Hip Pelvis.
2017 Dec;29(4):211-222. 10.5371/hp.2017.29.4.211.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Joint Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ewha Womans University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea.
- 5Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 6Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 7Department of Orthopedic Surgery, International St. Mary's Hospital, Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 8Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, St. Vincent's Hospital, Suwon, Korea. osong97@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2424246
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2017.29.4.211
Abstract
- Arthritis damages the cartilage within joints, resulting in degenerative changes, including loss of function and joint instability. Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the spine and bone-to-tendon attachment area within the sacroiliac joint leading to back pain and progressive spinal stiffness. In the final stages, AS causes hyperkyphosis-a condition closely tied to the human leukocyte antigen-B27 gene. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease characterized by the simultaneous inflammation of the synovium of multiple joints, leading to joint damage (e.g., destruction, deformation and disability). In the past, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARDs) have been used for the treatment of these autoimmune diseases, but biologic DMARDs have recently been introduced with excellent results. Gout is a chronic inflammatory disease that causes an alteration of joints resulting in severe pain. Specifically, gout is associated with an accumulation of uric acid within the body resulting from dysregulated purine metabolism, causing recurrent paroxysmal inflammation in the joints. Allopurinol and febuxostat are the primary treatment options for individuals with gout. It is necessary to have an accurate understanding of the pathogenesis, pathological ecology and treatment of AS, rheumatoid arthritis, and gouty arthritis, which are the representative diseases that may cause inflammatory arthritis.
MeSH Terms
-
Allopurinol
Antirheumatic Agents
Arthritis
Arthritis, Gouty
Arthritis, Reactive
Arthritis, Rheumatoid
Autoimmune Diseases
Back Pain
Cartilage
Diagnosis*
Ecology
Febuxostat
Gout
Humans
Inflammation
Joint Diseases*
Joint Instability
Joints*
Leukocytes
Metabolism
Sacroiliac Joint
Spine
Spondylitis, Ankylosing
Synovial Membrane
Uric Acid
Allopurinol
Antirheumatic Agents
Febuxostat
Uric Acid
Figure
Reference
-
1. Raychaudhuri SP, Deodhar A. The classification and diagnostic criteria of ankylosing spondylitis. J Autoimmun. 2014; 48-49:128–133.
Article2. Rostom S, Dougados M, Gossec L. New tools for diagnosing spondyloarthropathy. Joint Bone Spine. 2010; 77:108–114.
Article3. Calin A, Porta J, Fries JF, Schurman DJ. Clinical history as a screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. JAMA. 1977; 237:2613–2614.
Article4. Chen HA, Chen CH, Liao HT, et al. Factors associated with radiographic spinal involvement and hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 40:552–558.
Article5. Vander Cruyssen B, Muñoz-Gomariz E, Font P, et al. Hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: epidemiology and risk factors associated with hip replacement surgery. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49:73–81.
Article6. Zhao J, Zheng W, Zhang C, Li J, Liu D, Xu W. Radiographic hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: factors associated with severe hip diseases. J Rheumatol. 2015; 42:106–110.
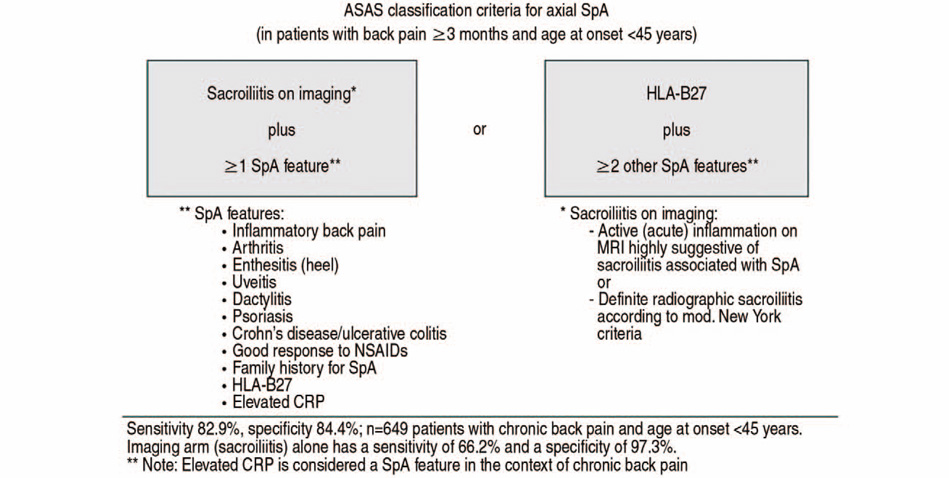
Article7. van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 27:361–368.8. Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009; 68:777–783.
Article9. Zochling J, van der Heijde D, Burgos-Vargas R, et al. ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006; 65:442–452.
Article10. Braun J, van den Berg R, Baraliakos X, et al. 2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:896–904.11. O'Dwyer T, O'Shea F, Wilson F. Exercise therapy for spondyloarthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2014; 34:887–902.12. Millner JR, Barron JS, Beinke KM, et al. Exercise for ankylosing spondylitis: An evidence-based consensus statement. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016; 45:411–427.
