Korean J Phys Anthropol.
2017 Dec;30(4):153-159. 10.11637/kjpa.2017.30.4.153.
Utilization of Second Digit to Fourth Digit Ratio (2D : 4D) as One of Physical Markers to Evaluate Aggression in Elementary School Students
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medical Service, Kongju National University, Korea.
- 2Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Korea. sikim@cnu.ac.kr
- 3Research Institute for Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Korea.
- KMID: 2424167
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11637/kjpa.2017.30.4.153
Abstract
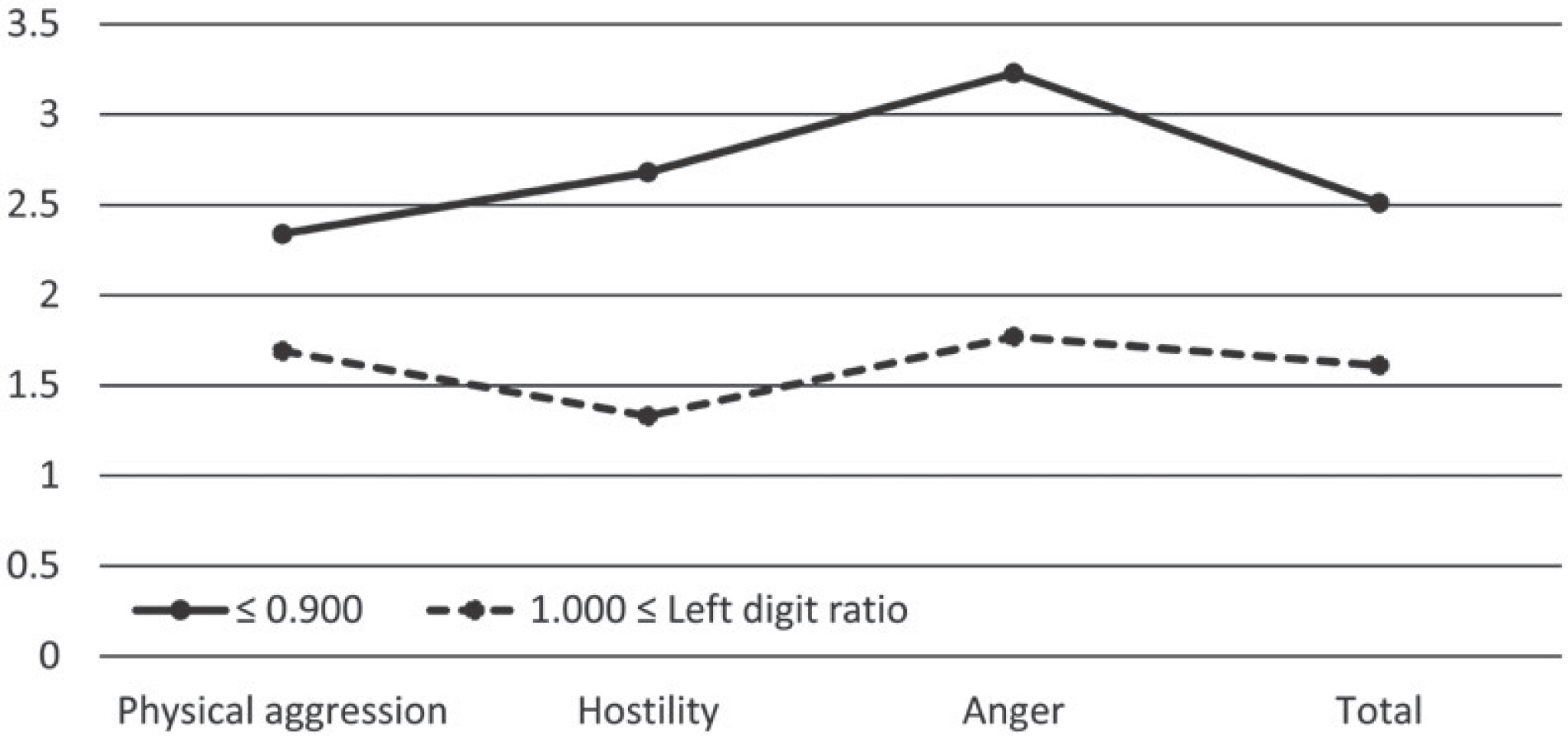
- The aim of this study is to provide basic data to prevent adolescent crime or violence by analyzing aggression according to second digit to fourth digit ratio (2D : 4D). Index and ring finger length on both hands by photocopy was measured using Callipers from ventral proximal crease to finger tip. This study was done on 187 elementary school students (98 males, 89 females). Data were collected by measuring index and ring finger length on both hands by photocopy and by completing self-reported questionnaire. The data were analyzed using SPSS win 21.0. This study showed that the 2D : 4D of males was significantly lower than female, and the aggression score of males was significantly higher than female. Especially, there was significantly differences between 0.900 or less than 0.900 digit ratio group and 1.000 or more than 1.000 digit ratio group only left hand of males. The results of this study suggest that left digit ratio of males in elementary school students are able to be used as one of physical markers to evaluate aggression.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Choi SY. Study on the Factor which Influences on Children's Aggressive Behavior. Unpublished Master's Thesis. Dongduk Women's University;. 2003.2. Do KB. A Study of Factors Influencing School Violence Behavior. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation. Daegu University;. 2007.3. Lee YS. Influence of Rearing Attitude of Parent that Child Perceive to Children's Aggression. Unpublished Master's Thesis. Yonsei University;. 1988.4. Block JH. Differential Premises Arising from Differential Socialization of the Sexes: Some conjectures. Child Dev. 1983; 54:1335–54.
