J Pathol Transl Med.
2018 Sep;52(5):267-274. 10.4132/jptm.2018.07.14.
C-reactive Protein Overexpression in the Background Liver of Hepatitis B Virus–Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is a Prognostic Biomarker
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ckim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2422092
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2018.07.14
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Peripheral blood C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration and CRP overexpression in HCC cells are proven to be prognostic markers for HCC, but the significance of CRP expression in non-neoplastic hepatocytes, which are the primary origin of CRP, has not been studied. This study was conducted to determine the clinicopathologic significance of CRP immunoreactivity in the background liver of HBV-associated HCC.
METHODS
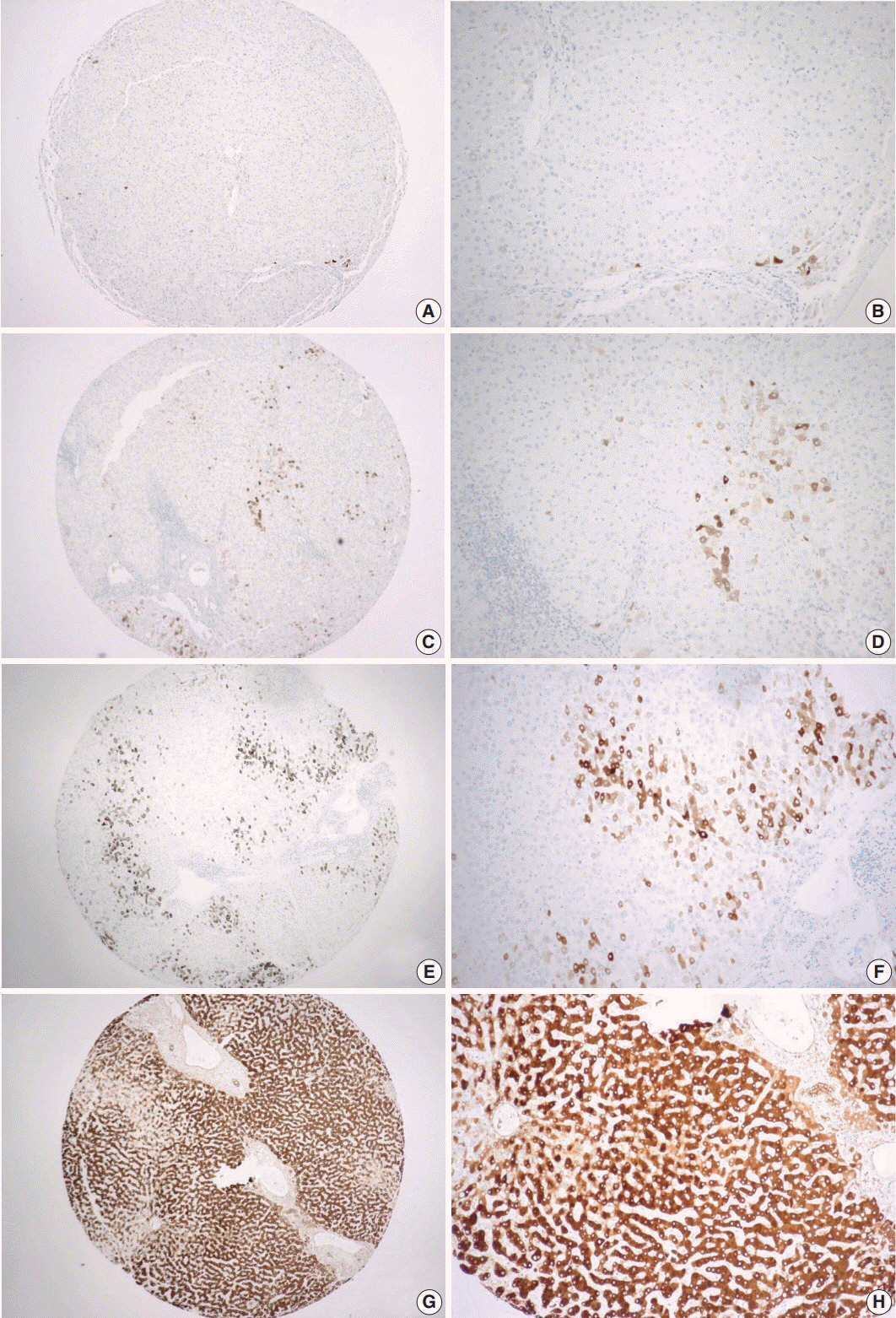
CRP immunostaining was done on tissue microarrays of non-neoplastic liver tissues obtained from surgically resected, treatment-naïve HBV-associated HCCs (n = 156). The relationship between CRP immunoreactivity and other clinicopathologic parameters including cancer-specific survival was analyzed. CRP immunoreactivity was determined using a 4-tier grading system: grades 0, 1, 2, and 3.
