Yonsei Med J.
2018 Mar;59(2):345-348. 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.2.345.
Alternative Surgical Methods in Patients with Recurrent Palmar Hyperhidrosis and Compensatory Hyperhidrosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. dylee4831@chamc.co.kr
- KMID: 2418802
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.2.345
Abstract
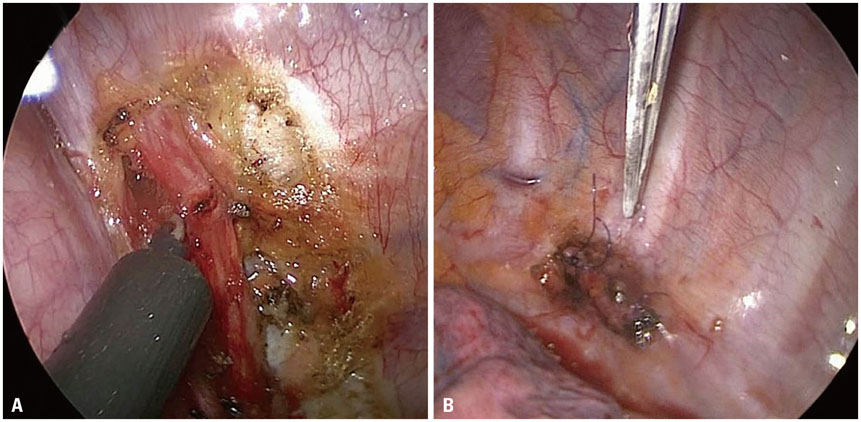
- Recurrent hyperhidrosis after thoracic sympathectomy is an uncomfortable condition, and compensatory hyperhidrosis (CH) is one of the most troublesome side effects. Here, we describe two patients with recurrent palmar hyperhidrosis (PH) and CH over the whole body simultaneously. They were treated with bilateral T4 sympathetic clipping and reconstruction of the sympathetic nerve from a T5 to T8 sympathetic nerve graft, which was transferred to the resected T3 sympathetic bed site. They reported improvements in sweating and were fully satisfied with the results. Our method can be considered as an alternative approach for patients with recurrent PH and CH.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chou SH, Kao EL, Lin CC, Chang YT, Huang MF. The importance of classification in sympathetic surgery and a proposed mechanism for compensatory hyperhidrosis: experience with 464 cases. Surg Endosc. 2006; 20:1749–1753.
Article2. Riet M, Smet AA, Kuiken H, Kazemier G, Bonjer HJ. Prevention of compensatory hyperhidrosis after thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis. Surg Endosc. 2001; 15:1159–1162.
Article3. Drott C, Claes G. Hyperhidrosis treated by thoracoscopic sympathicotomy. Cardiovasc Surg. 1996; 4:788–790.
Article4. Bryant AS, Cerfolio RJ. Satisfaction and compensatory hyperhidrosis rates 5 years and longer after video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathotomy for hyperhidrosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014; 147:1160–1163.
Article5. Cerfolio RJ, De Campos JR, Bryant AS, Connery CP, Miller DL, De-Camp MM, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons expert consensus for the surgical treatment of hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011; 91:1642–1648.
Article6. Ishy A, de Campos JR, Wolosker N, Kauffman P, Tedde ML, Chiavoni CR, et al. Objective evaluation of patients with palmar hyperhidrosis submitted to two levels of sympathectomy: T3 and T4. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2011; 12:545–548.
Article7. Wait SD, Killory BD, Lekovic GP, Ponce FA, Kenny KJ, Dickman CA. Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis: analysis of 642 procedures with special attention to Horner's syndrome and compensatory hyperhidrosis. Neurosurgery. 2010; 67:652–656.8. Lin CC, Mo LR, Lee LS, Ng SM, Hwang MH. Thoracoscopic T2-sympathetic block by clipping--a better and reversible operation for treatment of hyperhidrosis palmaris: experience with 326 cases. Eur J Surg. 1998; 164:suppl 580. 13–16.
Article9. Telaranta T. Secondary sympathetic chain reconstruction after endoscopic thoracic sympathicotomy. Eur J Surg. 1998; 164:suppl 580. 17–18.
Article10. Haam SJ, Park SY, Paik HC, Lee DY. Sympathetic nerve reconstruction for compensatory hyperhidrosis after sympathetic surgery for primary hyperhidrosis. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:597–601.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term Follow-up of Limited T3 Symathicotomy in Palmar Hyperhidrosis
- Limited Sympathetic Nervelipping of T2 Sympathetic Chain Block for Essential Hyperhidrosis
- Thoracoscopic Limited T3 Sympathicotomy for Primary Hyperhidrosis: Prevention for Compensatory Hyperhidrosis
- Ramicotomy of T2, 3 Sympathetic Ganglia for Palmar Hyperhidrosis
- Limited Sympathicotomy Using 2mm Endoscope in Palmar Hyperhidrosis