Korean J Neurotrauma.
2018 Oct;14(2):150-154. 10.13004/kjnt.2018.14.2.150.
Endovascular Treatment Following Gauze Packing for the Control of Massive Bleeding from Traumatic Transverse Sinus Lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery and Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. csfdiver@naver.com
- KMID: 2424330
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2018.14.2.150
Abstract
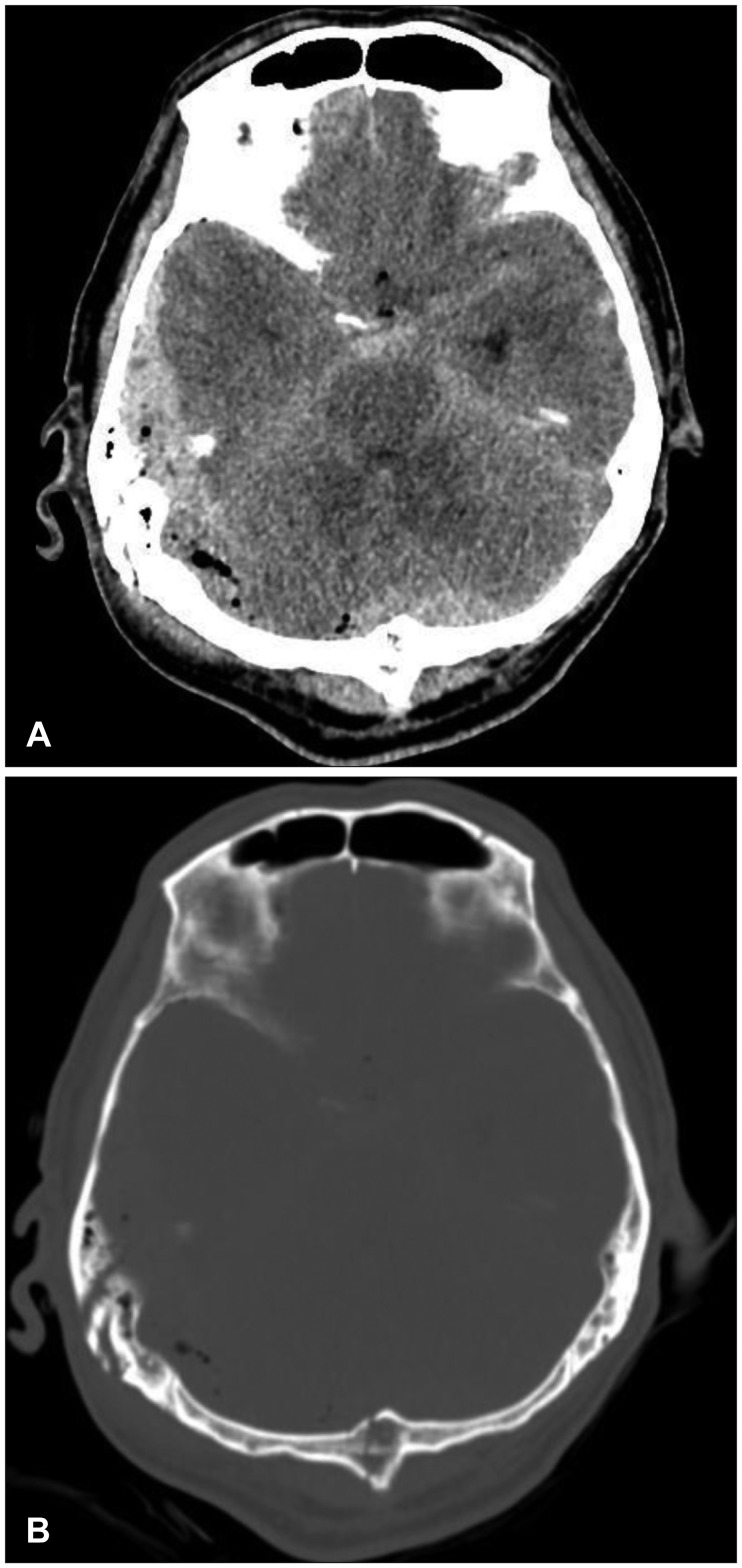
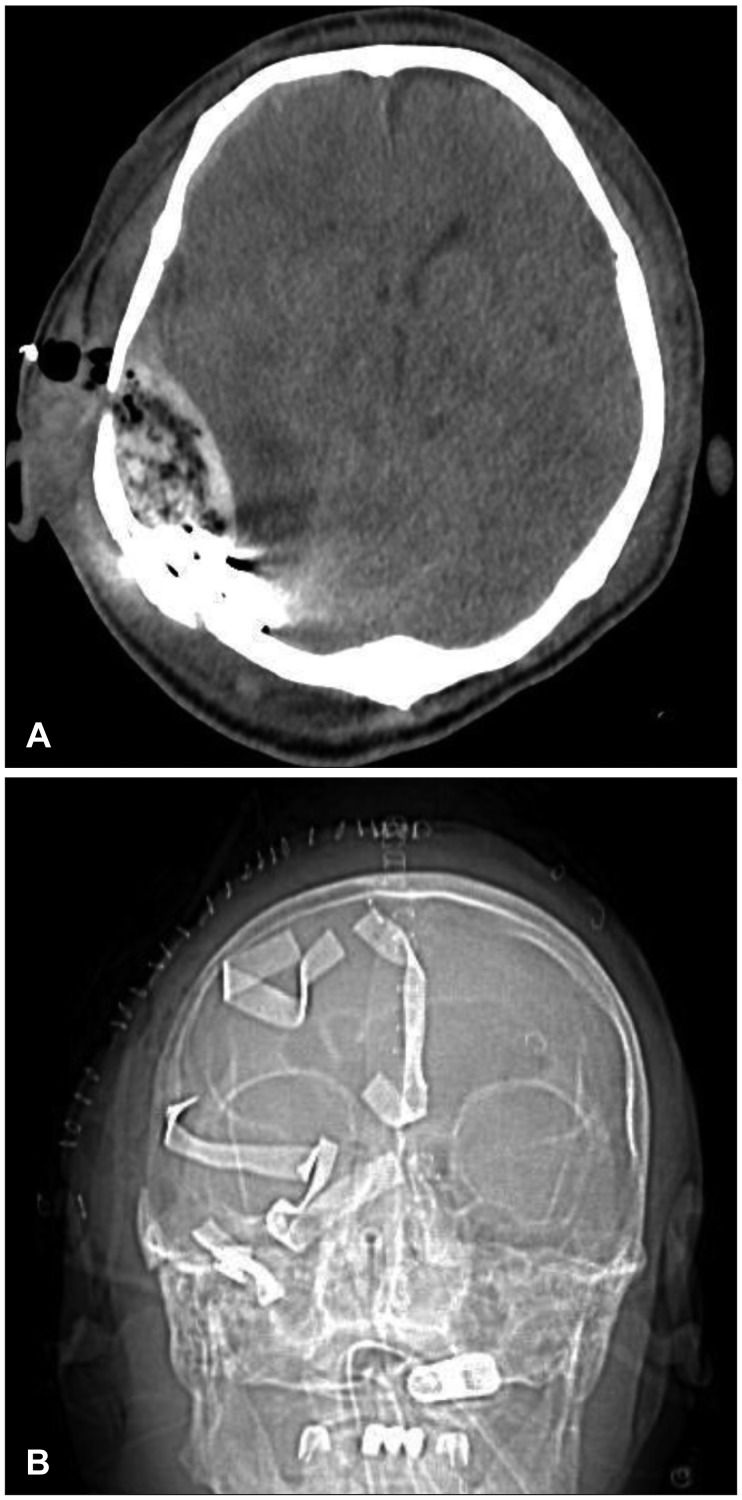
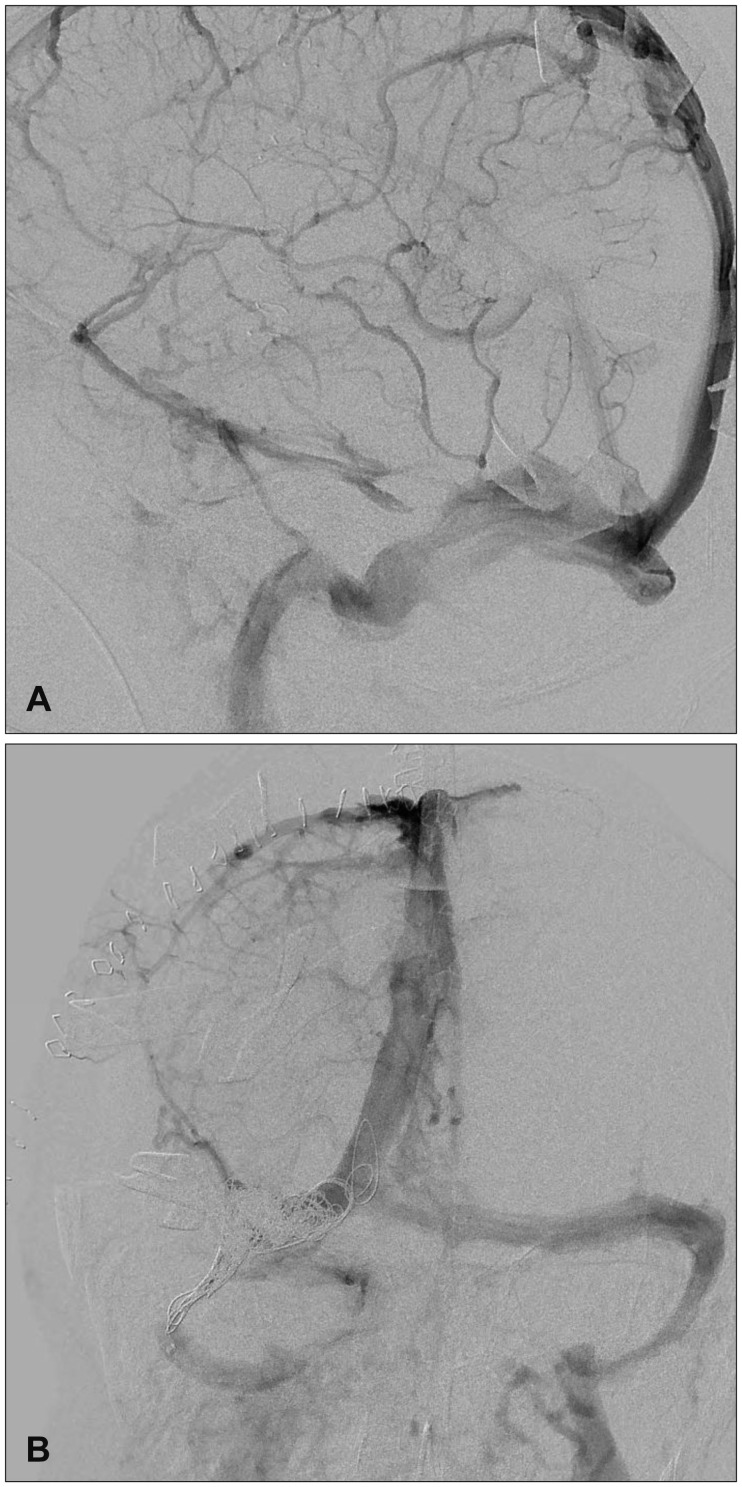
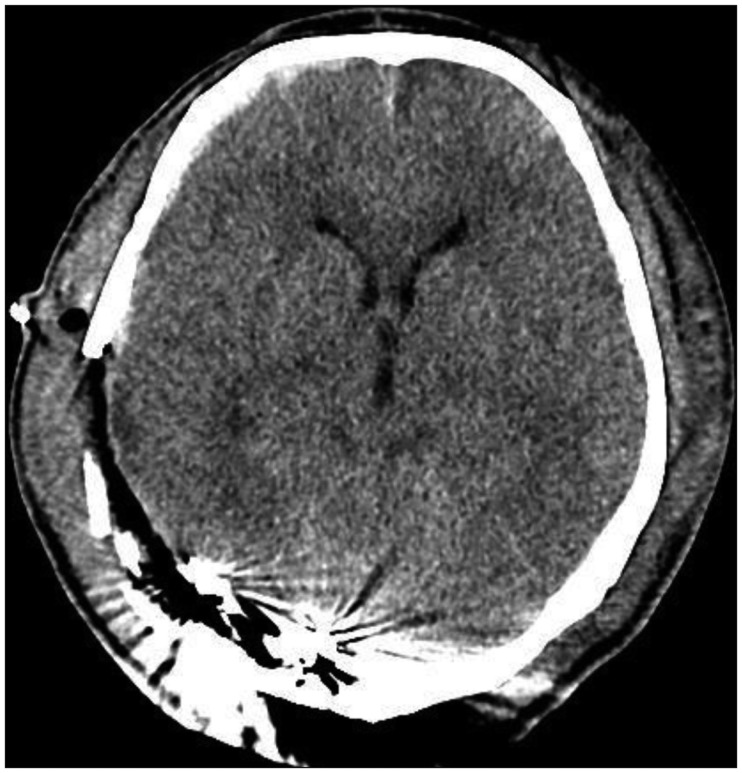
- Posterior fossa epidural hematoma (EDH) is uncommon, but the related clinical deterioration can occur suddenly. Accompanying venous sinus injury and lacerations are associated with 40% to 80% mortality. The authors present one clinical case of a patient with posterior fossa EDH from transverse sinus bleeding. A 57-year-old male was injured after falling while working. He was taken to the hospital, where computed tomography scans of his brain revealed a right posterior temporal and cerebellar EDH with a right temporo-occipital fracture. He underwent a right parieto-occipital craniotomy, incorporating the fracture line. Longitudinal laceration of the right transverse sinus extending to the sigmoid sinus with profuse bleeding was identified. Four gauzes were inserted in the epidural space for tamponade of the injured sinus. Conventional angiography and coil embolization for the injured sinus were immediately performed. Subsequently, the patient was transferred to the operating room, wherein staff members removed the gauzes and remnant hematoma. Based on this experience, the authors recommend that for posterior fossa EDH from transverse sinus bleeding, bleeding control should be performed by gauze packing and endovascular treatment.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Gauze Packing for the Massive Venous Sinus Bleeding in a Patient with Acute Subdural Hematoma of Posterior Fossa
Tae Ki Yang
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2019;15(2):164-169. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2019.15.e30.
