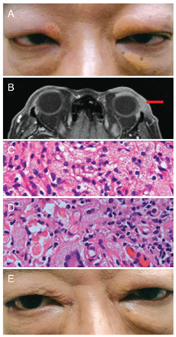
Korean J Ophthalmol.
2018 Oct;32(5):424-425. 10.3341/kjo.2017.0145.
Adult onset xanthogranuloma associated with IgG4-related disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Tung Wah Eastern Hospital, Hong Kong. HEYAYS@gmail.com
- 2Hong Kong University, Hong Kong.
- KMID: 2422073
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.0145
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. McKelvie P, McNab AA, Hardy T, Rathi V. Comparative study of clinical, pathological, radiological, and genetic features of patients with adult ocular adnexal xanthogranulomatous disease, Erdheim-Chester disease, and IgG4-related disease of the orbit/ocular adnexa. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017; 33:112–119.
Article2. Burris CK, Rodriguez ME, Raven ML, et al. Adult-onset asthma and periocular xanthogranulomas associated with systemic IgG4-related disease. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2016; 1:34–37.
Article3. London J, Martin A, Soussan M, et al. Adult onset asthma and periocular xanthogranuloma (AAPOX), a rare entity with a strong link to IgG4-related disease: an observational case report study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e1916.4. Singh K, Rajan KD, Eberhart C. Orbital necrobiotic xanthogranuloma associated with systemic IgG4 disease. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2010; 18:373–378.
Article5. Cheuk W, Yuen HK, Chan AC, et al. Ocular adnexal lymphoma associated with IgG4+ chronic sclerosing dacryoadenitis: a previously undescribed complication of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008; 32:1159–1167.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Xanthogranuloma in an Adult
- IgG4-related Ophthalmic Disease Associated with Adult Xanthogranulomatous Disease
- A case of xanthogranuloma in adult
- A Case of Multiple Xanthogranuloma Similar to the Histopathological Findings of Malignant Melanoma
- A Case of Adult-onset Xanthogranuloma on the Skin of the Third Toe