Arch Hand Microsurg.
2018 Sep;23(3):195-205. 10.12790/ahm.2018.23.3.195.
Revisiting the Posterior Interosseous Artery Flap
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University School of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, MS Jaegeon Hospital, Daegu, Korea. leegjosmd@daum.net
- KMID: 2419455
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.3.195
Abstract
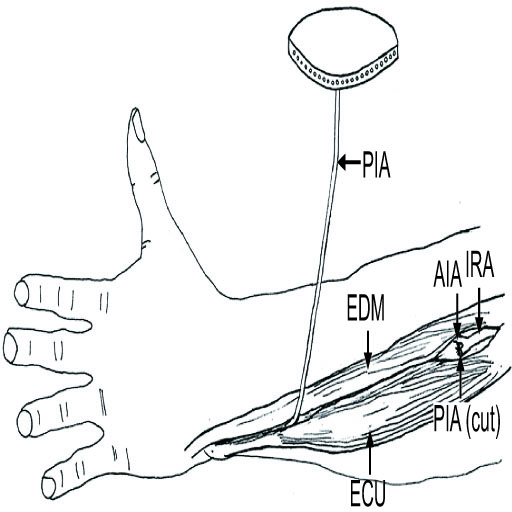
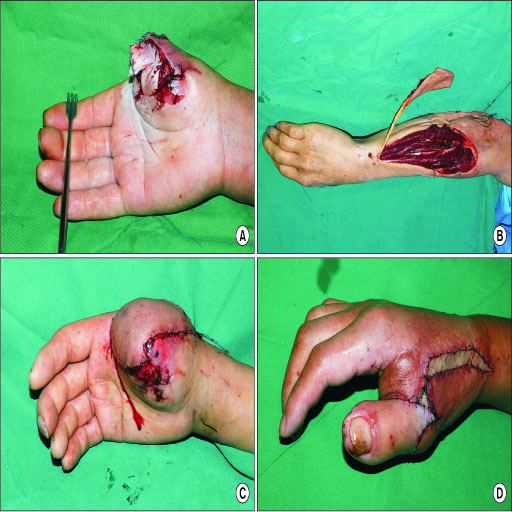
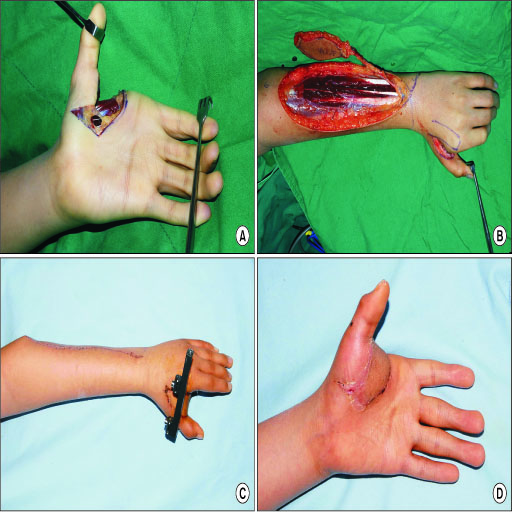
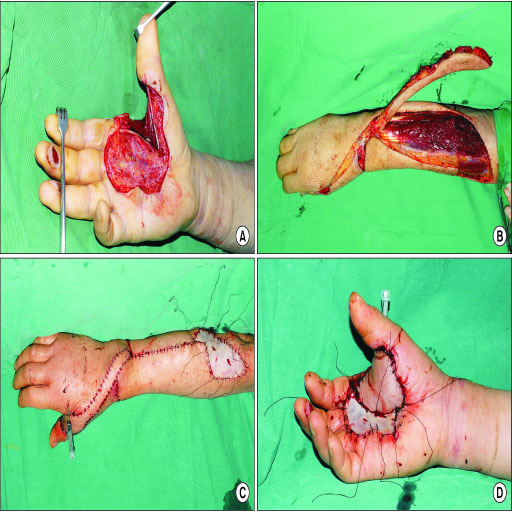
- The posterior interosseous artery (PIA) flap is one of the options for hand and upper extremity reconstruction. It does not sacrifice the main arteries of the hand, the radial and ulnar arteries and could be used even when either artery was damaged. The PIA is a branch of the common interosseous artery, which is about 1 cm in distance from the ulnar artery, and runs down longitudinally in the intermuscular septum between the extensor carpi ulnaris and extensor digiti minimi. PIA appears to be relatively constant in position, and pro a reliable blood supply in the posterior aspect of the forearm. The PIA flap is reliable in its designs, even to making it possible to close the donor site primarily. It provides not only a thin, pliable coverage of the hand and upper extremity, but also a neurosensory flap. Technically, the dissection of the PIA pedicle along its course needs a high learning curve, because it might present the risk of venous congestion, ischemic flap necrosis, and injury to the PIN. Although the flap dissection seems to be difficult, it still offers increased versatility in reconstructions of the hand, foot, and upper extremity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Free Posterior Interosseous Artery Flap for Treatment of First Web Space Contracture: Methods of Venous Anastomosis
Masao Fujiwara, Yuki Matsushita, Yoshikane Maeba, Ayano Suzuki, Hidekazu Fukamizu
Arch Hand Microsurg. 2019;24(4):408-415. doi: 10.12790/ahm.2019.24.4.408.
Reference
-
1. Zancolli EA, Angrigiani C. Posterior interosseous island forearm flap. J Hand Surg Br. 1988; 13:130–135.
Article2. Gavaskar AS. Posterior interosseous artery flap for resurfacing posttraumatic soft tissue defects of the hand. Hand (N Y). 2010; 5:397–402.
