Korean J Adult Nurs.
2018 Oct;30(5):455-469. 10.7475/kjan.2018.30.5.455.
Effect of Exercise Intervention on Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain in Older Adults: Meta-analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Doctoral Student, Graduate School, College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Associate Professor, College of Nursing, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. sh235@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2423837
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2018.30.5.455
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of exercise on chronic musculoskeletal pain in older adults.
METHODS
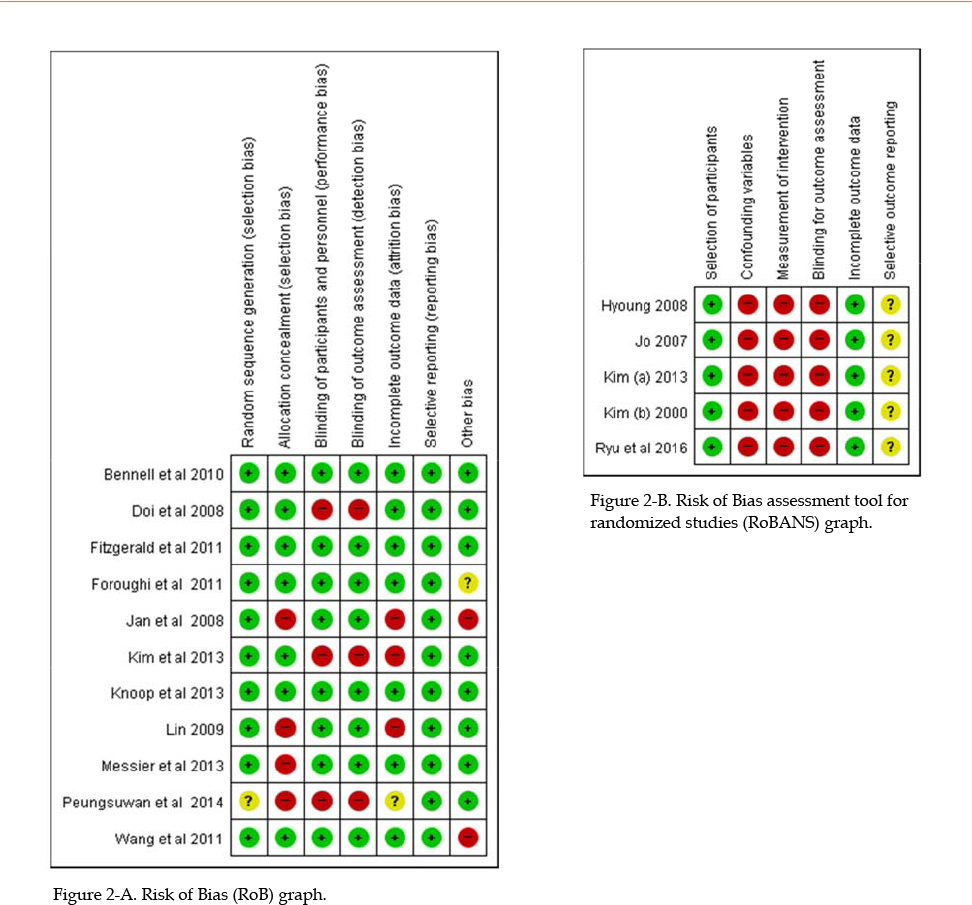
In order to conduct a meta-analysis, a total 7,186 studies were retrieved from seven databases (Pubmed, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, RISS, KISS, NDSL, KoreaMed) without restriction on publication year and the articles published until June 2018 were selected for this study. Sixteen studies were selected for the meta-analysis based on their satisfaction of the inclusion criteria and low risk of bias. Baseline demographic data, exercise features, and outcome data were extracted from all included trials. The data was analyzed using the RevMan 5.2 and CMA 3.0. program.
