J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2018 Aug;59(8):760-765. 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.8.760.
Changes in Types of Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia after Surgical Correction of Basic Type Intermittent Exotropia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. hjpaik@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2418503
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2018.59.8.760
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the surgical outcomes and changes in types of recurrent exotropia after surgical correction of basic type intermittent exotropia.
METHODS
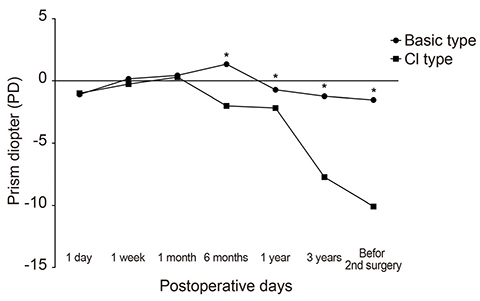
We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 91 patients who underwent reoperations for recurrent exotropia after primary surgical correction, and who visited our hospital for a period of at least one year after the reoperation. When distant deviation was >30 prism diopters (PD), we defined convergence insufficiency type (CI type) if the difference of the deviation angle was >10 PD and basic type exotropia if the difference was <10 PD. When distant deviation was <30 PD, we defined basic type exotropia if the difference of the deviation angle between at distant and near was <33% of the distant deviation angle, and CI type exotropia if the difference was >33% of the distant deviation angle.
RESULTS
The types of recurrent exotropia were similar to those of the preoperative condition in 68 patients (74.7%), and newly emergent CI type was observed in 23 patients (25.3%). With regard to the incidence of CI type, bilateral lateral rectus recession was more common than unilateral lateral rectus recession after primary surgery and medial rectus resection and unilateral lateral rectus recession, but the difference was not significant (p = 0.615). Recurrent CI type exotropia was observed 6 months after primary surgery (p < 0.001), but there was no significant difference in the timing of the reoperation between the two groups (p > 0.05). There was no significant difference in the success of reoperations between the two groups (p > 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The types of recurrent exotropia after surgical correction of primary basic type intermittent exotropia differed from those of preoperative exotropia, which was not related to various factors before surgery. Recurrent exotropia was successfully treated by appropriately selected reoperations, regardless of the type of exotropia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim WJ, Kim MM. The clinical course of recurrent intermittent exotropia after previous unilateral recess-resection surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1386–1391.
Article2. Chia A, Seenyen L, Long QB. Surgical experiences with two-muscle surgery for the treatment of intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS. 2006; 10:206–211.
Article3. Burian HM, Spivey BE. The surgical management of exodeviations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965; 59:603–620.4. Kushner BJ, Morton GV. Distance/near differences in intermittent exotropia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:478–486.
Article5. Cho KH, Kim HW, Choi DG, Lee JY. Type of the recurrent exotropia after bilateral rectus recession for intermittent exotropia. BMC Ophthalmol. 2016; 16:97.
Article6. Yam JC, Wu PK, Chong GS, et al. Long-term ocular alignment after bilateral lateral rectus recession in children with infantile and intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS. 2012; 16:274–279.
Article7. Han DH, Paik HJ. The minimal postoperative follow-up period to determine secondary surgery in patients with intermittent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:711–718.
Article8. Kim MJ, Kim SH. Factors associated with improved surgical outcomes in recurrent exotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2017; 58:692–697.
Article9. Ekdawi NS, Nusz KJ, Diehl NN, Mohney BG. Postoperative outcomes in children with intermittent exotropia from a population-based cohort. J AAPOS. 2009; 13:4–7.
Article10. Kim WJ, Kim MM. The clinical course of recurrent intermittent exotropia following one or two surgeries over 24 months postoperatively. Eye (Lond). 2014; 28:819–824.
Article11. Kim M, Choi MY. Result comparison after reoperation in recurrent exotropia according to the type of first operation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:726–733.
Article12. Kushner BJ. Selective surgery for intermittent exotropia based on distance/near differences. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:324–328.
Article13. Ohtsuki H, Hasebe S, Kono R, et al. Prism adaptation response is useful for predicting surgical outcome in selected types of intermittent exotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 131:117–122.
Article14. Raab EL, Parks MM. Recession of the lateral recti. Effect of preoperative fusion and distance-near relationship. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975; 93:584–586.15. Hermann JS. Surgical therapy of convergence insufficiency. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1981; 18:28–31.16. Choi MY, Hwang JM. Unilateral resection-recession based on near/distance deviation in children with exotropia of the convergence insufficiency type. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1669–1674.17. Lim SH, Hong JS, Kim MM. Prognostic factors for recurrence with unilateral recess-resect procedure in patients with intermittent exotropia. Eye. 2011; 25:449–454.
Article18. Rayner JW, Jampolsky A. Management of adult patients with large angle amblyopic exotropia. Ann Ophthalmol. 1973; 5:95–99.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Surgical Outcome of Intermittent Exotropia with Type Conversion Subsequent to Preoperative Part-Time Occlusion Therapy
- Clinical Features of Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia after Reoperation for Intermittent Exotropia
- The Clinical Course of Recurrent Intermittent Exotropia After Previous Unilateral Recess-Resection Surgery
- The Clinical Characteristics of Intermittent Exotropia and Their Relationship
- The influence of fusional divergence on the surgical results in intermittent exotropia