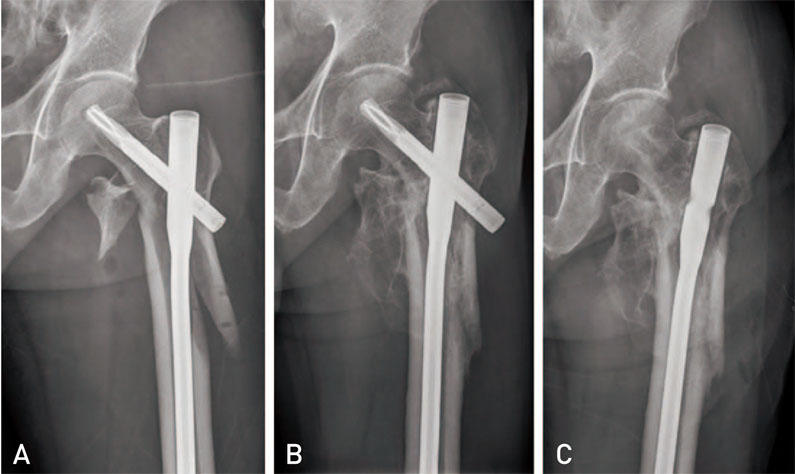
Hip Pelvis.
2017 Jun;29(2):113-119. 10.5371/hp.2017.29.2.113.
Clinical Results of Complex Subtrochanteric Femoral Fractures with Long Cephalomedullary Hip Nail
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon, Korea. yougunwon@gmail.com, ywon@bidmc.harvard.edu
- 2Harvard Medical School Orthopedic Trauma Initiative, Boston, MA, USA.
- 3Changwon Fatima Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2424239
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2017.29.2.113
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Good results of the cephalomedullary nails have been reported in proximal femoral fractures recently. Based on length of nails and shape of screws fixed in a femoral head for proximal fragment fixation, the proper nail length was in dispute. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiological results of a long cephalomedullary hip nail for the treatment of comminuted subtrochanteric femoral fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-one consecutive patients with severe subtrochanteric femoral fractures who had undergone intramedullary fixation using long-PFNA II between March 2010 and March 2013 were followed-up for over 12 months. Their mean age was 64.8 years old (range, 43-85 years). Sixteen of 22 cases were high energy trauma. According to Seinsheimer's classification, 5 cases were type IV and 16 cases were type V. For radiological assessment, time to union, change of neck-shaft angle, sliding length, tip-apex distance (TAD) and leg length discrepancy (LLD) were measured. For clinical evaluation, a modified Koval index was investigated.
RESULTS
Mean operation time was 96 minutes. An average decrease of neck-shaft angle was 4.5°. The average sliding length of the helical blade was 4.2 mm. Average LLD was 3.0 mm, and TAD was 23.0 mm. Mean modified Koval index score at final follow-up was 4.6 points. All the 21 subtrochanteric fractures healed uneventfully on an average of 24.2 weeks (range, 18-30 weeks).
CONCLUSION
Long cephalomedullary hip nail provides excellent clinical and radiological outcomes in the comminuted subtrochanteric fracture.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Min BW, Song KS, Bae KC, Cho CH, Son ES, Lee KJ. Nonsurgical treatment strategies after osteoporotic hip fractures. Hip Pelvis. 2015; 27:9–16.
Article2. Bedi A, Toan Le T. Subtrochanteric femur fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004; 35:473–483.
Article3. Fielding JW, Cochran GV, Zickel RE. Biomechanical characteristics and surgical management of subtrochanteric fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1974; 5:629–650.
Article4. Froimson AI. Treatment of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970; 131:465–472.5. Saini P, Kumar R, Shekhawat V, Joshi N, Bansal M, Kumar S. Biological fixation of comminuted subtrochanteric fractures with proximal femur locking compression plate. Injury. 2013; 44:226–231.
Article6. Kim JW, Chang JS, Lee H, Bae JY, Kim JJ. Clinical results of femoral subtrochanteric fractures. J Korean Hip Soc. 2010; 22:222–226.
Article7. Hotz TK, Zellweger R, Kach KP. Minimal invasive treatment of proximal femur fractures with the long gamma nail: indication, technique, results. J Trauma. 1999; 47:942–945.
Article8. Ruff ME, Lubbers LM. Treatment of subtrochanteric fractures with a sliding screw-plate device. J Trauma. 1986; 26:75–80.
Article9. Lee JY, Lee SY. Treatment of the proximal femoral extracapsular fracture with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): Comparison with proximal femoral nail (PFN). J Korean Hip Soc. 2007; 19:183–189.
