Diabetes Metab J.
2018 Apr;42(2):155-163. 10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.155.
Hemorheologic Alterations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Presented with an Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Veterans Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. woongwa@yu.ac.kr
- 3Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Chemical Pathology, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Department of Chemical Pathology, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2418708
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.155
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Hemorheologic indices are known to be related to vascular complications in variable clinical settings. However, little is known about the associations between hemorheologic parameters and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the changes of hemorheologic environment inside of blood using hemorheologic parameters, especially the elongation index (EI) and critical shear stress (CSS) in diabetics with versus without AMI.
METHODS
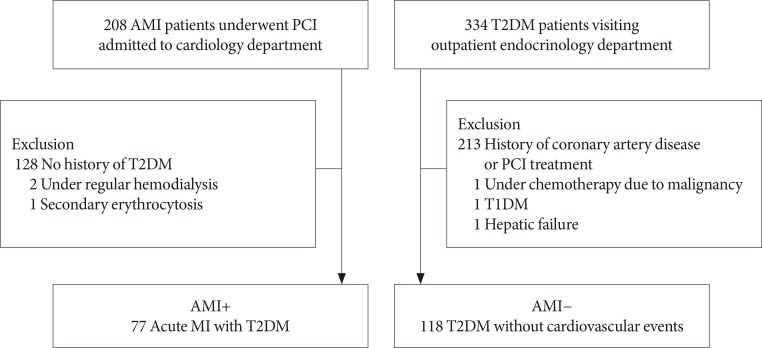
A total of 195 patients with T2DM were enrolled. Patients were divided into the study group with AMI (AMI+, n = 77) and control group (AMI−, n = 118) who had no history of coronary artery disease. Hemorheologic parameters such as EI and CSS were measured and compared between the two groups.
RESULTS
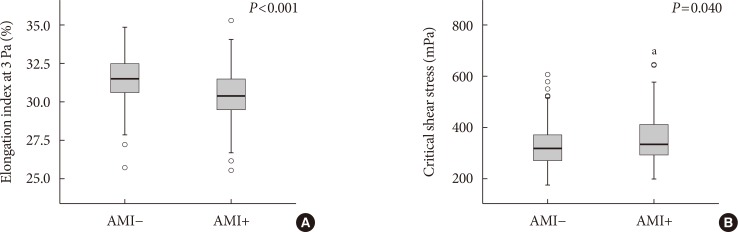
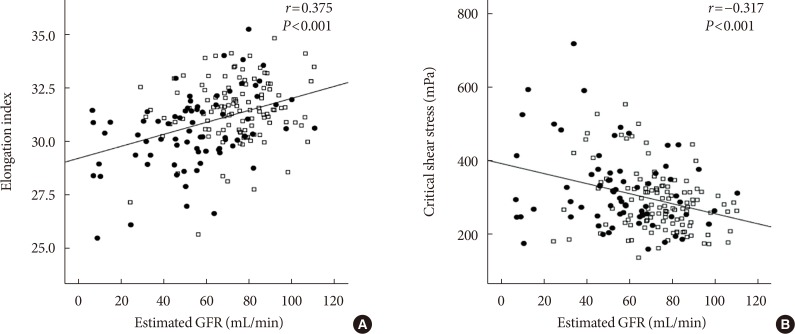
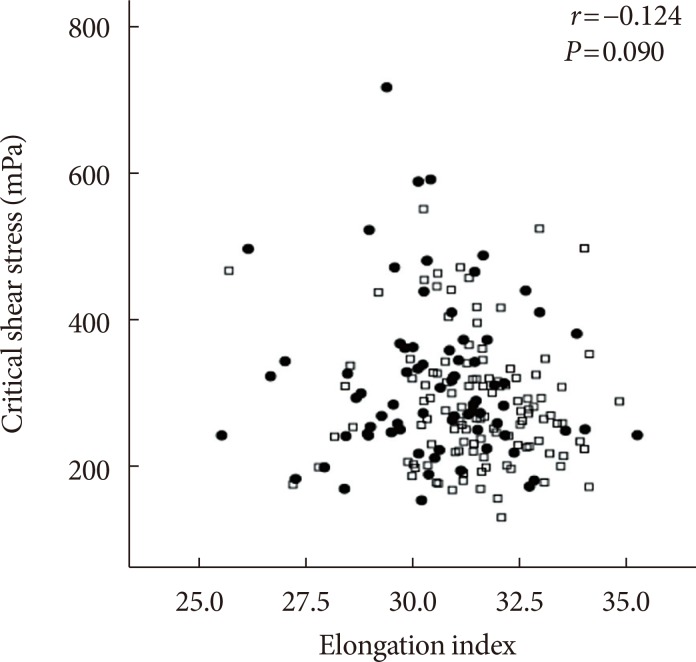
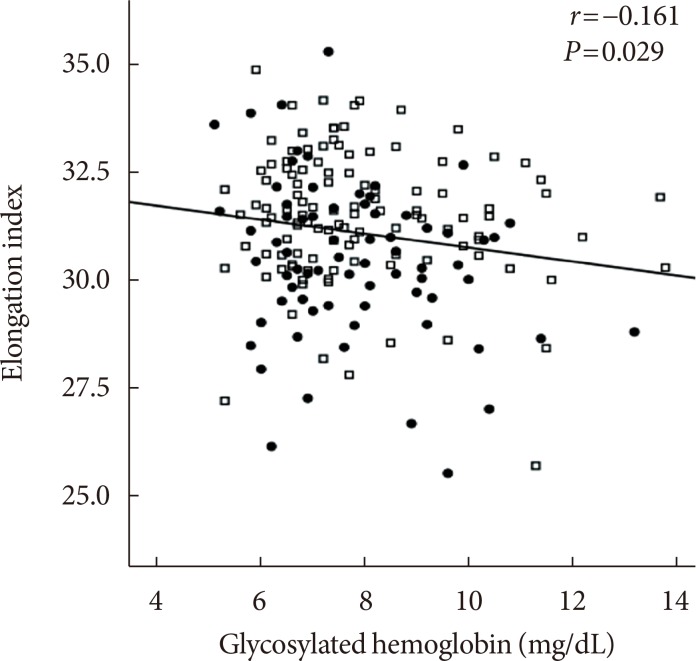