Article5. Gelles RJ. Child Abuse as Psychopathology. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1973; 43:611–21.6. Lutchmaya S, Baron-Cohen S, Raggatt P, Knickmeyer R, Manning JT. 2nd to 4th Digit Ratios, Fetal Testosterone and Estradiol. Early Hum Dev. 2004; 77:23–8.
Article7. Malas MA, Dogan S, Evcil EH, Desdicioglu K. Fetal Development of the Hand, Digits and Digit ratio (2D: 4D). Early Hum Dev. 2006; 82:469–75.8. Butovskaya M, Fedenok J, Burkova V, Manning J. Sex Differences in 2D: 4D and Aggression in Children and Adolescents From Five Regions of Russia. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2013; 152:130–9.9. Cho HJ. The Relationship Between the Putative Marker of Prenatal Androgen Exposure, and Physical Fitness in Elementary School Students. Unpublished Master's Thesis. Seoul National University;. 2010.10. Kim SI, Cho KJ. Second to Fourth Digit Ratio as a Sex Determination in Korean. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2012; 25:137–44.11. Cho KJ, Kim SI. Change of Second to Fourth Digit Ratio According to Age in Korean Children. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2015; 28:197–203.
Article12. Sim K. The Relationship Between Sex Typical Body Shape and Quality Indicators. J Soc Evol Cult Psychol. 2013; 7:97–120.13. Fink B, Thanzami V, Seydel H, Manning JT. Digit Ratio and Hand-Grip Strength in German and Mizos Men: Cross-Cultural Evidence for an Organizing Effect of Prenatal Testosterone on Strength. Am J Hum Biol. 2006; 18:776–82.
Article14. Bennett M, Manning JT, Cook CJ, Kilduff LP. Digit Ratio (2D: 4D) and Performance in Elite Rugby Players. J Sports Sci. 2010; 28:1415–21.15. Sapienza P, Zingales L, Maestripieri D. Gender Differences in Financial Risk Aversion and Career Choices are Affected by Testosterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009; 106:15268–73.
Article16. Harris CR, Jenkins M, Glaser D. Gender Differences in Risk Assessment: Why Do Women Take Fewer Risks Than Men. Judgm Decis Mak. 2006; 1:48–63.17. Joyce CW, Kelly JC, Chan JC, Colgan G, O'Briain D, Mc Cabe JP, et al. Second to Fourth Digit Ratio Confirms Aggressive Tendencies in Patients with Boxers Fractures. Injury. 2013; 44:1636–9.
Article18. Archer J. Sex Differences in Aggression in Real-World Settings: A Meta-Analytic Review. Rev Gen Psychol. 2004; 8:291–322.19. Sim KO, Chun WY. Psychological Significance of Finger Length Ratio: 2D: 4D as a Marker of Prenatal Testosterone. Korean J Psychol. 2014; 33:787–814.20. Manning JT, Stewart A, Bundred PE, Trivers RL. Sex and Ethnic Differences in 2nd to 4th Digit Ratio of Children. Early Hum Dev. 2004; 80:161–8.
Article21. McIntyre MH, Barrett ES, McDermott R, Johnson DDP, Cowden J, Rosen SP. Finger Length Ratio (2D: 4D) and Sex Differences in Aggression During a Simulated War Game. Pers Individ Dif. 2007; 42:755–64.22. Kim SI, Cho KJ. Difference of Second to Fourth Digit Ratio According to the Methods of Measuring length. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2013; 26:25–32.
Article23. Lee EA. Development and Validation of Aggression Scale for Elementary School Students. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation. Kyungsung University;. 2011.24. Seong KW. Relationship Among Aggression, Academy Achievement and Second Digit to Fourth Digit Ratio in Elementary School Students. Unpublished Master's Thesis. Konkuk University;. 2014.25. Butovskaya M, Burkova V, Karelin D, Fink B. Digit Ratio (2D: 4D), Aggression, and Dominance in the Hadza and the Datoga of Tanzania. Am J Hum Biol. 2015; 27:620–7.26. Bailey AA, Hurd PL. Finger Length Ratio (2D: 4D) Correlates with Physical Aggression in Men but Not in Women. Biol Psychol. 2005; 68:215–21.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Relationship between 2nd Digit/4th Digit Ratio and Empathy, Aggression, and Sex Role in College Students
- A Relationship between 2nd to 4th Digit Length Ratio and Aggression Related-Sports Entries Characteristics in Female Athletics of Korean National Teams
- The Ratio of Second and Fourth Digit Length: A Biomarker for Methamphetamine Dependence?
- The Relationship between Second-to-Fourth Digit Ratios, Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms, Aggression, and Intelligence Levels in Boys with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- The Difference of the 2nd to 4th Digit Length Ratio betweenType I and Type II Alcoholism