Article3. Shibata M, Iwabuchi Y, Kubota S, Matsuzaki H. Comparison of free and reversed pedicled posterior interosseous cutaneous flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997; 99:791–802.
Article4. Bayon P, Pho RW. Anatomical basis of dorsal forearm flap. Based on posterior interosseous vessels. J Hand Surg Br. 1988; 13:435–439.
Article5. Chen HC, Tang YB, Chuang D, Wei FC, Noordhoff MS. Microvascular free posterior interosseous flap and a comparison with the pedicled posterior interosseous flap. Ann Plast Surg. 1996; 36:542–550.
Article6. Costa H, Pinto A, Zenha H. The posterior interosseous flap - a prime technique in hand reconstruction. The experience of 100 anatomical dissections and 102 clinical cases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007; 60:740–747.
Article7. Fujiwara M, Kawakatsu M, Yoshida Y, Sumiya A. Modified posterior interosseous flap in hand reconstruction. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2003; 7:102–109.
Article8. Zhang YX, Qian Y, Pu Z, et al. Reverse bipaddle posterior interosseous artery perforator flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 131:552e–562e.
Article9. Cavadas PC. Posterior interosseous free flap with extended pedicle for hand reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 108:897–901.
Article10. Park JJ, Kim JS, Chung JI. Posterior interosseous free flap: various types. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997; 100:1186–1197. discussion 1198-9.
Article11. Giunta R, Lukas B. Impossible harvest of the posterior interosseous artery flap: a report of an individualised salvage procedure. Br J Plast Surg. 1998; 51:642–645.
Article12. Angrigiani C, Grilli D, Dominikow D, Zancolli EA. Posterior interosseous reverse forearm flap: experience with 80 consecutive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1993; 92:285–293.13. Penteado CV, Masquelet AC, Chevrel JP. The anatomic basis of the fascio-cutaneous flap of the posterior interosseous artery. Surg Radiol Anat. 1986; 8:209–215.
Article14. Pahl S, Schmidt HM. [Clinical anatomy of the interosseous arteries of the forearm]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 1994; 26:246–250. German.15. Sheetz KK, Bishop AT, Berger RA. The arterial blood supply of the distal radius and ulna and its potential use in vascularized pedicled bone grafts. J Hand Surg Am. 1995; 20:902–914.