The EI was lower (30.44%±1.77% in AMI+ and 31.47%±1.48% in AMI−, P < 0.001) but the level of CSS was higher (316.13±108.20 mPa in AMI+ and 286.80±85.34 mPa in AMI−, P = 0.040) in the AMI+. The CSS was significantly related to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (R² = 0.497, P < 0.001) and use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (R² = 0.574, P = 0.048).
CONCLUSION
Diabetics with AMI resulted in adverse hemorheologic changes with lower EI and higher CSS compared to diabetic subjects without AMI. Evaluation of the hemorheologic parameters may provide valuable supplementary information for managing patients with AMI and T2DM.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. DeMaria AN. Lies, damned lies, and statistics. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 52:1430–1431. PMID: 18940535.
Article2. Damaske A, Muxel S, Fasola F, Radmacher MC, Schaefer S, Jabs A, Orphal D, Wild P, Parker JD, Fineschi M, Munzel T, Forconi S, Gori T. Peripheral hemorheological and vascular correlates of coronary blood flow. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2011; 49:261–269. PMID: 22214697.
Article3. Lee BK, Durairaj A, Mehra A, Wenby RB, Meiselman HJ, Alexy T. Hemorheological abnormalities in stable angina and acute coronary syndromes. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2008; 39:43–51. PMID: 18503109.
Article4. Hacioglu G, Yalcin O, Bor-Kucukatay M, Ozkaya G, Baskurt OK. Red blood cell rheological properties in various rat hypertension models. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2002; 26:27–32. PMID: 11904468.5. Carter C, McGee D, Reed D, Yano K, Stemmermann G. Hematocrit and the risk of coronary heart disease: the Honolulu Heart Program. Am Heart J. 1983; 105:674–679. PMID: 6837420.