RESULTS
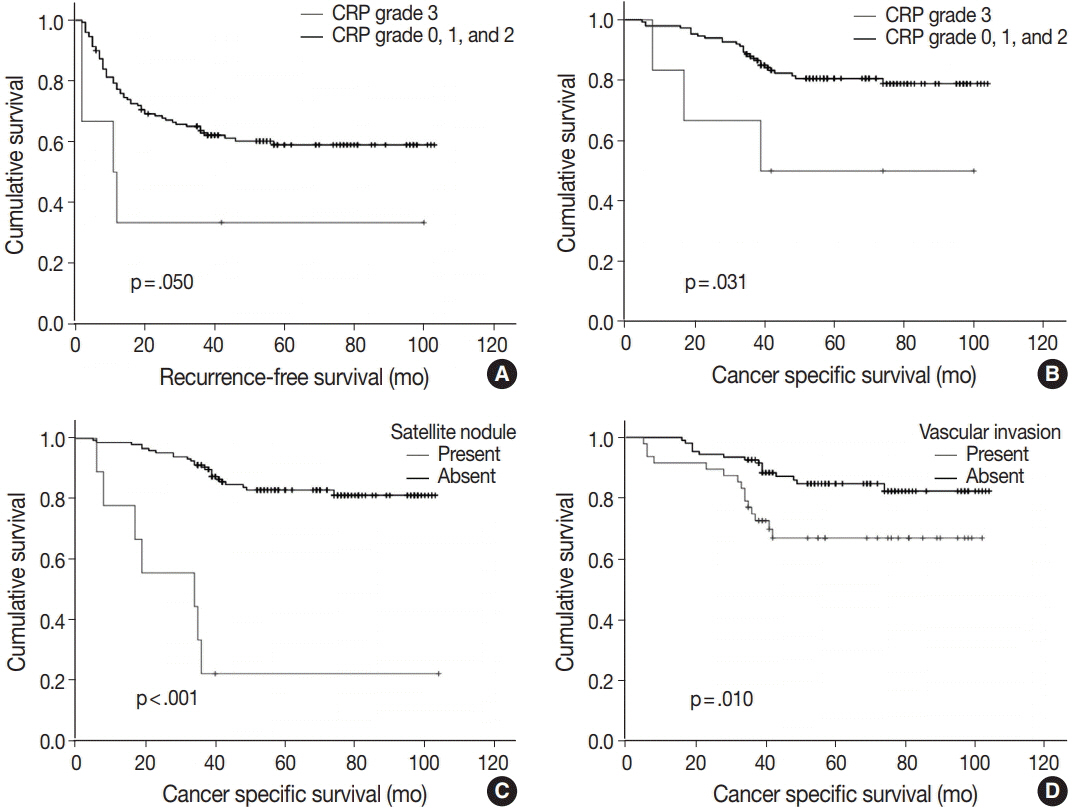
CRP was positive in 139 of 156 cases (89.1%) of non-neoplastic liver in patients with HCCs: grade 1 in 83 cases (53.2%); grade 2 in 50 cases (32.1%); and grade 3 in six cases (3.8%). The patients with diffuse CRP immunoreactivity (grade 3) had decreased cancer-specific survival (p = .031) and a tendency for shorter interval before early recurrence (p = .050). The degree of CRP immunoreactivity correlated with serum CRP concentration (p < .001).
CONCLUSIONS
CRP immunoreactivity in non-neoplastic liver is a novel biomarker for poor cancer-specific survival of HBV-associated HCC and correlates with serum CRP concentration.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Hepatocellular adenomas: recent updates
Haeryoung Kim, Young Nyun Park
J Pathol Transl Med. 2021;55(3):171-180. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2021.02.27.
Reference
-
1. Kushner I, Feldmann G. Control of the acute phase response. Demonstration of C-reactive protein synthesis and secretion by hepatocytes during acute inflammation in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1978; 148:466–77.
Article2. Eklund CM. Proinflammatory cytokines in CRP baseline regulation. Adv Clin Chem. 2009; 48:111–36.3. Ganter U, Arcone R, Toniatti C, Morrone G, Ciliberto G. Dual control of C-reactive protein gene expression by interleukin-1 and interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989; 8:3773–9.
