stage III colon cancer: pooled analysis of NSABP C-01 through C-05. A baseline from which to compare modern adjuvant trials. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:959–66.
Article4. Efficacy of adjuvant fluorouracil and folinic acid in B2 colon cancer. International Multicentre Pooled Analysis of B2 Colon Cancer Trials (IMPACT B2) Investigators. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:1356–63.5. Buyse M, Piedbois P. Should Dukes' B patients receive adjuvant therapy? A statistical perspective. Semin Oncol. 2001; 28(1 Suppl 1):20–4.
Article6. Casadaban L, Rauscher G, Aklilu M, Villenes D, Freels S, Maker AV. Adjuvant chemotherapy is associated with improved survival in patients with stage II colon cancer. Cancer. 2016; 122:3277–87.
Article7. Booth CM, Nanji S, Wei X, Peng Y, Biagi JJ, Hanna TP, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer: practice patterns and effectiveness in the general population. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2017; 29:e29–38.
Article8. Breugom AJ, Bastiaannet E, Boelens PG, Iversen LH, Martling A, Johansson R, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy and relative survival of patients with stage II colon cancer: A EURECCA international comparison between the Netherlands, Denmark, Sweden, England, Ireland, Belgium, and Lithuania. Eur J Cancer. 2016; 63:110–7.9. Verhoeff SR, van Erning FN, Lemmens VE, de Wilt JH, Pruijt JF. Adjuvant chemotherapy is not associated with improved survival for all high-risk factors in stage II colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 2016; 139:187–93.
Article10. Kumar A, Kennecke HF, Renouf DJ, Lim HJ, Gill S, Woods R, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy use and outcomes of patients with high-risk versus low-risk stage II colon cancer. Cancer. 2015; 121:527–34.
Article11. Lewis C, Xun P, He K. Effects of adjuvant chemotherapy on recurrence, survival, and quality of life in stage II colon cancer patients: a 24-month follow-up. Support Care Cancer. 2016; 24:1463–71.
Article12. Jee SH, Moon SM, Shin US, Yang HM, Hwang DY. Effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy with 5-FU/leucovorin and prognosis in stage II colon cancer. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2011; 27:322–8.
Article13. Sato H, Maeda K, Sugihara K, Mochizuki H, Kotake K, Teramoto T, et al. High-risk stage II colon cancer after curative resection. J Surg Oncol. 2011; 104:45–52.
Article14. Abraham A, Habermann EB, Rothenberger DA, Kwaan M, Weinberg AD, Parsons HM, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III colon cancer in the oldest old: results beyond clinical guidelines. Cancer. 2013; 119:395–403.15. Sanoff HK, Carpenter WR, Sturmer T, Goldberg RM, Martin CF, Fine JP, et al. Effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on survival of patients with stage III colon cancer diagnosed after age 75 years. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:2624–34.
Article16. Hines RB, Bimali M, Johnson AM, Bayakly AR, Collins TC. Prevalence and survival benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in stage III colon cancer patients: comparison of overall and age-stratified results by multivariable modeling and propensity score methodology in a population-based cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016; 44:77–83.
Article17. Hermosillo-Rodriguez J, Anaya DA, Sada Y, Walder A, Amspoker AB, Berger DH, et al. The effect of age and comorbidity on patient-centered health outcomes in patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. J Geriatr Oncol. 2013; 4:99–106.
Article18. Efficacy of adjuvant fluorouracil and folinic acid in colon cancer. International Multicentre Pooled Analysis of Colon Cancer Trials (IMPACT) investigators. Lancet. 1995; 345:939–44.19. O'Connell MJ, Mailliard JA, Kahn MJ, Macdonald JS, Haller DG, Mayer RJ, et al. Controlled trial of fluorouracil and low-dose leucovorin given for 6 months as postoperative adjuvant therapy for colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1997; 15:246–50.20. Shah MA, Renfro LA, Allegra CJ, Andre T, de Gramont A, Schmoll HJ, et al. Impact of patient factors on recurrence risk and time dependency of oxaliplatin benefit in patients with colon cancer: analysis from modern-era adjuvant studies in the Adjuvant Colon Cancer End Points (ACCENT) database. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:843–53.
Article21. Andre T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, et al. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:3109–16.22. Kuebler JP, Wieand HS, O'Connell MJ, Smith RE, Colangelo LH, Yothers G, et al. Oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: results from NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:2198–204.
Article23. Gill S, Loprinzi CL, Sargent DJ, Thome SD, Alberts SR, Haller DG, et al. Pooled analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: who benefits and by how much? J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:1797–806.
Article24. Tofthagen C. Surviving chemotherapy for colon cancer and living with the consequences. J Palliat Med. 2010; 13:1389–91.
Article25. Watson MM, Soreide K. The prognostic yield of biomarkers harvested in chemotherapy-naive stage II colon cancer: can we separate the wheat from the chaff? Mol Med. 2016; 22:271–3.
Article26. Smith JJ, Tilney HS, Heriot AG, Darzi AW, Forbes H, Thompson MR, et al. Social deprivation and outcomes in colorectal cancer. Br J Surg. 2006; 93:1123–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The efficacy of chemotherapy in the patients with stage II colon cancer associated with number of high-risk factors
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Colon Cancer
- Oncologic outcomes of early adjuvant chemotherapy initiation in patients with stage III colon cancer
- Adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with stage II colon cancer
- Effectiveness of oral fluoropyrimidine monotherapy as adjuvant chemotherapy for high-risk stage II colon cancer