Article10. Borens O, Wettstein M, Kombot C, Chevalley F, Mouhsine E, Garofalo R. Long gamma nail in the treatment of subtrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004; 124:443–447.
Article11. Windolf M, Braunstein V, Dutoit C, Schwieger K. Is a helical shaped implant a superior alternative to the Dynamic Hip Screw for unstable femoral neck fractures? A biomechanical investigation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009; 24:59–64.
Article12. Strauss E, Frank J, Lee J, Kummer FJ, Tejwani N. Helical blade versus sliding hip screw for treatment of unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures: a biomechanical evaluation. Injury. 2006; 37:984–989.
Article13. Ahrengart L, Törnkvist H, Fornander P, et al. A randomized study of the compression hip screw and Gamma nail in 426 fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; (401):209–222.
Article14. Chung PH, Kang S, Kim JP, Kim YS, Lee HM, Huh DJ. Treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fractures with a long intramedullary nail. Hip Pelvis. 2013; 25:51–56.
Article15. Menezes DF, Gamulin A, Noesberger B. Is the proximal femoral nail a suitable implant for treatment of all trochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 439:221–227.
Article16. Ongkiehonga BD, Leemansb R. Proximal femoral nail failure in a subtrochanteric fracture: the importance of fracture to distal locking screw distance. Injry Extra. 2007; 38:445–450.
Article17. Rockwood CA, Green DP, Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, Court-Brown CM, Tornetta P. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2010.18. Park J, Yang KH. Correction of malalignment in proximal femoral nailing--Reduction technique of displaced proximal fragment. Injury. 2010; 41:634–638.
Article19. Yang KH, Won Y, Kang DH, Oh JC, Kim SJ. Role of appositional screw fixation in minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibial fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2015; 29:e331–e335.
Article20. Ogata K, Goldsand EM. A simple biplanar method of measuring femoral anteversion and neck-shaft angle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979; 61:846–851.
Article21. Bendo JA, Weiner LS, Strauss E, Yang E. Collapse of intertrochanteric hip fractures fixed with sliding screws. Orthop Rev. 1994; Suppl:30–37.22. Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM, Keggi JM. The value of the tip-apex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:1058–1064.
Article23. Koval KJ, Skovron ML, Aharonoff GB, Meadows SE, Zuckerman JD. Ambulatory ability after hip fracture. A prospective study in geriatric patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; (310):150–159.24. Jiang LS, Shen L, Dai LY. Intramedullary fixation of subtrochanteric fractures with long proximal femoral nail or long gamma nail: technical notes and preliminary results. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2007; 36:821–826.25. Windolf J, Hollander DA, Hakimi M, Linhart W. Pitfalls and complications in the use of the proximal femoral nail. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2005; 390:59–65.
Article26. Tencer AF, Johnson KD, Johnston DW, Gill K. A biomechanical comparison of various methods of stabilization of subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Orthop Res. 1984; 2:297–305.
Article27. Won Y, Yang KH, Kim KK, Weaver MJ, Allen EM. Amputated limb by cerclage wire of femoral diaphyseal fracture: a case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016; 136:1691–1694.
Article28. Okcu G, Ozkayin N, Okta C, Topcu I, Aktuglu K. Which implant is better for treating reverse obliquity fractures of the proximal femur: a standard or long nail? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471:2768–2775.
Article29. Lindvall E, Ghaffar S, Martirosian A, Husak L. Short versus long intramedullary nails in the treatment of pertrochanteric hip fractures: incidence of ipsilateral fractures and costs associated with each implant. J Orthop Trauma. 2016; 30:119–124.
Article30. Wang WY, Yang TF, Fang Y, Lei MM, Wang GL, Liu L. Treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fracture with long proximal femoral nail antirotation. Chin J Traumatol. 2010; 13:37–41.31. Im GI, Shin YW, Song YJ. Potentially unstable intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:5–9.
Article32. McConnell T, Tornetta P 3rd, Benson E, Manuel J. Gluteus medius tendon injury during reaming for gamma nail insertion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (407):199–202.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Treatment of Subtrochanteric Fracture with Cephallomedually Nail: Minimal Incision and Lowman Clamp Assisted Reduction
- Internal Fixation of Pauwels Type-3 Undisplacedincomplete Insufficiency Femoral Neck Fractures with Cephalomedullary Nails
- New Approach in the Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fracture Using a Cephalomedullary Nail
- Surgical Treatment of Subtrochanteric Fracture of Femur with Spiral Blade Unreamed Intramedullary Femoral Nail
- What is the Optimal Nail Length to Treat Osteoporotic Subtrochanteric Fractures? A Finite Element Analysis