J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2018 Aug;44(4):191-197. 10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.4.191.
Nasolabial and extended nasolabial flaps for reconstruction in oral submucous fibrosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Specialist Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon, 112 Military Dental Centre, Combined Military Hospital, Kharian Cantt, Pakistan. mumarqayyum@gmail.com
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Allied Hospital, Faisalabad, Pakistan.
- 3Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon, Combined Military Hospital, Kharian Cantt, Pakistan.
- 4Specialist Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon, Department of Dentistry, Cleft Hospital Gujrat Pakistan, Gujrat, Pakistan.
- KMID: 2419235
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.4.191
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The objective of the study was to evaluate the results of nasolabial/extended nasolabial flaps as a modality for treatment of oral submucous fibrosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
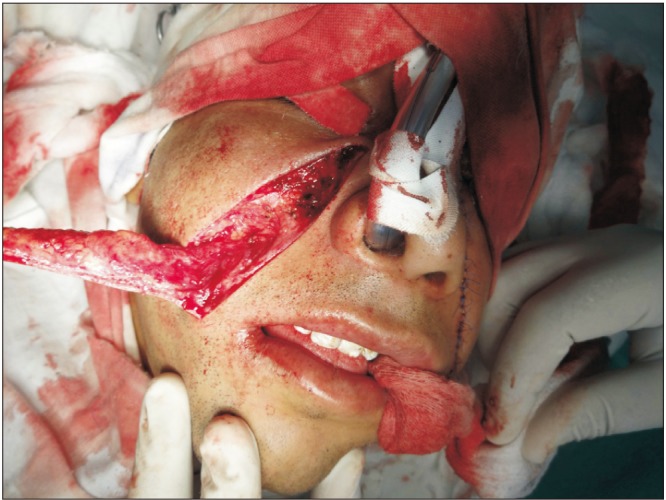
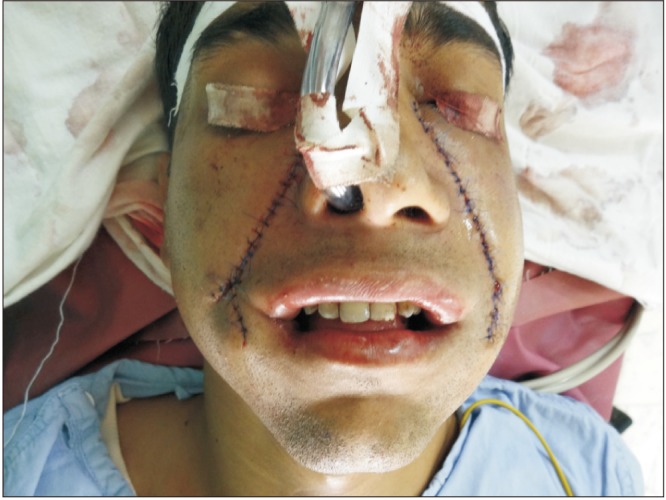
Eleven patients of Stage III or IVa maximum interincisal opening were selected to be operated. Nasolabial/extended nasolabial flaps were done for both the sides. All of the flaps were done in a single stage and were inferiorly based. A similar flap harvest/surgical technique was utilized for all the cases.
RESULTS
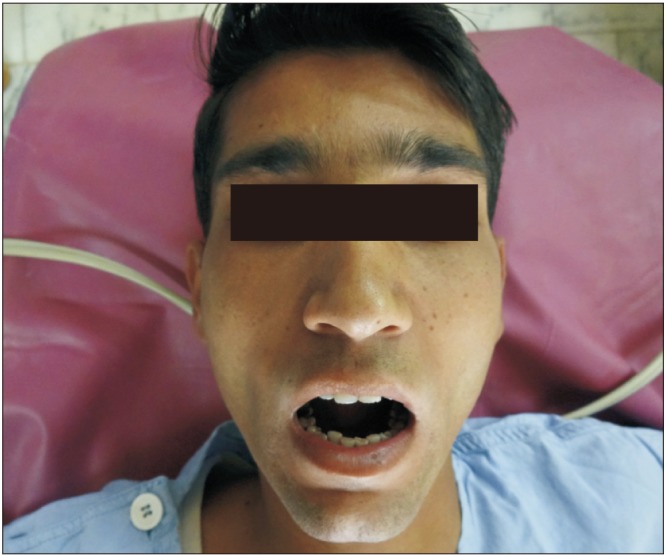
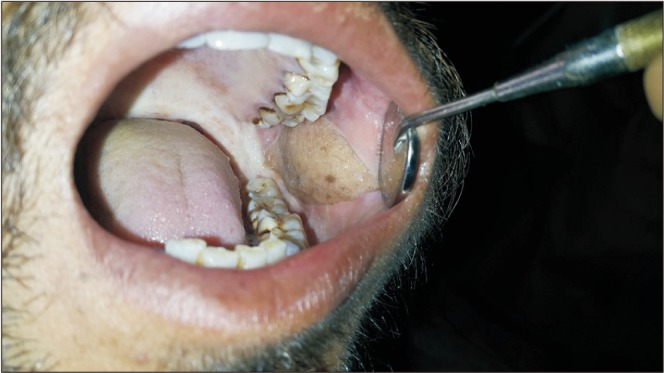
The preoperative mouth opening ranged from 5 to 16 mm, with a mean of 10.09 mm. At 6 months the mouth opening ranged from 29 to 39 mm. Some of the complications encountered were poor scar, wisdom tooth traumatising the flap, decreased mouth opening due to non compliance and too much bulk. All of theses were managed satisfactorily.