Article4. Thompson PA, Khatami M, Baglole CJ, et al. Environmental immune disruptors, inflammation and cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 2015; 36 Suppl 1:S232–53.
Article5. Anuja K, Roy S, Ghosh C, Gupta P, Bhattacharjee S, Banerjee B. Prolonged inflammatory microenvironment is crucial for pro-neoplastic growth and genome instability: a detailed review. Inflamm Res. 2017; 66:119–28.
Article6. Sicking I, Edlund K, Wesbuer E, et al. Prognostic influence of preoperative C-reactive protein in node-negative breast cancer patients. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e111306.
Article7. Mori S, Kita J, Kato M, Shimoda M, Kubota K. Usefulness of a new inflammation-based scoring system for prognostication of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Am J Surg. 2015; 209:187–93.
Article8. Kogo M, Sunaga T, Nakamura S, et al. Prognostic index for survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with third-generation agents. Chemotherapy. 2017; 62:239–45.
Article9. Liu Y, Chen S, Zheng C, et al. The prognostic value of the preoperative c-reactive protein/albumin ratio in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 2017; 17:285.
Article10. Chen S, Yang X, Feng JF. A novel inflammation-based prognostic score for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the c-reactive protein/prognostic nutritional index ratio. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:62123–32.
Article11. Takeda H, Takai A, Inuzuka T, Marusawa H. Genetic basis of hepatitis virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: linkage between infection, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. J Gastroenterol. 2017; 52:26–38.
Article12. Shin JH, Kim CJ, Jeon EJ, et al. Overexpression of C-reactive protein as a poor prognostic marker of resectable hepatocellular carcinomas. J Pathol Transl Med. 2015; 49:105–11.
Article13. El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2012; 142:1264–73. e1.
Article14. Levrero M, Zucman-Rossi J. Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2016; 64(1 Suppl):S84–S101.
Article15. Yang X, Wu L, Lin J, et al. Distinct hepatitis B virus integration patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and adjacent normal liver tissue. Int J Cancer. 2017; 140:1324–30.
Article16. Zhao LH, Liu X, Yan HX, et al. Genomic and oncogenic preference of HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:12992.
Article17. Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Imai N, Nishino H, Tajiri H. C-reactive protein as a prognostic marker in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015; 62:966–70.18. Zhao X, Luo J, Li B, Liu S, Li D. The association between preoperative serum C-reactive protein and hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection--a retrospective study. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0116909.
Article19. Nagaoka S, Yoshida T, Akiyoshi J, et al. Serum C-reactive protein levels predict survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2007; 27:1091–7.
Article20. Shen S, Gong J, Yang Y, et al. Molecular mechanism of C-reaction protein in promoting migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. Int J Oncol. 2017; Mar. 13. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.3911.
Article21. Liu F, Chen HY, Huang XR, et al. C-reactive protein promotes diabetic kidney disease in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2011; 54:2713–23.
Article22. Yang J, Wezeman M, Zhang X, et al. Human C-reactive protein binds activating Fcgamma receptors and protects myeloma tumor cells from apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 2007; 12:252–65.23. Hu RH, Lee PH, Yu SC. Secretion of acute-phase proteins before and after hepatocellular carcinoma resection. J Formos Med Assoc. 1999; 98:85–91.24. Li Z, Xue TQ, Chen XY. Predictive values of serum VEGF and CRP levels combined with contrast enhanced MRI in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after TACE. Am J Cancer Res. 2016; 6:2375–85.25. Jiang FQ, Lu W, Yang C, et al. Curative effect of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation in treating hepatic cell carcinoma and its effect on serum markers. Cancer Biomark. 2017; 20:17–22.
Article26. Liu YB, Ying J, Kuang SJ, et al. Elevated preoperative serum Hs-CRP level as a prognostic factor in patients who underwent resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e2209.
Article27. Kim JM, Kwon CH, Joh JW, et al. C-reactive protein may be a prognostic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma with malignant portal vein invasion. World J Surg Oncol. 2013; 11:92.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of primary hepatocellular carcinoma following vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus in a child
- Hepatitis C virus antibodies in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis
- Obesity and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Relevance of reactive oxygen species in liver disease observed in transgenic mice expressing the hepatitis B virus X protein
- Hepatitis B Precore Protein: Pathogenic Potential and Therapeutic Promise