Article13. Hsieh LF, Wei JC, Lee HY, Chuang CC, Jiang JS, Chang KC. Aerobic capacity and its correlates in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016; 19:490–499.
Article14. van der Esch M, van't Hul AJ, Heijmans M, Dekker J. Respiratory muscle performance as a possible determinant of exercise capacity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Aust J Physiother. 2004; 50:41–45.
Article15. Smidt N, de Vet HC, Bouter LM, et al. Effectiveness of exercise therapy: a best-evidence summary of systematic reviews. Aust J Physiother. 2005; 51:71–85.
Article16. Saracoglu I, Kurt G, Okur EO, et al. The effectiveness of specific exercise types on cardiopulmonary functions in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2017; 37:409–421.
Article17. Altan L, Korkmaz N, Dizdar M, Yurtkuran M. Effect of Pilates training on people with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32:2093–2099.
Article18. Karapolat H, Eyigor S, Zoghi M, Akkoc Y, Kirazli Y, Keser G. Are swimming or aerobic exercise better than conventional exercise in ankylosing spondylitis patients? A randomized controlled study. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2009; 45:449–457.19. Lee EN, Kim YH, Chung WT, Lee MS. Tai chi for disease activity and flexibility in patients with ankylosing spondylitis--a controlled clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2008; 5:457–462.
Article20. Jenkinson TR, Mallorie PA, Whitelock HC, Kennedy LG, Garrett SL, Calin A. Defining spinal mobility in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The Bath AS Metrology Index. J Rheumatol. 1994; 21:1694–1698.21. Dundar U, Solak O, Toktas H, et al. Effect of aquatic exercise on ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized controlled trial. Rheumatol Int. 2014; 34:1505–1511.
Article22. Karagülle M, Kardes¸ S, Karagülle MZ. Real-life effectiveness of spa therapy in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: a retrospective study of 819 patients. Int J Biometeorol. 2017; 61:1945–1956.
Article23. Şilte Karamanlioğlu D, Aktas I, Ozkan FU, Kaysin M, Girgin N. Effectiveness of ultrasound treatment applied with exercise therapy on patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Rheumatol Int. 2016; 36:653–661.
Article24. Dagfinrud H, Kvien TK, Hagen KB. The Cochrane review of physiotherapy interventions for ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 2005; 32:1899–1906.25. van der Heijde D, Ramiro S, Landewé R, et al. 2016 update of the ASAS-EULAR management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76:978–991.
Article26. Ward MM, Deodhar A, Akl EA, et al. American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network 2015 recommendations for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016; 68:151–166.
Article27. Kim YC, Moon SW. Etanercept treatment in ankylosing spondylitis hip lesions. Hip Pelvis. 2013; 25:135–140.
Article28. Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31:315–324.
Article29. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:2569–2581.
Article30. Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, et al. 2015 American college of rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68:1–26.
Article31. Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017; 76:960–977.32. Choi HK, Mount DB, Reginato AM. American College of Physicians. American Physiological Society. Pathogenesis of gout. Ann Intern Med. 2005; 143:499–516.
Article33. Zhu Y, Pandya BJ, Choi HK. Prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia in the US general population: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2008. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:3136–3141.
Article34. Taylor WJ, Fransen J, Dalbeth N, et al. Diagnostic arthrocentesis for suspicion of gout is safe and well tolerated. J Rheumatol. 2016; 43:150–153.
Article35. Neogi T, Jansen TL, Dalbeth N, et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015; 74:1789–1798.
Article36. Campion EW, Glynn RJ, DeLabry LO. Asymptomatic hyperuricemia. Risks and consequences in the Normative Aging Study. Am J Med. 1987; 82:421–426.
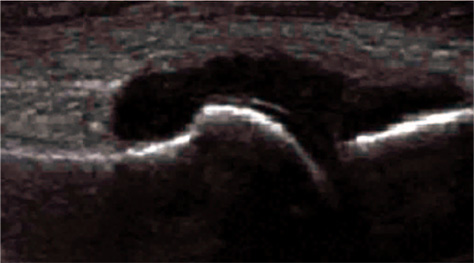
Article37. Kim HS, Kim HR. Diagnostic imaging of gouty arthritis. Korean J Med. 2016; 91:32–36.
Article38. Rettenbacher T, Ennemoser S, Weirich H, et al. Diagnostic imaging of gout: comparison of high-resolution US versus conventional X-ray. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:621–630.
Article39. Kang MH, Moon KW, Jeon YH, Cho SW. Sonography of the first metatarsophalangeal joint and sonographically guided intraarticular injection of corticosteroid in acute gout attack. J Clin Ultrasound. 2015; 43:179–186.
Article40. Lee EB. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of gout. Korean J Med. 2011; 80:255–259.41. Arellano F, Sacristán JA. Allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome: a review. Ann Pharmacother. 1993; 27:337–343.
Article42. Khanna D, Fitzgerald JD, Khanna PP, et al. 2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for management of gout. Part 1: systematic nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapeutic approaches to hyperuricemia. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:1431–1446.
Article