Investig Clin Urol.
2018 Sep;59(5):321-327. 10.4111/icu.2018.59.5.321.
Unplanned 30-day readmission rates in patients undergoing endo-urological surgeries for upper urinary tract calculi
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, King George's Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India. sid1420@gmail.com
- KMID: 2419415
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2018.59.5.321
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To see the 30-day unplanned readmission rates in patients underdoing endo-urological surgeries for upper urinary tract calculi we conducted this retrospective study at King George's Medical University, Lucknow, India. Unplanned readmissions not only add to healthcare costs but also are bothersome for the patients. There are many studies on 30-day unplanned readmissions in general surgical patients. Although similar studies have been done in certain urological procedures, no study has reported readmission rates or its risk factors in patients undergoing surgeries for upper urinary tract calculi.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed our prospectively maintained database from 1st January 2009 to 31st December 2017, for the patients who underwent endo-urological procedures for upper urinary tract calculi and identified the patients who were re-admitted within 30 days of discharge.
RESULTS
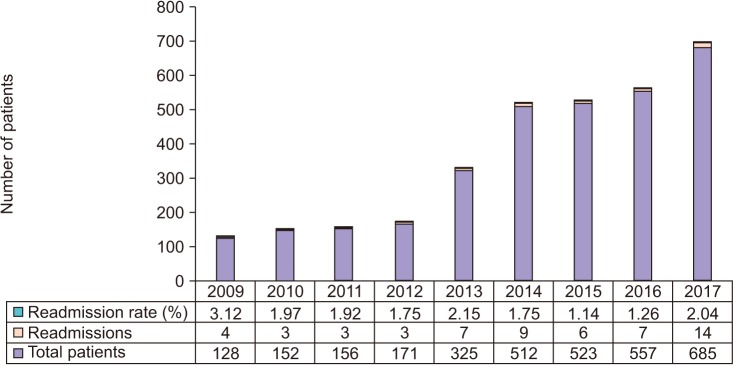
Out of the total 3,209 patients undergoing endo-urological procedures for upper urinary tract calculi 56 were re-admitted. The readmission rate was 1.74% over the study period. The most common etiology for readmission was sepsis followed by hematuria. The significant risk factors for readmission in bivariate analysis included male gender, age >65 years, current smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes mellitus, bleeding disorder, prior cardiac disease, and American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class ≥3. In multivariate risk adjusted logistic regression analysis ASA class ≥3 was the only independent risk factor for readmission.
CONCLUSIONS
The readmission rates in endo-urological procedures for urolithiasis are less compared to other procedures. ASA class ≥3 is the most important independent predictor of unplanned 30-day readmissions.
MeSH Terms
-
Calculi*
Diabetes Mellitus
Health Care Costs
Heart Diseases
Hematuria
Hemorrhage
Humans
India
Logistic Models
Male
Nephrostomy, Percutaneous
Patient Readmission
Prospective Studies
Pulmonary Disease, Chronic Obstructive
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Sepsis
Smoke
Smoking
Ureteroscopy
Urinary Calculi
Urinary Tract*
Urolithiasis
Smoke
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hockenberry JM, Burgess JF Jr, Glasgow J, Vaughan-Sarrazin M, Kaboli PJ. Cost of readmission: can the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) experience inform national payment policy? Med Care. 2013; 51:13–19. PMID: 22683595.2. Orszag PR, Emanuel EJ. Health care reform and cost control. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:601–603. PMID: 20554975.
Article3. Balarajan Y, Selvaraj S, Subramanian SV. Health care and equity in India. Lancet. 2011; 377:505–515. PMID: 21227492.
Article4. Kassin MT, Owen RM, Perez SD, Leeds I, Cox JC, Schnier K, et al. Risk factors for 30-day hospital readmission among general surgery patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2012; 215:322–330. PMID: 22726893.
Article5. Amodu LI, Alexis J, Soleiman A, Akerman M, Addison P, Iurcotta T, et al. Predictors of 30-day readmission following pancreatic surgery: a retrospective review. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018; 17:269–274. PMID: 29716791.
Article6. Marwah S, Singla P, Singh M, Sharma H. Risk factors for 30-day unplanned readmission among patients undergoing laparotomy for perforation peritonitis. Int Surg J. 2017; 4:637–644.
Article7. Rambachan A, Matulewicz RS, Pilecki M, Kim JY, Kundu SD. Predictors of readmission following outpatient urological surgery. J Urol. 2014; 192:183–188. PMID: 24518788.
Article8. Stone BV, Cohn MR, Donin NM, Schulster M, Wysock JS, Makarov DV, et al. Evaluation of unplanned hospital readmissions after major urologic inpatient surgery in the era of accountable care. Urology. 2017; 109:94–100. PMID: 28801217.
Article9. Raslan M, Floyd M, Itam S, Mukherjee R, Irwin P, Maddineni S. Unplanned urology readmissions in a district general hospital: are we meeting the standard? J Clin Urol. 2013; 6:289–294.
Article10. Feigenbaum P, Neuwirth E, Trowbridge L, Teplitsky S, Barnes CA, Fireman E, et al. Factors contributing to all-cause 30-day readmissions: a structured case series across 18 hospitals. Med Care. 2012; 50:599–605. PMID: 22354212.11. Sommer F, Ehsan A, Caspers HP, Klotz T, Engelmann U. Risk adjustment for evaluating the outcome of urological operative procedures. J Urol. 2001; 166:968–972. PMID: 11490257.
Article12. Lojanapiwat B. Infective complication following percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Urol Sci. 2016; 27:8–12.
Article13. Kreydin EI, Eisner BH. Risk factors for sepsis after percutaneous renal stone surgery. Nat Rev Urol. 2013; 10:598–605. PMID: 23999583.
Article14. Rashid AO, Fakhulddin SS. Risk factors for fever and sepsis after percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Asian J Urol. 2016; 3:82–87. PMID: 29264169.
Article15. Nevo A, Mano R, Baniel J, Lifshitz DA. Ureteric stent dwelling time: a risk factor for post-ureteroscopy sepsis. BJU Int. 2017; 120:117–122. PMID: 28145037.
Article16. Srivastava A, Singh KJ, Suri A, Dubey D, Kumar A, Kapoor R, et al. Vascular complications after percutaneous nephrolithotomy: are there any predictive factors? Urology. 2005; 66:38–40. PMID: 15992882.
Article17. El-Nahas AR, Shokeir AA, El-Assmy AM, Mohsen T, Shoma AM, Eraky I, et al. Post-percutaneous nephrolithotomy extensive hemorrhage: a study of risk factors. J Urol. 2007; 177:576–579. PMID: 17222636.
Article18. Nouralizadeh A, Ziaee SA, Hosseini Sharifi SH, Basiri A, Tabibi A, Sharifiaghdas F, et al. Delayed postpercutaneous nephrolithotomy hemorrhage: prevalence, predictive factors and management. Scand J Urol. 2014; 48:110–115. PMID: 24256570.
Article19. Perera M, Papa N, Kinnear N, Wetherell D, Lawrentschuk N, Webb D, et al. Urolithiasis treatment in australia: the age of ureteroscopic intervention. J Endourol. 2016; 30:1194–1199. PMID: 27629239.
Article20. Doyle DJ, Garmon EH. American Society of Anesthesiologists Classification (ASA Class). StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing;2018.