CONCLUSION
The nasolabial flap is a very reliable flap to restore the function of oral cavity. Important adjuvant measures are habit cessation, lifestyle changes, and aggressive physiotherapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Exploring the role of angiogenesis in fibrosis and malignant transformation in oral submucous fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Keerthika R, Akhilesh Chandra, Dinesh Raja, Mahesh Khairnar, Rahul Agrawal
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024;50(5):243-252. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2024.50.5.243.
Reference
-
1. Pindborg JJ, Murti PR, Bhonsle RB, Gupta PC, Daftary DK, Mehta FS. Oral submucous fibrosis as a precancerous condition. Scand J Dent Res. 1984; 92:224–229. PMID: 6589738.
Article2. Khanna JN, Andrade NN. Oral submucous fibrosis: a new concept in surgical management. Report of 100 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995; 24:433–439. PMID: 8636640.3. Mehrotra D, Pradhan R, Gupta S. Retrospective comparison of surgical treatment modalities in 100 patients with oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 107:e1–e10.
Article4. Gupta D, Sharma SC. Oral submucous fibrosis--a new treatment regimen. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988; 46:830–833. PMID: 3171741.
Article5. Yeh CJ. Application of the buccal fat pad to the surgical treatment of oral submucous fibrosis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996; 25:130–133. PMID: 8727586.
Article6. Aziz SR. Oral submucous fibrosis: case report and review of diagnosis and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:2386–2389. PMID: 18940512.
Article7. Bhishagratna KKL. Chapter XVI. Diagnosis of disease of mouth. In : Bhishagratna KKL, editor. An English translation of the Susruta Samhita: Nidána-Sthána to Kalapa-Sthána. Vol 2. Calcutta: Selbstverl;1911. p. 111–112.8. Borle RM, Nimonkar PV, Rajan R. Extended nasolabial flaps in the management of oral submucous fibrosis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 47:382–385. PMID: 18995935.
Article9. Jiang X, Hu J. Drug treatment of oral submucous fibrosis: a review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67:1510–1515. PMID: 19531426.
Article10. Huang IY, Wu CF, Shen YS, Yang CF, Shieh TY, Hsu HJ, et al. Importance of patient's cooperation in surgical treatment for oral submucous fibrosis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:699–703. PMID: 18355593.
Article11. Mokal NJ, Raje RS, Ranade SV, Prasad JS, Thatte RL. Release of oral submucous fibrosis and reconstruction using superficial temporal fascia flap and split skin graft--a new technique. Br J Plast Surg. 2005; 58:1055–1060. PMID: 16055096.
Article12. Chao CK, Chang LC, Liu SY, Wang JJ. Histologic examination of pedicled buccal fat pad graft in oral submucous fibrosis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002; 60:1131–1134. PMID: 12378485.
Article13. Chang YM, Tsai CY, Kildal M, Wei FC. Importance of coronoidotomy and masticatory muscle myotomy in surgical release of trismus caused by submucous fibrosis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 113:1949–1954. PMID: 15253182.
Article14. Lee JT, Cheng LF, Chen PR, Wang CH, Hsu H, Chien SH, et al. Bipaddled radial forearm flap for the reconstruction of bilateral buccal defects in oral submucous fibrosis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 36:615–619. PMID: 17499479.
Article15. Huang JJ, Wallace C, Lin JY, Tsao CK, Kao HK, Huang WC, et al. Two small flaps from one anterolateral thigh donor site for bilateral buccal mucosa reconstruction after release of submucous fibrosis and/or contracture. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010; 63:440–445. PMID: 19359228.
Article16. Lai DR, Chen HR, Lin LM, Huang YL, Tsai CC. Clinical evaluation of different treatment methods for oral submucous fibrosis. A 10-year experience with 150 cases. J Oral Pathol Med. 1995; 24:402–406. PMID: 8537913.
Article17. Ko EC, Shen YH, Yang CF, Huang IY, Shieh TY, Chen CM. Artificial dermis as the substitute for split-thickness skin graft in the treatment of oral submucous fibrosis. J Craniofac Surg. 2009; 20:443–445. PMID: 19276824.
Article18. Gewirtz HS, Eilber FR, Zarem HA. Use of nasolabial flap for reconstruction of the floor of the mouth. Am J Surg. 1978; 136:508–511. PMID: 360855.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Versatility of Modified Nasolabial Flap in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Usage of nasolabial skin flaps for the reconstruction of various intraoral defects
- Delayed bipedicled nasolabial flap in facial reconstruction
- Cranially-based nasolabial flaps for the reconstruction of nasal surgical defects
- Use of Subcutaneous Pedicle Flap in Nasolabial Reconstruction