Article16. Zaidenberg EE, Farias-Cisneros E, Pastrana MJ, Zaidenberg CR. Extended posterior interosseous artery flap: anatomical and clinical study. J Hand Surg Am. 2017; 42:182–189.
Article17. Büchler U, Frey HP. Retrograde posterior interosseous flap. J Hand Surg Am. 1991; 16:283–292.
Article18. Lu LJ, Gong X, Liu ZG, Zhang ZX. Antebrachial reverse island flap with pedicle of posterior interosseous artery: a report of 90 cases. Br J Plast Surg. 2004; 57:645–652.
Article19. Sun C, Wang YL, Ding ZH, et al. Anatomical basis of a proximal fasciocutaneous extension of the distal-based posterior interosseous flap that allows exclusion of the proximal posterior interosseous artery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2015; 68:17–25.
Article20. Costa H, Soutar DS. The distally based island posterior interosseous flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1988; 41:221–227.
Article21. Balakrishnan G, Kumar BS, Hussain SA. Reverse-flow posterior interosseous artery flap revisited. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 111:2364–2369.
Article22. Gong X, Lu LJ. Reconstruction of severe contracture of the first web space using the reverse posterior interosseous artery flap. J Trauma. 2011; 71:1745–1749.
Article23. Sieg P, Dericioglu M, Hansmann C, Jacobsen HC, Trenkle T, Hakim SG. Long-term functional donor site morbidity after ulnar forearm flap harvest. Head Neck. 2012; 34:1312–1316.
Article24. Neuwirth M, Hubmer M, Koch H. The posterior interosseous artery flap: clinical results with special emphasis on donor site morbidity. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013; 66:623–628.
Article25. Özalp B, Elbey H, Aydin A, Özkan T. Distally based subcutaneous veins for venous insufficiency of the reverse posterior interosseous artery flap. Microsurgery. 2016; 36:384–390.
Article26. Kola N, Isaraj S, Xhepa G, Belba M, Belba G. Posterior interosseous forearm flap in reconstruction of first web space. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2009; 22:104–106.27. Pan ZH, Jiang PP, Wang JL. Posterior interosseous free flap for finger re-surfacing. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010; 63:832–837.
Article28. Xu G, Lai-jin L. Coverage of skin defects in spaghetti wrist trauma: application of the reverse posterior interosseous flap and its anatomy. J Trauma. 2007; 63:402–404.
Article29. Jones ME, Rider MA, Hughes J, Tonkin MA. The use of a proximally based posterior interosseous adipofascial flap to prevent recurrence of synostosis of the elbow joint and forearm. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2007; 32:143–147.
Article30. Vögelin E, Langer M, Büchler U. How reliable is the posterior interosseous artery island flap? A review of 88 patients. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2002; 34:190–194.31. Inoue Y, Taylor GI. The angiosomes of the forearm: anatomic study and clinical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996; 98:195–210.
Article32. Lin SD, Lai CS, Chiu CC. Venous drainage in the reverse forearm flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984; 74:508–512.
Article33. Puri V, Mahendru S, Rana R. Posterior interosseous artery flap, fasciosubcutaneous pedicle technique: a study of 25 cases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007; 60:1331–1337.
Article34. Reyad KA, Shaker AA, Elbarbary AS, Sayed MA, Elghareeb MA. The number of perforators included in reversed flow posterior interosseous artery flap: does it affect the incidence of venous congestion? Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016; 4:e1162.35. Acharya AM, Bhat AK, Bhaskaranand K. The reverse posterior interosseous artery flap: technical considerations in raising an easier and more reliable flap. J Hand Surg Am. 2012; 37:575–582.
Article36. Brunelli F, Valenti P, Dumontier C, Panciera P, Gilbert A. The posterior interosseous reverse flap: experience with 113 flaps. Ann Plast Surg. 2001; 47:25–30.