RESULTS
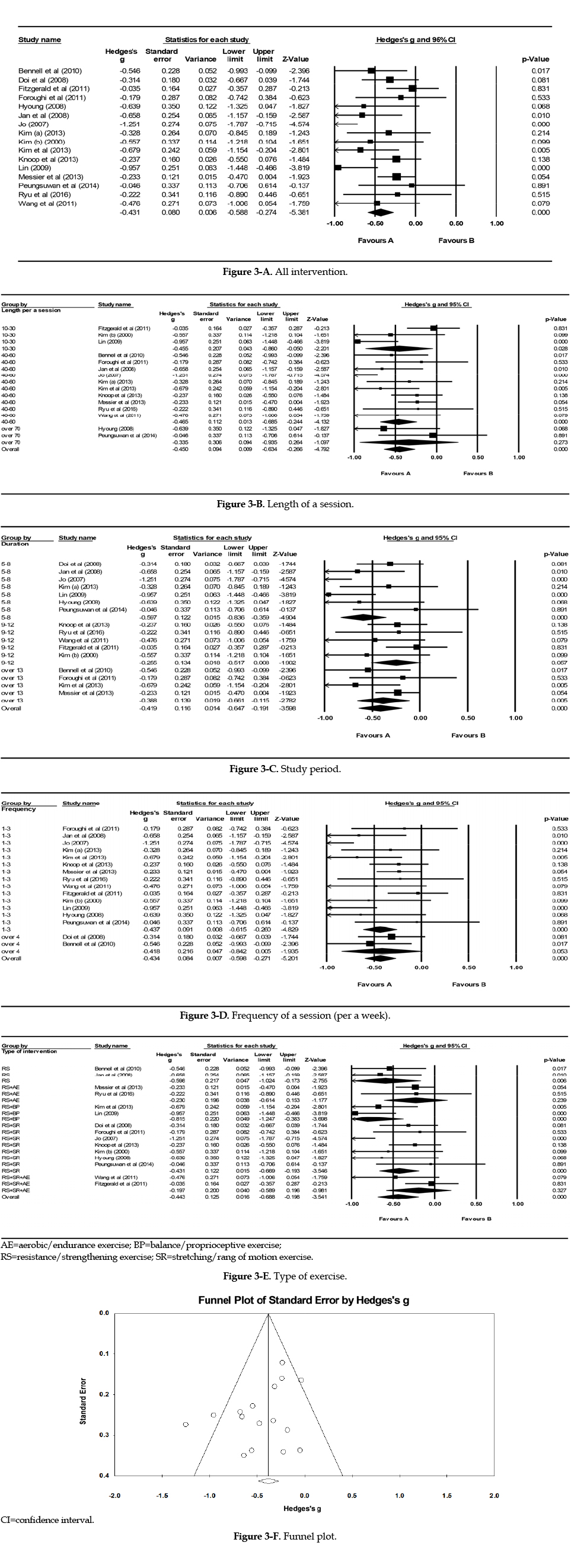
The results of the meta-analysis (n=16) revealed that the exercise intervention was found to be significantly superior to control group on pain (Standardized Mean Difference [Hedges'g]=−0.43, 95% Confidence Interval [CI]=−0.59~−0.27). Also, meta-ANOVA was performed using study period, length and frequency of session and type of exercise, but no statistically significant moderators were found.
CONCLUSION
In this study, the exercise demonstrated significant reduction in pain intensity in older adults and there was no difference in pain reduction according to type or duration of exercise. Therefore, exercise that older adults prefers and is feasible in where they are, should be adopted as a nursing intervention for older adults' chronic musculoskeletal pain management.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung KH, Oh YH, Kang EN, Kim JH, Seon WD, Oh MA, et al. An Investigation of Elderly Conditions. Policy Report. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare;2014. Report No.: 11-1352000-001426-12.2. AGS Panel on Persistent pain in Older Persons. The management of persistent pain in older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002; 50(S6):S205–S224.3. Yang YJ. Exercise therapy for musculoskeletal pain. Korean J Fam Pract. 2014; 4(3):186–193.4. Choi YH, Shin KR, Ko SH, Gong SJ, Gong ES, Kim MA, et al. Eldery and Health. 4th ed. Seoul: Hyunmoonsa;2009. p. 1–748.5. Batterham SI, Heywood S, Keating JL. Systematic review and meta-analysis comparing land and aquatic exercise for people with hip or knee arthritis on function, mobility and other health outcomes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011; 12(1):123–135. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-123.
Article6. Li Y, Su Y, Chen S, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Liu C, et al. The effects of resistance exercise in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rehabil. 2016; 30(10):947–959. DOI: 10.1177/0269215515610039.
Article7. Kim YI, Choi HS, Han JH, Kim JY, Kim GE. Aquatic exercise for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review & meta analysis. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2015; 16(9):6099–6111. DOI: 10.5762/KAIS.2015.16.9.6099.8. Kim DH, Chon TJ, Lee SB. Analysis of the effects of exercise programs for the adults and elderly. J Korean Soc Wellness. 2010; 5(2):93–104.9. Jung YS. A meta-analysis of effects of exercise programs in the elderly [dissertation]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;2006. 1–86.10. Cha JW. Meta-regression analysis of variables related to effects of exercise program applied to the elderly. J Korean Phys Edu Assoc Girls Women. 2012; 26(1):203–220.11. Yun CG, An CS. The effect of exercise program on pain and quality of life for patients with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Muscle Joint Health. 2014; 21(3):173–183. DOI: 10.5953/JMJH.2014.21.3.173.