Reference
-
1. Alvis-Miranda HR, Milena Castellar-Leones S, Alcala-Cerra G, Rafael Moscote-Salazar L. Cerebral sinus venous thrombosis. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013; 4:427–438. PMID: 24347950.
Article2. Bor-Seng-Shu E, Aguiar PH, de Almeida Leme RJ, Mandel M, Andrade AF, Marino R Jr. Epidural hematomas of the posterior cranial fossa. Neurosurg Focus. 2004; 16:ECP1.
Article3. Bozbuğa M, Izgi N, Polat G, Gürel I. Posterior fossa epidural hematomas: observations on a series of 73 cases. Neurosurg Rev. 1999; 22:34–40. PMID: 10348205.
Article4. Braff SB, Khoshyomn S, D'Angelo WF, Tranmer BI, Wilson JT. Traumatic transverse sinus laceration. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2004; 40:143–144. PMID: 15367807.
Article5. Chee CP, Habib ZA. Hypodense bubbles in acute extradural haematomas following venous sinus tear. A CT scan appearance. Neuroradiology. 1991; 33:152–154. PMID: 2046901.6. Cordobés F, Lobato RD, Rivas JJ, Muñoz MJ, Chillon D, Portillo JM, et al. Observations on 82 patients with extradural hematoma. Comparison of results before and after the advent of computerized tomography. J Neurosurg. 1981; 54:179–186. PMID: 7452331.7. Frank E, Berger TS, Tew JM Jr. Bilateral epidural hematomas. Surg Neurol. 1982; 17:218–222. PMID: 7079941.
Article8. Freeman JL, Winston KR, Byers JT, Beauchamp K. Damage-control neurosurgery: Packing to halt relentless intracranial bleeding. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015; 79:865–869. PMID: 26496114.9. Gallagher JP, Browder EJ. Extradural hematoma. Experience with 167 patients. J Neurosurg. 1968; 29:1–12. PMID: 5674087.10. Gazzeri R, Galarza M, Fiore C, Callovini G, Alfieri A. Use of tissue-glue-coated collagen sponge (TachoSil) to repair minor cerebral dural venous sinus lacerations: technical note. Neurosurgery. 2015; 11(Suppl 2):32–36. PMID: 25584959.11. Jang JW, Lee JK, Seo BR, Kim SH. Traumatic epidural haematoma of the posterior cranial fossa. Br J Neurosurg. 2011; 25:55–61. PMID: 20925589.
Article12. Kumar J, Prakash A, Harsh V, Kumar A. Vertex extradural hematoma: A diagnostic dilemma. Asian J Neurosurg. 2017; 12:718–720. PMID: 29114292.
Article13. Leitgeb J, Mauritz W, Brazinova A, Majdan M, Wilbacher I. Outcome after severe brain trauma associated with epidural hematoma. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133:199–207. PMID: 23161150.
Article14. Li LM, Kolias AG, Guilfoyle MR, Timofeev I, Corteen EA, Pickard JD, et al. Outcome following evacuation of acute subdural haematomas: a comparison of craniotomy with decompressive craniectomy. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 154:1555–1561. PMID: 22752713.
Article15. Meier U, Gärtner F, Knopf W, Klötzer R, Wolf O. The traumatic dural sinus injury--a clinical study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1992; 119:91–93. PMID: 1481760.16. Schöggl A, Reddy M, Saringer W, Matula C. An unusual management of an open compound depressed skull fracture with venous sinus involvement. A case report. J Neurosurg Sci. 1999; 43:311–314. PMID: 10864395.17. Siddiqui FM, Kamal AK. Complications associated with cerebral venous thrombosis. J Pak Med Assoc. 2006; 56:547–551. PMID: 17183989.18. Winston KR, Byers JT, Freeman J, Beauchamp K. Packing to tamponade severe intracranial hemorrhage in pediatric patients. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2015; 50:63–67. PMID: 25824532.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gauze Packing for the Massive Venous Sinus Bleeding in a Patient with Acute Subdural Hematoma of Posterior Fossa
- Retroperitoneal Gauze Packing with Vacuum-Associated Closure for Pelvic Fracture with Hemodynamic Instability
- Transanal gauze packing to manage massive presacral bleeding secondary to prescral abscess caused by rectal anastomotic leakage: a novel approach
- Intra-Abdominal Gauze Packing for Uncontrolled Hemorrhage in Non-Trauma Patients
- An unstable patient with a large sucking chest wound managed with gauze packing for preventing tension and bleeding control before surgery in Korea: a case report