Article37. Akinci M, Ay S, Kamiloglu S, Erçetin O. The reverse posterior interosseous flap: a solution for flap necrosis based on a review of 87 cases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006; 59:148–152.
Article38. Chen HC, Cheng MH, Schneeberger AG, Cheng TJ, Wei FC, Tang YB. Posterior interosseous flap and its variations for coverage of hand wounds. J Trauma. 1998; 45:570–574.
Article39. Fong PL, Chew WY. Posterior interosseous artery flap: our experience and review of modifications done. Hand Surg. 2014; 19:181–187.
Article40. Tiengo C, Monticelli A, Bonvini S, Wassermann V, Venezia ED, Bassetto F. Critical upper limb ischemia due to brachial tourniquet in misdiagnosed thoracic outlet syndrome after carpal tunnel decompression: a case report. World J Plast Surg. 2017; 6:375–379.41. Costa H, Smith R, McGrouther DA. Thumb reconstruction by the posterior interosseous osteocutaneous flap. Br J Plast Surg. 1988; 41:228–233.
Article42. Suzuki S, Iwamoto T, Koshima I. Adipofascial turnover perforator flap for dorsal hand reconstruction based on both the posterior interosseous artery and radial artery. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2012; 37:178–180.
Article43. Li KW, Song DJ, Liu J, Xie SL. Tripaddle posterior interosseous artery flap design for 3-finger defects: an evaluation of 3 surgical approaches. Ann Plast Surg. 2016; 77:406–412.44. Sungpet A, Patradul A. The new flap based on the longitudinal fascial branches of the posterior interosseous artery. J Med Assoc Thai. 1998; 81:458–461.45. Prasad R, Balakrishnan TM. Role of interosseous recurrent artery perforators in the posterior interosseous artery flap. J Hand Microsurg. 2015; 7:36–41.
Article46. Martin D, Legaillard P, Bakhach J, Hu W, Baudet J. [Reverse flow YV pedicle extension: a method of doubling the arc of rotation of a flap under certain conditions]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 1994; 39:403–414. French.47. Zhuang YH, Lin J, Fu FH, Cai ZD, Huang HM, Zheng HP. The posterolateral mid-forearm perforator flap: anatomical study and clinical application. Microsurgery. 2013; 33:638–645.
Article48. Gao W, Yan H, Li Z, et al. The free dorsoradial forearm perforator flap: anatomical study and clinical application in finger reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 2011; 66:53–58.49. Yoon CS, Noh HJ, Malzone G, Suh HS, Choi DH, Hong JP. Posterior interosseous artery perforator-free flap: treating intermediate-size hand and foot defects. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014; 67:808–814.
Article50. Usami S, Okazaki M. Fingertip reconstruction with a posterior interosseous artery perforator flap: a minimally invasive procedure for donor and recipient sites. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2017; 70:166–172.
Article51. Vögelin E, Bignion D, Constantinescu M, Büchler U. [Revision surgery after carpal tunnel release using a posterior interosseous artery island flap]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2008; 40:122–127. German.52. Pagnotta A, Taglieri E, Molayem I, Sadun R. Posterior interosseous artery distal radius graft for ulnar nonunion treatment. J Hand Surg Am. 2012; 37:2605–2610.
Article53. Cavadas PC. Posterior interosseous flap based on a septal perforator, in the absence of the distal artery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999; 104:592.
Article54. Liu J, Song D, Xu J, Li J, Li K, Lv H. Use of free modified innervated posterior interosseous artery perforator flap to repair digital skin and soft tissue defects. Indian J Surg. 2015; 77:Suppl 3. 886–892.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reverse Posterior Interosseous Artery Flap: A Reliable, Comfortable and Versatile Flap for Coverage of Soft Tissue Defects of Hand
- Free Posterior Interosseous Artery Flap for Treatment of First Web Space Contracture: Methods of Venous Anastomosis
- Morphological Study on the Dorsalis Pedis and First Dorsal Metatarsal Arteries in Koreans
- Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome: Report of 4 Cases
- Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome: Case of Report