Ann Rehabil Med.
2018 Aug;42(4):626-629. 10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.626.
Late-Onset Post-radiation Lymphedema Provoked by Bee Venom Therapy: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Eulji University Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. jylimmd@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2420057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2018.42.4.626
Abstract
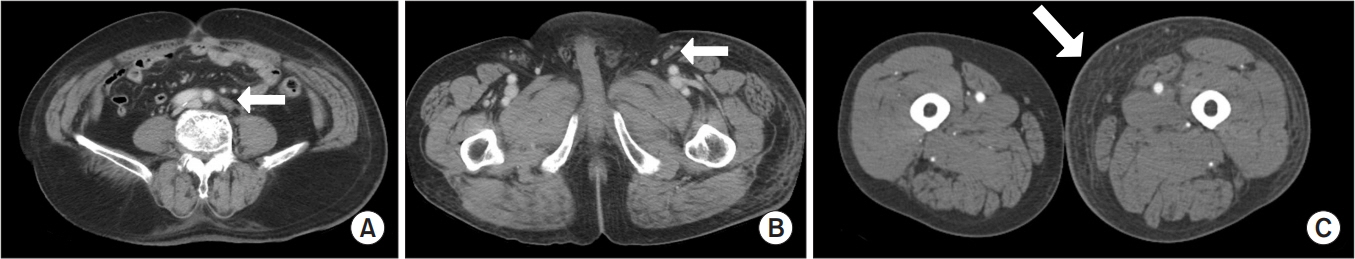
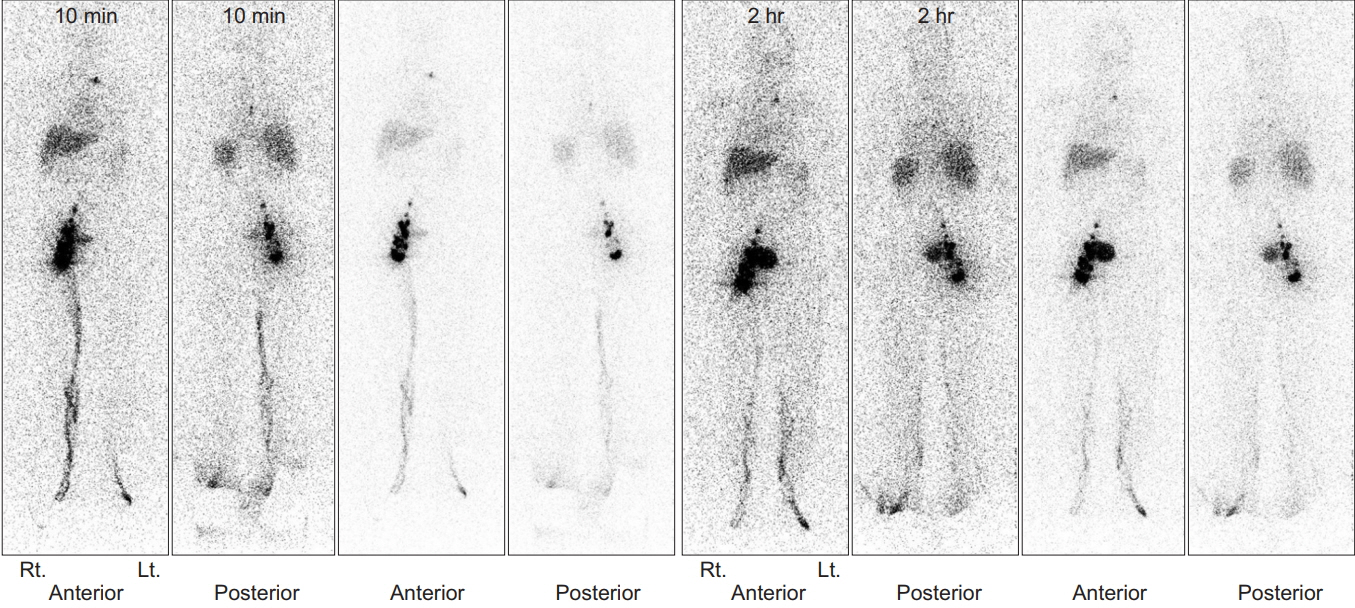
- Lymphedema is a common complication associated with cancer itself or with cancer treatment. Lymphedema infrequently occurs after drug therapy. Bee venom is one of the materials used in acupuncture, and it has been used in the treatment of a variety of inflammatory diseases including arthritis. We report a 74-year-old male patient with late-onset post-radiation lymphedema provoked by bee venom therapy. He was free of lymphedema for 5 years after the complete remission of prostate cancer which had been treated with transurethral resection and radiation therapy. The patient developed left leg swelling after undergoing bee venom therapy for left hip pain. Computed tomography and lymphoscintigraphy showed lymphedema without tumor recurrence or infection. The lymphatic system was suspected to be injured by bee venom therapy and lymphedema was provoked. Bee venom therapy should be used cautiously in patients prone to lymphedema.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cassileth BR, Van Zee KJ, Yeung KS, Coleton MI, Cohen S, Chan YH, et al. Acupuncture in the treatment of upper-limb lymphedema: results of a pilot study. Cancer. 2013; 119:2455–61.2. Li L, Yuan L, Chen X, Wang Q, Tian J, Yang K, et al. Current treatments for breast cancer-related lymphoedema: a systematic review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016; 17:4875–83.3. Keegan KA, Cookson MS. Complications of pelvic lymph node dissection for prostate cancer. Curr Urol Rep. 2011; 12:203–8.
Article4. Hossen MS, Shapla UM, Gan SH, Khalil MI. Impact of bee venom enzymes on diseases and immune responses. Molecules. 2016; 22:25.
Article5. Orsolic N. Bee venom in cancer therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012; 31:173–94.
Article6. Ahn YJ, Shin JS, Lee J, Lee YJ, Kim MR, Shin YS, et al. Safety of essential bee venom pharmacopuncture as assessed in a randomized controlled double-blind trial. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016; 194:774–80.
Article7. Park JH, Yim BK, Lee JH, Lee S, Kim TH. Risk associated with bee venom therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0126971.
Article8. Abdulsalam MA, Ebrahim BE, Abdulsalam AJ. Immune thrombocytopenia after bee venom therapy: a case report. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016; 16:107.
Article9. Huh JE, Baek YH, Lee MH, Choi DY, Park DS, Lee JD. Bee venom inhibits tumor angiogenesis and metastasis by inhibiting tyrosine phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 in LLC-tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Lett. 2010; 292:98–110.
Article10. Ersoy A, Koca N. Everolimus-induced lymphedema in a renal transplant recipient: a case report. Exp Clin Transplant. 2012; 10:296–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bee Venom Therapy for Musculoskeletal Disorders
- A Case of Newly Developed Pemphigus Foliaceus and Possible Association with Alternative Bee-Venom Therapy
- A New Onset of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Developed After Bee Venom Therapy
- A Case of Ischemic Stroke Following Bee Venom Acupuncture
- Serum sickness reaction with skin involvement induced by bee venom injection therapy