Article12. Kelley GA, Kelley KS. Effects of exercise on depressive symptoms in adults with arthritis and other rheumatic disease: a systematic review of meta-analyses. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014; 15(1):121–130. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-121.
Article13. Brosseau L, Pelland L, Wells G, MacLeay L, Lamothe C, Michaud G, et al. Efficacy of aerobic exercises for osteoarthritis (part II): a meta-analysis. Phys Ther Rev. 2004; 9(3):125–145. DOI: 10.1179/108331904225005061.
Article14. Fransen M, McConnell S, Hemandez-Molina G, Reichenbach S. Does land-based exercise reduce pain and disability associated with hip osteoarthritis? a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(5):613–620. DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2010.01.003.
Article15. Tanaka R, Ozawa J, Kito N, Moriyama H. Efficacy of strengthening or aerobic exercise on pain relief in people with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rehabil. 2013; 27(12):1059–1071. DOI: 10.1177/0269215513488898.
Article16. Meng XG, Yue SW. Efficacy of aerobic exercise for treatment of chronic low back pain: a meta-analysis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015; 94(5):358–365. DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000188.17. O'Connor SR, Tully MA, Ryan B, Bleakley CM, Baxter GD, Bradley JM, et al. Walking exercise for chronic musculoskeletal pain: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015; 96(4):724–734. DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2014.12.003.18. Clijsen R, Fuchs J, Taeymans J. Effectiveness of exercise therapy in treatment of patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys Ther. 2014; 94(12):1697–1708. DOI: 10.2522/ptj.20130310.
Article19. American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM's Resource Manual for Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Presciption. 6th ed. USA: Lippincott Williams & Wolters Kluwer Health;2010. p. 1–896.20. Hedges LV, Olkin I. Statistical methods for meta-analysis. 1st ed. USA: Academic Press;1985. p. 1–369.21. Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0 [Internet]. London, UK: The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. cited 2011 March 2. Available from: http://handbook.cochrane.org/.22. Hwang SD. Understanding and use of the meta-analysis. Daegu: Kyungpook national university Social Science Research Institute data analysis center;2013. p. 1–236.23. Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315(7109):629–634. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629.
Article24. Baek SR, Lim JY, Lim JY, Park JH, Lee JJ, Lee SB, et al. Prevalence of musculoskeletal pain in an elderly Korean population: results from the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLoSHA). Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2010; 51(3):e46–e51. DOI: 10.1016/j.archger.2009.11.01.
Article25. Roddy E, Zhang W, Doherty M. Aerobic walking or strengthening exercise for osteoarthritis of the knee? a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005; 64:544–548. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.028746.
Article26. Jansen MJ, Viechtbauer W, Lenssen AF, Hendriks EJM, de Bie RA. Strength training alone, exercise therapy alone, and exercise therapy with passive manual mobilisation each reduce pain and disability in people with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. J Physiother. 2011; 57(1):11–20. DOI: 10.1016/S1836-9553(11)70002-9.
Article27. Juhl C, Christensen R, Roos EM, Zhang W, Lund H. Impact of exercise type and dose on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014; 66(3):622–636. DOI: 10.1002/art.38290.
Article28. Weng MC, Lee CL, Chen CH, Hsu JJ, Lee WD, Huang MH, et al. Effects of different stretching techniques on the outcomes of isokinetic exercise in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2009; 25(6):306–315. DOI: 10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70521-2.
Article29. Lee EY, Kim JI, Choi HJ. Extension exercise and aquatic exercise. 1st ed. Seoul: Shinkwang publisher;1998. p. 1–282.30. Kim SB, Kwak H, Han SH. Exercise prescription for older adults with osteoarthritis. Korean J Clin Geriatr. 2005; 6(4):419–443.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Auriculotherapy on Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- A Survey on the Customized Visiting Nurse's Assessment and Management of Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain in Older Adults
- Effectiveness of exercise for improving physical and renal function in older adults with pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of medication adherence interventions for older adults with chronic illnesses: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- The Relationship between Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain and Sarcopenia Risk in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study