Article6. Corti R, Fuster V, Badimon JJ. Pathogenetic concepts of acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003; 41(4 Suppl S):7S–14S. PMID: 12644335.
Article7. Marossy A, Svorc P, Kron I, Gresova S. Hemorheology and circulation. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2009; 42:239–258. PMID: 19628890.
Article8. Shin S, Ku YH, Ho JX, Kim YK, Suh JS, Singh M. Progressive impairment of erythrocyte deformability as indicator of microangiopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2007; 36:253–261. PMID: 17361027.9. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2014. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37(Suppl 1):S14–S80. PMID: 24357209.10. Singh M, Gersh BJ, McClelland RL, Ho KK, Willerson JT, Penny WF, Holmes DR Jr. Predictive factors for ischemic target vessel revascularization in the Prevention of Restenosis with Tranilast and its Outcomes (PRESTO) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 45:198–203. PMID: 15653015.
Article11. Shin S, Ku Y. Hemorheology and clinical application: association of impairment of red blood cell deformability with diabetic nephropathy. Korea Aust Rheol J. 2005; 17:117–123.12. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–419. PMID: 3899825.13. Napoli C, Ignarro LJ. Nitric oxide-releasing drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003; 43:97–123. PMID: 12540742.
Article14. Bor-Kucukatay M, Wenby RB, Meiselman HJ, Baskurt OK. Effects of nitric oxide on red blood cell deformability. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003; 284:H1577–H1584. PMID: 12521942.
Article15. Singh M, Shin S. Changes in erythrocyte aggregation and deformability in diabetes mellitus: a brief review. Indian J Exp Biol. 2009; 47:7–15. PMID: 19317346.16. Marcinkowska-Gapinska A, Kowal P. Blood fluidity and thermography in patients with diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease in comparison to healthy subjects. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2006; 35:473–479. PMID: 17148846.17. Singleton JR, Smith AG, Russell JW, Feldman EL. Microvascular complications of impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 2003; 52:2867–2873. PMID: 14633845.
Article18. Ando J, Yamamoto K. Vascular mechanobiology: endothelial cell responses to fluid shear stress. Circ J. 2009; 73:1983–1992. PMID: 19801852.19. Cade WT. Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular diseases in the physical therapy setting. Phys Ther. 2008; 88:1322–1335. PMID: 18801863.
Article20. Kesmarky G, Toth K, Habon L, Vajda G, Juricskay I. Hemorheological parameters in coronary artery disease. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 1998; 18:245–251. PMID: 9741664.21. Cecchi E, Marcucci R, Paniccia R, Bandinelli B, Valente S, Giglioli C, Lazzeri C, Gensini GF, Abbate R, Mannini L. Effect of blood hematocrit and erythrocyte deformability on adenosine 5’-diphosphate platelet reactivity in patients with acute coronary syndromes on dual antiplatelet therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2009; 104:764–768. PMID: 19733708.
Article22. Resmi H, Akhunlar H, Temiz Artmann A, Guner G. In vitro effects of high glucose concentrations on membrane protein oxidation, G-actin and deformability of human erythrocytes. Cell Biochem Funct. 2005; 23:163–168. PMID: 15386536.
Article23. Brown CD, Ghali HS, Zhao Z, Thomas LL, Friedman EA. Association of reduced red blood cell deformability and diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005; 67:295–300. PMID: 15610255.
Article24. Xue S, Lee BK, Shin S. Disaggregating shear stress: the roles of cell deformability and fibrinogen concentration. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2013; 55:231–240. PMID: 23089881.
Article25. Shin S, Nam JH, Hou JX, Suh JS. A transient, microfluidic approach to the investigation of erythrocyte aggregation: the threshold shear-stress for erythrocyte disaggregation. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2009; 42:117–125. PMID: 19433885.
Article26. Satoh K. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: emerging player for vascular protection. Circ J. 2013; 77:1156–1157. PMID: 23386273.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corrigendum: Hemorheologic Alterations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Presented with an Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Clinical Significance of Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus in the Era of DES for Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Clinical Study on Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Treatment guideline for diabetes
- Ventricular premature complexes and associated factors in the early postinfarction period